PA28 and the proteasome immunosubunits play a central and independent role in the production of MHC class I-binding peptides in vivo
- PMID: 21360704
- PMCID: PMC3100532
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.201041040
PA28 and the proteasome immunosubunits play a central and independent role in the production of MHC class I-binding peptides in vivo
Abstract
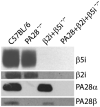
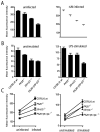
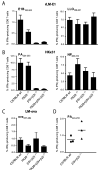
Proteasomes play a fundamental role in the processing of intracellular antigens into peptides that bind to MHC class I molecules for the presentation of CD8(+) T cells. Three IFN-γ-inducible catalytic proteasome (immuno)subunits as well as the IFN-γ-inducible proteasome activator PA28 dramatically accelerate the generation of a subset of MHC class I-presented antigenic peptides. To determine whether these IFN-γ-inducible proteasome components play a compounded role in antigen processing, we generated mice lacking both PA28 and immunosubunits β5i/LMP7 and β2i/MECL-1. Analyses of MHC class I cell-surface levels ex vivo demonstrated that PA28 deficiency reduced the production of MHC class I-binding peptides both in cells with and without immunosubunits, in the latter cells further decreasing an already diminished production of MHC ligands in the absence of immunoproteasomes. In contrast, the immunosubunits but not PA28 appeared to be of critical importance for the induction of CD8(+) T-cell responses to multiple dominant Influenza and Listeria-derived epitopes. Taken together, our data demonstrate that PA28 and the proteasome immunosubunits use fundamentally different mechanisms to enhance the supply of MHC class I-binding peptides; however, only the immunosubunit-imposed effects on proteolytic epitope processing appear to have substantial influence on the specificity of pathogen-specific CD8(+) T-cell responses.
Copyright © 2011 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

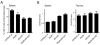
Similar articles
-
Differential influence on cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitope presentation by controlled expression of either proteasome immunosubunits or PA28.J Exp Med. 2000 Aug 21;192(4):483-94. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.4.483. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 10952718 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the proteasome in the generation of MHC class I ligands and immune responses.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011 May;68(9):1491-502. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0657-y. Epub 2011 Mar 9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21387144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rates of processing determine the immunogenicity of immunoproteasome-generated epitopes.J Immunol. 2007 Jun 15;178(12):7557-62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.12.7557. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17548590
-
The proteasome immunosubunits, PA28 and ER-aminopeptidase 1 protect melanoma cells from efficient MART-126-35 -specific T-cell recognition.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Dec;45(12):3257-68. doi: 10.1002/eji.201445243. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26399368
-
Interferon-gamma, the functional plasticity of the ubiquitin-proteasome system, and MHC class I antigen processing.Immunol Rev. 2005 Oct;207:19-30. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00308.x. Immunol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16181324 Review.
Cited by
-
The Functional and Mechanistic Roles of Immunoproteasome Subunits in Cancer.Cells. 2021 Dec 20;10(12):3587. doi: 10.3390/cells10123587. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34944095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterozygous Truncating Variants in POMP Escape Nonsense-Mediated Decay and Cause a Unique Immune Dysregulatory Syndrome.Am J Hum Genet. 2018 Jun 7;102(6):1126-1142. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.04.010. Epub 2018 May 24. Am J Hum Genet. 2018. PMID: 29805043 Free PMC article.
-
PA28 modulates antigen processing and viral replication during coxsackievirus B3 infection.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 9;12(3):e0173259. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173259. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28278207 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoproteasomes: structure, function, and antigen presentation.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012;109:75-112. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-397863-9.00003-1. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012. PMID: 22727420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Ubiquitin-Proteasome System in Immune Cells.Biomolecules. 2021 Jan 5;11(1):60. doi: 10.3390/biom11010060. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33466553 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Deol P, Zaiss DM, Monaco JJ, Sijts AJ. Rates of processing determine the immunogenicity of immunoproteasome-generated epitopes. J. Immunol. 2007;178:7557–7562. - PubMed
-
- Probst HC, Tschannen K, Gallimore A, Martinic M, Basler M, Dumrese T, Jones E, van den Broek MF. Immunodominance of an antiviral cytotoxic T cell response is shaped by the kinetics of viral protein expression. J. Immunol. 2003;171:5415–5422. - PubMed
-
- Deng Y, Yewdell JW, Eisenlohr LC, Bennink JR. MHC affinity, peptide liberation, T cell repertoire, and immunodominance all contribute to the paucity of MHC class I-restricted peptides recognized by antiviral CTL. J. Immunol. 1997;158:1507–1515. - PubMed
-
- Sijts AJ, Standera S, Toes RE, Ruppert T, Beekman NJ, van Veelen PA, Ossendorp FA, et al. MHC class I antigen processing of an adenovirus CTL epitope is linked to the levels of immunoproteasomes in infected cells. J. Immunol. 2000;164:4500–4506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

