S-adenosyl-L-methionine induces compaction of nascent peptide chain inside the ribosomal exit tunnel upon translation arrest in the Arabidopsis CGS1 gene
- PMID: 21335553
- PMCID: PMC3083191
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.211656
S-adenosyl-L-methionine induces compaction of nascent peptide chain inside the ribosomal exit tunnel upon translation arrest in the Arabidopsis CGS1 gene
Abstract
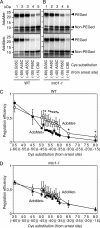
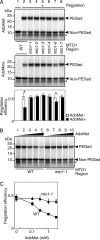
Expression of the Arabidopsis CGS1 gene, encoding the first committed enzyme of methionine biosynthesis, is feedback-regulated in response to S-adenosyl-L-methionine (AdoMet) at the mRNA level. This regulation is first preceded by temporal arrest of CGS1 translation elongation at the Ser-94 codon. AdoMet is specifically required for this translation arrest, although the mechanism by which AdoMet acts with the CGS1 nascent peptide remained elusive. We report here that the nascent peptide of CGS1 is induced to form a compact conformation within the exit tunnel of the arrested ribosome in an AdoMet-dependent manner. Cysteine residues introduced into CGS1 nascent peptide showed reduced ability to react with polyethyleneglycol maleimide in the presence of AdoMet, consistent with a shift into the ribosomal exit tunnel. Methylation protection and UV cross-link assays of 28 S rRNA revealed that induced compaction of nascent peptide is associated with specific changes in methylation protection and UV cross-link patterns in the exit tunnel wall. A 14-residue stretch of amino acid sequence, termed the MTO1 region, has been shown to act in cis for CGS1 translation arrest and mRNA degradation. This regulation is lost in the presence of mto1 mutations, which cause single amino acid alterations within MTO1. In this study, both the induced peptide compaction and exit tunnel change were found to be disrupted by mto1 mutations. These results suggest that the MTO1 region participates in the AdoMet-induced arrest of CGS1 translation by mediating changes of the nascent peptide and the exit tunnel wall.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ribosomes in a stacked array: elucidation of the step in translation elongation at which they are stalled during S-adenosyl-L-methionine-induced translation arrest of CGS1 mRNA.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 2;289(18):12693-704. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.526616. Epub 2014 Mar 20. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24652291 Free PMC article.
-
Nascent peptide-mediated translation elongation arrest of Arabidopsis thaliana CGS1 mRNA occurs autonomously.Plant Cell Physiol. 2008 Apr;49(4):549-56. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcn028. Epub 2008 Feb 19. Plant Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18285355
-
Nascent peptide-mediated translation elongation arrest coupled with mRNA degradation in the CGS1 gene of Arabidopsis.Genes Dev. 2005 Aug 1;19(15):1799-810. doi: 10.1101/gad.1317105. Epub 2005 Jul 18. Genes Dev. 2005. PMID: 16027170 Free PMC article.
-
Arrest peptides: cis-acting modulators of translation.Annu Rev Biochem. 2013;82:171-202. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-080211-105026. Annu Rev Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23746254 Review.
-
Ribosome regulation by the nascent peptide.Microbiol Rev. 1996 Jun;60(2):366-85. doi: 10.1128/mr.60.2.366-385.1996. Microbiol Rev. 1996. PMID: 8801438 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Translation drives mRNA quality control.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Jun 5;19(6):594-601. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2301. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22664987 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism and Regulatory Functions of O-Acetylserine, S-Adenosylmethionine, Homocysteine, and Serine in Plant Development and Environmental Responses.Front Plant Sci. 2021 May 7;12:643403. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.643403. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34025692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased freedom of movement in the nascent chain results in dynamic changes in the structure of the SecM arrest motif.Biosci Rep. 2019 Jan 18;39(1):BSR20181246. doi: 10.1042/BSR20181246. Print 2019 Jan 31. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30563926 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolite Control of Translation by Conserved Peptide uORFs: The Ribosome as a Metabolite Multisensor.Plant Physiol. 2020 Jan;182(1):110-122. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.00940. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Plant Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31451550 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomes in a stacked array: elucidation of the step in translation elongation at which they are stalled during S-adenosyl-L-methionine-induced translation arrest of CGS1 mRNA.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 2;289(18):12693-704. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.526616. Epub 2014 Mar 20. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24652291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim J., Leustek T. (1996) Plant Mol. Biol. 32, 1117–1124 - PubMed
-
- Matthews B. F. (1999) in Plant Amino Acids: Biochemistry and Biotechnology (Singh B. K. ed) pp. 205–225, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York
-
- Chiba Y., Ishikawa M., Kijima F., Tyson R. H., Kim J., Yamamoto A., Nambara E., Leustek T., Wallsgrove R. M., Naito S. (1999) Science 286, 1371–1374 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

