Induction of reaper ortholog mx in mosquito midgut cells following baculovirus infection
- PMID: 21331076
- PMCID: PMC3172108
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2011.8
Induction of reaper ortholog mx in mosquito midgut cells following baculovirus infection
Abstract
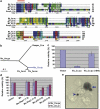
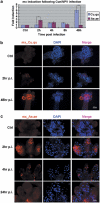
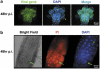
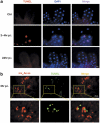
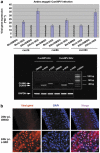
Many vertebrate and insect viruses possess antiapoptotic genes that are required for their infectivity. This led to the hypothesis that apoptosis is an innate immunoresponse important for limiting virus infections. The role of apoptosis may be especially important in insect antiviral defense because of the lack of adaptive immunity. However, the cellular mechanism that elicits apoptosis in response to viral infection in insects has not been determined. Using an in vivo infection system with the mosquito baculovirus CuniNPV (Culex nigripalpus nucleopolyhedrovirus), we demonstrated that michelob_x (mx), the mosquito ortholog of Drosophila proapoptotic gene reaper, is specifically induced in larval midgut cells following viral infection. Interestingly, the dynamics of mx induction corresponds with the outcome of the infection. In the permissive mosquito C. quinquefasciatus, a slow induction of mx failed to induce prompt apoptosis, and the infected cells eventually undergo necrosis with heavy loads of encapsulated viruses. In contrast, in the refractory mosquito Aedes aegypti, a rapid induction of mx within 30 min p.i. is followed by apoptosis within 2-6 h p.i., suggesting a possible role for apoptosis in limiting viral infection. When the execution of apoptosis was delayed by caspase inhibitors, viral gene expression became detectable in the A. aegypti larvae.
Figures
Similar articles
-
P53-mediated rapid induction of apoptosis conveys resistance to viral infection in Drosophila melanogaster.PLoS Pathog. 2013 Feb;9(2):e1003137. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003137. Epub 2013 Feb 7. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23408884 Free PMC article.
-
Infectivity and pathogenicity of a novel baculovirus, CuniNPV from Culex nigripalpus (Diptera: Culicidae) for thirteen species and four genera of mosquitoes.J Med Entomol. 2003 Jul;40(4):512-7. doi: 10.1603/0022-2585-40.4.512. J Med Entomol. 2003. PMID: 14680119
-
Effects of inducing or inhibiting apoptosis on Sindbis virus replication in mosquito cells.J Gen Virol. 2008 Nov;89(Pt 11):2651-2661. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.2008/005314-0. J Gen Virol. 2008. PMID: 18931060 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the canon: Non-classical mosquito genes at the interface of arboviral infection.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 Jun;109:72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2019.04.004. Epub 2019 Apr 7. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30970277 Review.
-
Insect defenses against virus infection: the role of apoptosis.Int Rev Immunol. 2003 Sep-Dec;22(5-6):401-24. doi: 10.1080/08830180305215. Int Rev Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12959752 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Group II Baculovirus IAPs on Virus-Induced Apoptosis in Insect Cells.Genes (Basel). 2022 Apr 24;13(5):750. doi: 10.3390/genes13050750. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35627135 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-Apoptotic Function Analysis of the Reaper Homologue IBM1 in Spodoptera frugiperda.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 15;21(8):2729. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082729. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32326478 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Cell Death by IAPs and Their Antagonists.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015;114:185-208. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2015.07.026. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26431568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of Apoptosis and Subsequent Phagocytosis of Virus-Infected Cells As an Antiviral Mechanism.Front Immunol. 2017 Sep 28;8:1220. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01220. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29033939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P53-mediated rapid induction of apoptosis conveys resistance to viral infection in Drosophila melanogaster.PLoS Pathog. 2013 Feb;9(2):e1003137. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003137. Epub 2013 Feb 7. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23408884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benedict CA, Norris PS, Ware CF. To kill or be killed: viral evasion of apoptosis. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:1013–1018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

