G-actin participates in RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription elongation by recruiting positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb)
- PMID: 21378166
- PMCID: PMC3083233
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.184374
G-actin participates in RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription elongation by recruiting positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb)
Abstract
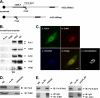
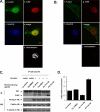
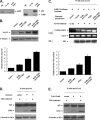
Actin is a key regulator of RNA polymerase (Pol) II-dependent transcription. Positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb), a Cdk9/cyclin T1 heterodimer, has been reported to play a critical role in transcription elongation. However, the relationship between actin and P-TEFb is still not clear. In this study, actin was found to interact with Cdk9, a catalytic subunit of P-TEFb, in elongation complexes. Using immunofluorescence and immunoprecipitation assays, Cdk9 was found to bind to G-actin through the conserved Thr-186 in the T-loop. Overexpression and in vitro kinase assays showed that G-actin promotes P-TEFb-dependent phosphorylation of the Pol II C-terminal domain. An in vitro transcription experiment revealed that the interaction between G-actin and Cdk9 stimulated Pol II transcription elongation. ChIP and immobilized template assays indicated that actin recruited Cdk9 to a transcriptional template in vivo and in vitro. Using cytokine IL-6-inducible p21 gene expression system, we revealed that actin recruited Cdk9 to endogenous gene. Moreover, overexpression of actin and Cdk9 increased histone H3 acetylation and acetylized histone H3 binding to a transcriptional template through the interaction with histone acetyltransferase, p300. Taken together, our results suggested that actin participates in transcription elongation by recruiting Cdk9 for phosphorylation of the Pol II C-terminal domain, and the actin-Cdk9 interaction promotes chromatin remodeling.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Actin associates with actively elongating genes and binds directly to the Cdk9 subunit of P-TEFb.J Biol Chem. 2024 Mar;300(3):105698. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.105698. Epub 2024 Jan 30. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38301887 Free PMC article.
-
A positive feedback loop links opposing functions of P-TEFb/Cdk9 and histone H2B ubiquitylation to regulate transcript elongation in fission yeast.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(8):e1002822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002822. Epub 2012 Aug 2. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22876190 Free PMC article.
-
T-loop phosphorylated Cdk9 localizes to nuclear speckle domains which may serve as sites of active P-TEFb function and exchange between the Brd4 and 7SK/HEXIM1 regulatory complexes.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Jul;224(1):84-93. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22096. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20201073 Free PMC article.
-
P-TEFb goes viral.Bioessays. 2016 Jul;38 Suppl 1:S75-85. doi: 10.1002/bies.201670912. Bioessays. 2016. PMID: 27417125 Review.
-
The emerging picture of CDK9/P-TEFb: more than 20 years of advances since PITALRE.Mol Biosyst. 2017 Jan 31;13(2):246-276. doi: 10.1039/c6mb00387g. Mol Biosyst. 2017. PMID: 27833949 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel role of CAP1 in regulation RNA polymerase II-mediated transcription elongation depends on its actin-depolymerization activity in nucleoplasm.Oncogene. 2021 May;40(20):3492-3509. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01789-3. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 33911205
-
Transcriptional regulation and nuclear reprogramming: roles of nuclear actin and actin-binding proteins.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Sep;70(18):3289-302. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1235-7. Epub 2012 Dec 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23275942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear Actin Is Required for Transcription during Drosophila Oogenesis.iScience. 2018 Nov 30;9:63-70. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2018.10.010. Epub 2018 Oct 15. iScience. 2018. PMID: 30384134 Free PMC article.
-
Rho, nuclear actin, and actin-binding proteins in the regulation of transcription and gene expression.Small GTPases. 2014;5:e27539. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.27539. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 24603113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
To be or not to be assembled: progressing into nuclear actin filaments.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Nov;14(11):693-7. doi: 10.1038/nrm3681. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24088744 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

