Costimulation through the CD137/4-1BB pathway protects human melanoma tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from activation-induced cell death and enhances antitumor effector function
- PMID: 21389874
- PMCID: PMC3063939
- DOI: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e318209e7ec
Costimulation through the CD137/4-1BB pathway protects human melanoma tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from activation-induced cell death and enhances antitumor effector function
Abstract
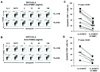
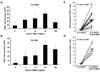
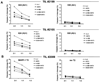
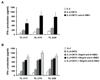
Adoptive T-cell therapy (ACT) using expanded tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) with high-dose interleukin-2 is a promising form of immunotherapy for stage IV melanoma having clinical response rates of 50% or more. One of the major problems preventing further success of this therapy is that the current protocols used to highly expand TIL for infusion drive CD8(+) T cells to differentiate into effector cells losing key costimulatory molecules such as CD28 and CD27. This has been associated with a lack of persistence in vivo for reasons not entirely clear. In this study, we demonstrate that while human melanoma CD8(+) TIL lost CD27 and CD28 expression during the rapid expansion for ACT, they gained expression of the alternative costimulatory molecule CD137/4-1BB, and to a lesser extent CD134/OX40. Postrapid expansion protocol (REP) TIL were found to be highly sensitive to activation-induced cell death when reactivated through the T-cell receptor with low levels of OKT3 antibody. However, coligation of 4-1BB using 2 different agonistic anti-4-1BB antibodies potently prevented activation-induced cell death of post-REP CD8(+) TIL, including those specific for melanoma antigen recognized by T cells, and facilitated even further cell expansion. This was correlated with increased levels of bcl-2 and bcl-xL together with decreased bim expression. 4-1BB costimulated post-REP TIL also expressed increased levels of the cytolytic granule proteins and exhibited enhanced cytotoxic T-cell activity against melanoma cells. Lastly, post-REP CD8(+) TIL were protected from cell death by anti-4-1BB ligation when exposed to human leukocyte antigen-matched melanoma cells. Our results indicate that 4-1BB costimulation may significantly improve TIL survival during melanoma ACT and boost antitumor cytolytic activity.
Figures


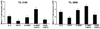
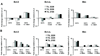


Similar articles
-
Co-stimulation through 4-1BB/CD137 improves the expansion and function of CD8(+) melanoma tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes for adoptive T-cell therapy.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60031. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060031. Epub 2013 Apr 1. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23560068 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-beta1 induces preferential rapid expansion and persistence of tumor antigen-specific CD8+ T cells for adoptive immunotherapy.J Immunother. 2010 May;33(4):371-81. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181cd1180. J Immunother. 2010. PMID: 20386469
-
Manipulating the tumor microenvironment ex vivo for enhanced expansion of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes for adoptive cell therapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Feb 1;21(3):611-21. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1934. Epub 2014 Dec 3. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25472998 Free PMC article.
-
Costimulation of T cells by OX40, 4-1BB, and CD27.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003 Jun-Aug;14(3-4):265-73. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(03)00025-x. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003. PMID: 12787564 Review.
-
Adoptive cell therapy for the treatment of patients with metastatic melanoma.Curr Opin Immunol. 2009 Apr;21(2):233-40. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2009.03.002. Epub 2009 Mar 21. Curr Opin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19304471 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Boosting Cancer Immunotherapy with Anti-CD137 Antibody Therapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Jul 15;21(14):3113-20. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0263. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25908780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neoantigen-Specific Adoptive Cell Therapies for Cancer: Making T-Cell Products More Personal.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 26;11:1215. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01215. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32695101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation and propagation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes on clinical-grade designer artificial antigen-presenting cells for adoptive immunotherapy of melanoma.J Immunother. 2014 Nov-Dec;37(9):448-60. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000056. J Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25304728 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-targeted 4-1BB agonists for combination with T cell bispecific antibodies as off-the-shelf therapy.Sci Transl Med. 2019 Jun 12;11(496):eaav5989. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav5989. Sci Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31189721 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis-regulated low-avidity cancer-specific CD8(+) T cells can be rescued to eliminate HER2/neu-expressing tumors by costimulatory agonists in tolerized mice.Cancer Immunol Res. 2014 Apr;2(4):307-19. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-13-0145. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Cancer Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 24764578 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li Y, et al. MART-1--specific melanoma tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes maintaining CD28 expression have improved survival and expansion capability following antigenic restimulation in vitro. J Immunol. 184(1):452–465. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

