Role of M1, M3, and M5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in cholinergic dilation of small arteries studied with gene-targeted mice
- PMID: 21335473
- PMCID: PMC3094072
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00982.2010
Role of M1, M3, and M5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in cholinergic dilation of small arteries studied with gene-targeted mice
Abstract
Acetylcholine regulates perfusion of numerous organs via changes in local blood flow involving muscarinic receptor-induced release of vasorelaxing agents from the endothelium. The purpose of the present study was to determine the role of M₁, M₃, and M₅ muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in vasodilation of small arteries using gene-targeted mice deficient in either of the three receptor subtypes (M1R(-/-), M3R(-/-), or M5R(-/-) mice, respectively). Muscarinic receptor gene expression was determined in murine cutaneous, skeletal muscle, and renal interlobar arteries using real-time PCR. Moreover, respective arteries from M1R(-/-), M3R(-/-), M5R(-/-), and wild-type mice were isolated, cannulated with micropipettes, and pressurized. Luminal diameter was measured using video microscopy. mRNA for all five muscarinic receptor subtypes was detected in all three vascular preparations from wild-type mice. However, M(3) receptor mRNA was found to be most abundant. Acetylcholine produced dose-dependent dilation in all three vascular preparations from M1R(-/-), M5R(-/-), and wild-type mice. In contrast, cholinergic dilation was virtually abolished in arteries from M3R(-/-) mice. Deletion of either M₁, M₃, or M₅ receptor genes did not affect responses to nonmuscarinic vasodilators, such as substance P and nitroprusside. These findings provide the first direct evidence that M₃ receptors mediate cholinergic vasodilation in cutaneous, skeletal muscle, and renal interlobar arteries. In contrast, neither M₁ nor M₅ receptors appear to be involved in cholinergic responses of the three vascular preparations tested.
Figures

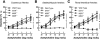
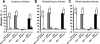
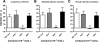
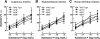
Similar articles
-
Cholinergic responses of ophthalmic arteries in M3 and M5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor knockout mice.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009 Oct;50(10):4822-7. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-3600. Epub 2009 Apr 30. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19407017 Free PMC article.
-
Muscarinic (M) receptors in coronary circulation: gene-targeted mice define the role of M2 and M3 receptors in response to acetylcholine.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004 Jul;24(7):1253-8. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000130661.82773.ca. Epub 2004 May 6. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004. PMID: 15130910
-
Identification of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtype mediating cholinergic vasodilation in murine retinal arterioles.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Sep 27;52(10):7479-84. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-7370. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21873683 Free PMC article.
-
Novel insights into M5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor function by the use of gene targeting technology.Life Sci. 2003 Dec 5;74(2-3):345-53. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2003.09.022. Life Sci. 2003. PMID: 14607263 Review.
-
Novel insights into muscarinic acetylcholine receptor function using gene targeting technology.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003 Aug;24(8):414-20. doi: 10.1016/S0165-6147(03)00195-0. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003. PMID: 12915051 Review.
Cited by
-
Monoaminergic Receptors as Modulators of the Perivascular Sympathetic and Sensory CGRPergic Outflows.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020;18(9):790-808. doi: 10.2174/1570159X18666200503223240. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32364079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KCa channel activation normalizes endothelial function in Type 2 Diabetic resistance arteries by improving intracellular Ca2+ mobilization.Metabolism. 2021 Jan;114:154390. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154390. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Metabolism. 2021. PMID: 33039407 Free PMC article.
-
Home proximity to flower plantations and higher systolic blood pressure among children.Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2018 Sep;221(8):1077-1084. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2018.08.006. Epub 2018 Aug 18. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2018. PMID: 30131222 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular, Synaptic and Network Effects of Acetylcholine in the Neocortex.Front Neural Circuits. 2019 Apr 12;13:24. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2019.00024. eCollection 2019. Front Neural Circuits. 2019. PMID: 31031601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtype in murine ophthalmic arteries after endothelial removal.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Jan 29;55(1):625-31. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-13549. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24408978 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altiere RJ, Travis DC, Roberts J, Thompson DC. Pharmacological characterization of muscarinic receptors mediating acetylcholine-induced contraction and relaxation in rabbit intrapulmonary arteries. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270: 269–276, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Beny JL, Nguyen MN, Marino M, Matsui M. Muscarinic receptor knockout mice confirm involvement of M3 receptor in endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in mouse arteries. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 51: 505–512, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Bridges TM, Marlo JE, Niswender CM, Jones CK, Jadhav SB, Gentry PR, Plumley HC, Weaver CD, Conn PJ, Lindsley CW. Discovery of the first highly M5-preferring muscarinic acetylcholine receptor ligand, an M5 positive allosteric modulator derived from a series of 5-trifluoromethoxy N-benzyl isatins. J Med Chem 52: 3445–3448, 2009 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bruning TA, Chang PC, Hendriks MG, Vermeij P, Pfaffendorf M, van Zwieten PA. In vivo characterization of muscarinic receptor subtypes that mediate vasodilatation in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension 26: 70–77, 1995 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

