Dynamics of DNA damage response proteins at DNA breaks: a focus on protein modifications
- PMID: 21363960
- PMCID: PMC3049283
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.2021311
Dynamics of DNA damage response proteins at DNA breaks: a focus on protein modifications
Abstract
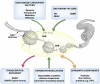
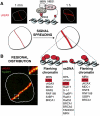
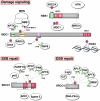
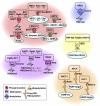
Genome integrity is constantly monitored by sophisticated cellular networks, collectively termed the DNA damage response (DDR). A common feature of DDR proteins is their mobilization in response to genotoxic stress. Here, we outline how the development of various complementary methodologies has provided valuable insights into the spatiotemporal dynamics of DDR protein assembly/disassembly at sites of DNA strand breaks in eukaryotic cells. Considerable advances have also been made in understanding the underlying molecular mechanisms for these events, with post-translational modifications of DDR factors being shown to play prominent roles in controlling the formation of foci in response to DNA-damaging agents. We review these regulatory mechanisms and discuss their biological significance to the DDR.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of non-homologous end joining via post-translational modifications of components of the ligation step.Curr Genet. 2017 Aug;63(4):591-605. doi: 10.1007/s00294-016-0670-7. Epub 2016 Dec 3. Curr Genet. 2017. PMID: 27915381 Review.
-
Similarities and differences between "uncapped" telomeres and DNA double-strand breaks.Chromosoma. 2012 Apr;121(2):117-30. doi: 10.1007/s00412-011-0357-2. Epub 2011 Dec 28. Chromosoma. 2012. PMID: 22203190 Review.
-
RAP80 and RNF8, key players in the recruitment of repair proteins to DNA damage sites.Cancer Lett. 2008 Nov 28;271(2):179-90. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.04.046. Epub 2008 Jun 11. Cancer Lett. 2008. PMID: 18550271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromatin modulation and the DNA damage response.Exp Cell Res. 2006 Aug 15;312(14):2677-86. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.06.031. Epub 2006 Jun 30. Exp Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16893724 Review.
-
Give me a break, but not in mitosis: the mitotic DNA damage response marks DNA double-strand breaks with early signaling events.Cell Cycle. 2011 Apr 15;10(8):1215-21. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.8.15334. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 21412056 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Damage-induced BRCA1 phosphorylation by Chk2 contributes to the timing of end resection.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(3):437-48. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.972901. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25659039 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between Ubiquitin, SUMO, and Poly(ADP-Ribose) in the Cellular Response to Genotoxic Stress.Front Genet. 2016 Apr 19;7:63. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00063. eCollection 2016. Front Genet. 2016. PMID: 27148359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cumulative Dose from Recurrent CT Scans: Exploring the DNA Damage Response in Human Non-Transformed Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 27;25(13):7064. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137064. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000171 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Ku70 predicts results of radiotherapy in prostate cancer.Strahlenther Onkol. 2017 Jan;193(1):29-37. doi: 10.1007/s00066-016-1023-7. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Strahlenther Onkol. 2017. PMID: 27465041 Clinical Trial. English.
-
The AID-induced DNA damage response in chromatin.Mol Cell. 2013 May 9;50(3):309-21. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.04.017. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23664375 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahel I, Ahel D, Matsusaka T, Clark AJ, Pines J, Boulton SJ, West SC 2008. Poly(ADP-ribose)-binding zinc finger motifs in DNA repair/checkpoint proteins. Nature 451: 81–85 - PubMed
-
- Alpi AF, Patel KJ 2009. Monoubiquitylation in the Fanconi anemia DNA damage response pathway. DNA Repair (Amst) 8: 430–435 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
