Membrane-coating lattice scaffolds in the nuclear pore and vesicle coats: commonalities, differences, challenges
- PMID: 21327078
- PMCID: PMC3027038
- DOI: 10.4161/nucl.1.4.11798
Membrane-coating lattice scaffolds in the nuclear pore and vesicle coats: commonalities, differences, challenges
Abstract
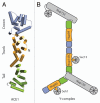
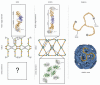
The nuclear pore complex (NPC) regulates all traffic between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. It is a large protein assembly composed of multiple copies of ∼30 nucleoporins (nups). Structural studies of the NPC have been limited by its considerable size and complexity. Progress toward understanding the structure of this nanomachine has benefited from its modular nature, which allows for this 40-60 MDa assembly to be broken down into subcomplexes that can be studied individually. While recent work by both crystallographers and electron microscopists has greatly enhanced our model of the NPC, the resolution gap between crystal and EM structures remains too large to confidently place individual proteins within the context of the fully assembled NPC. In an effort to arrive at a veritable model of the NPC, we solved the structure of several scaffold nups and defined the ancestral coatomer element (ACE1) common to a set of nucleoporins and COPII vesicle coat proteins. Subsequently, we proposed a lattice-like model of the NPC, analogous to the COPII lattice, in which ACE1 proteins form the edge elements and β-propellers form the vertex elements. Here, we review our recent studies, speculate on how interactions between subcomplexes of the NPC are mediated, and outline the steps and challenges that lay ahead on the path to understanding this enormous assembly in molecular detail.
Keywords: ACE1; assembly; membrane-coating; nuclear pore complex; nucleoporin; ²-propeller.
Figures
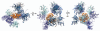
Similar articles
-
Molecular architecture of the Nup84-Nup145C-Sec13 edge element in the nuclear pore complex lattice.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009 Nov;16(11):1173-7. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1713. Epub 2009 Oct 25. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19855394 Free PMC article.
-
Structural evidence for common ancestry of the nuclear pore complex and vesicle coats.Science. 2008 Nov 28;322(5906):1369-73. doi: 10.1126/science.1165886. Epub 2008 Oct 30. Science. 2008. PMID: 18974315 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the Sec13-Sec16 edge element, a template for assembly of the COPII vesicle coat.J Cell Biol. 2010 Aug 9;190(3):347-61. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201003092. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20696705 Free PMC article.
-
From the resolution revolution to evolution: structural insights into the evolutionary relationships between vesicle coats and the nuclear pore.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2018 Oct;52:32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2018.07.012. Epub 2018 Aug 11. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2018. PMID: 30103204 Review.
-
Structure and Assembly of the Nuclear Pore Complex.Annu Rev Biophys. 2019 May 6;48:515-536. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-052118-115308. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Annu Rev Biophys. 2019. PMID: 30943044 Review.
Cited by
-
An inside-out origin for the eukaryotic cell.BMC Biol. 2014 Oct 28;12:76. doi: 10.1186/s12915-014-0076-2. BMC Biol. 2014. PMID: 25350791 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative structure-function mapping of the nucleoporin Nup133 suggests a conserved mechanism for membrane anchoring of the nuclear pore complex.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014 Nov;13(11):2911-26. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M114.040915. Epub 2014 Aug 19. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 25139911 Free PMC article.
-
The nuclear pore complex function of Sec13 protein is required for cell survival during retinal development.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 25;289(17):11971-11985. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.547190. Epub 2014 Mar 13. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24627485 Free PMC article.
-
A Tumor suppressor complex with GAP activity for the Rag GTPases that signal amino acid sufficiency to mTORC1.Science. 2013 May 31;340(6136):1100-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1232044. Science. 2013. PMID: 23723238 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of human Sec16B: indications of specialized, non-redundant functions.Sci Rep. 2011;1:77. doi: 10.1038/srep00077. Epub 2011 Aug 30. Sci Rep. 2011. PMID: 22355596 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tran EJ, Wente SR. Dynamic nuclear pore complexes: life on the edge. Cell. 2006;125:1041–1053. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
