Rad51 inhibition is an effective means of targeting DNA repair in glioma models and CD133+ tumor-derived cells
- PMID: 21363882
- PMCID: PMC3093331
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nor010
Rad51 inhibition is an effective means of targeting DNA repair in glioma models and CD133+ tumor-derived cells
Abstract
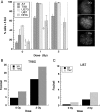
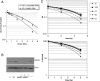
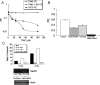
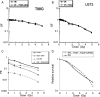
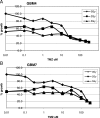
High grade gliomas (HGGs) are characterized by resistance to radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Targeting Rad51-dependent homologous recombination repair may be an effective target for chemo- and radiosensitization. In this study we assessed the role of Rad51-dependent repair on sensitivity to radiation and temozolomide (TMZ) as single agents or in combination. Repair protein levels in established glioma cell lines, early passage glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cell lines, and normal human astrocytes (NHAs) were measured using western blot. Viability and clonogenic survival assays were used to measure the effects of Rad51 knockdown with radiation (XR) and TMZ. Immunocytochemistry was used to evaluate kinetics of Rad51 and γ-H2AX repair foci. Immunohistochemistry was used to assess Rad51 protein levels in glioma specimens. Repair proteins including Rad51 are upregulated in HGG cells compared with NHA. Established glioma cell lines show a dose-dependent increase in Rad51 foci formation after XR and TMZ. Rad51 levels are inversely correlated with radiosensitivity, and downregulation markedly increases the cytotoxicity of TMZ. Rad51 knockdown also promotes more residual γ-H2AX foci 24 h after combined treatment. Newly established GBM cell lines also have high Rad51 levels and are extremely sensitive to Rad51 knockdown. Clinical samples from recently resected gliomas of varying grades demonstrate that Rad51 levels do not correlate with tumor grade. Rad51-dependent repair makes a significant contribution to DNA repair in glioma cells and contributes to resistance to both XR and TMZ. Agents targeting Rad51-dependent repair would be effective adjuvants in standard combination regimens.
Figures



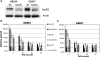

Similar articles
-
Integrin αVβ3 silencing sensitizes malignant glioma cells to temozolomide by suppression of homologous recombination repair.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 25;8(17):27754-27771. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10897. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27487141 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of BRCA1-BRCA2-containing complex subunit 3 sensitizes glioma cells to temozolomide.Oncotarget. 2014 Nov 15;5(21):10901-15. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2543. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25337721 Free PMC article.
-
N-methylpurine DNA glycosylase and DNA polymerase beta modulate BER inhibitor potentiation of glioma cells to temozolomide.Neuro Oncol. 2011 May;13(5):471-86. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nor011. Epub 2011 Mar 3. Neuro Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21377995 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840 Review.
-
Targeting tumor hypoxia and mitochondrial metabolism with anti-parasitic drugs to improve radiation response in high-grade gliomas.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 7;39(1):208. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01724-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33028364 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A multiplexed bioluminescent reporter for sensitive and non-invasive tracking of DNA double strand break repair dynamics in vitro and in vivo.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Sep 25;48(17):e100. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa669. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32797168 Free PMC article.
-
DNA repair genes in astrocytoma tumorigenesis, progression and therapy resistance.Genet Mol Biol. 2019 Dec 13;43(1 suppl 1):e20190066. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2019-0066. eCollection 2019. Genet Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31930277 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoblastoma Binding Protein 4 Modulates Temozolomide Sensitivity in Glioblastoma by Regulating DNA Repair Proteins.Cell Rep. 2016 Mar 22;14(11):2587-98. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.02.045. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 26972001 Free PMC article.
-
CD133 expression is associated with less DNA repair, better response to chemotherapy and survival in ER-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Nov;208(2):415-427. doi: 10.1007/s10549-024-07434-3. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 39017815
-
Regulation of DNA Alkylation Damage Repair: Lessons and Therapeutic Opportunities.Trends Biochem Sci. 2017 Mar;42(3):206-218. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2016.10.001. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017. PMID: 27816326 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Douglas JG, Stelzer KJ, Mankoff DA, et al. [F-18]-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography for targeting radiation dose escalation for patients with glioblastoma multiforme: clinical outcomes and patterns of failure. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;64:886–891. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.08.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459–466. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70025-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tisdale MJ. Antitumor imidazotetrazines–XV. Role of guanine O6 alkylation in the mechanism of cytotoxicity of imidazotetrazinones. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;36:457–462. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(87)90351-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:997–1003. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa043331. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ceccotti S, Aquilina G, Macpherson P, et al. Processing of O6-methylguanine by mismatch correction in human cell extracts. Curr Biol. 1996;6:1528–1531. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(96)00758-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

