Drosophila S2 cells are non-permissive for vaccinia virus DNA replication following entry via low pH-dependent endocytosis and early transcription
- PMID: 21347205
- PMCID: PMC3039670
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017248
Drosophila S2 cells are non-permissive for vaccinia virus DNA replication following entry via low pH-dependent endocytosis and early transcription
Abstract
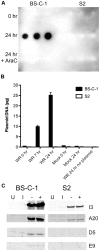
Vaccinia virus (VACV), a member of the chordopox subfamily of the Poxviridae, abortively infects insect cells. We have investigated VACV infection of Drosophila S2 cells, which are useful for protein expression and genome-wide RNAi screening. Biochemical and electron microscopic analyses indicated that VACV entry into Drosophila S2 cells depended on the VACV multiprotein entry-fusion complex but appeared to occur exclusively by a low pH-dependent endocytic mechanism, in contrast to both neutral and low pH entry pathways used in mammalian cells. Deep RNA sequencing revealed that the entire VACV early transcriptome, comprising 118 open reading frames, was robustly expressed but neither intermediate nor late mRNAs were made. Nor was viral late protein synthesis or inhibition of host protein synthesis detected by pulse-labeling with radioactive amino acids. Some reduction in viral early proteins was noted by Western blotting. Nevertheless, synthesis of the multitude of early proteins needed for intermediate gene expression was demonstrated by transfection of a plasmid containing a reporter gene regulated by an intermediate promoter. In addition, expression of a reporter gene with a late promoter was achieved by cotransfection of intermediate genes encoding the late transcription factors. The requirement for transfection of DNA templates for intermediate and late gene expression indicated a defect in viral genome replication in VACV-infected S2 cells, which was confirmed by direct analysis. Furthermore, VACV-infected S2 cells did not support the replication of a transfected plasmid, which occurs in mammalian cells and is dependent on all known viral replication proteins, indicating a primary restriction of DNA synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mutations Near the N Terminus of Vaccinia Virus G9 Protein Overcome Restrictions on Cell Entry and Syncytium Formation Imposed by the A56/K2 Fusion Regulatory Complex.J Virol. 2020 May 4;94(10):e00077-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00077-20. Print 2020 May 4. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32132239 Free PMC article.
-
Derepression of a novel class of vaccinia virus genes upon DNA replication.EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3487-92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03224.x. EMBO J. 1988. PMID: 2850166 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Nonreplicating Vaccinia Virus Vector Enhances Expression of Heterologous Genes and Suppresses Synthesis of Endogenous Viral Proteins.mBio. 2017 Jun 6;8(3):e00790-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00790-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28588133 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccinia Virus Activation and Antagonism of Cytosolic DNA Sensing.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 1;11:568412. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.568412. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33117352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Entry and Disassembly of Large DNA Viruses: Electron Microscopy Leads the Way.J Mol Biol. 2018 Jun 8;430(12):1714-1724. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.04.019. Epub 2018 Apr 24. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29702107 Review.
Cited by
-
Human genome-wide RNAi screen reveals a role for nuclear pore proteins in poxvirus morphogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Feb 26;110(9):3519-24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1300708110. Epub 2013 Feb 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23401514 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus α-toxin modulates skin host response to viral infection.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012 Sep;130(3):683-691.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.06.019. Epub 2012 Jul 26. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22840852 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila as a Model for Human Viral Neuroinfections.Cells. 2022 Aug 29;11(17):2685. doi: 10.3390/cells11172685. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36078091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of vaccinia virus L1 N-myristoylation by the host N-myristoyltransferase inhibitor IMP-1088 generates non-infectious virions defective in cell entry.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Oct 10;18(10):e1010662. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010662. eCollection 2022 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 36215331 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse genetics analysis of poxvirus intermediate transcription factors.J Virol. 2012 Sep;86(17):9514-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06902-11. Epub 2012 Jun 27. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22740406 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moss B. Poxviridae: the viruses and their replication. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields Virology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. pp. 2905–2946.
-
- Langridge WH. Detection of Amsacta moorei entomopoxvirus and vaccinia virus proteins in cell cultures restrictive for poxvirus multiplication. J Invertebr Pathol. 1983;42:77–82. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Yuan S, Moyer RW. The non-permissive infection of insect (Gypsy moth) LD-652 cells by vaccinia virus. Virology. 1998;248:74–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

