Eritoran tetrasodium (E5564) treatment for sepsis: review of preclinical and clinical studies
- PMID: 21323610
- PMCID: PMC3065179
- DOI: 10.1517/17425255.2011.558190
Eritoran tetrasodium (E5564) treatment for sepsis: review of preclinical and clinical studies
Abstract
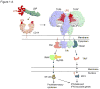
Introduction: Sepsis remains a leading cause of death worldwide. Despite years of extensive research, effective drugs that inhibit the pro-inflammatory effects of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and improve outcome when added to conventional sepsis treatments are lacking. Eritoran tetrasodium (E5564) is a promising candidate therapy for sepsis belonging to a new class of such drugs which inhibit LPS-induced inflammation by blocking toll-like receptor 4.
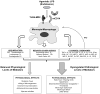
Areas covered: This review focuses on the rationale for the use of eritoran tetrasodium in sepsis as well as on its pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, efficacy and safety. Preclinical and clinical studies from a MEDLINE/PubMed literature search in August 2010 with the search terms 'eritoran' and 'E5564' are discussed.
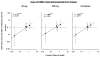
Expert opinion: Preclinical in vitro and in vivo studies of eritoran tetrasodium indicate it can limit excessive inflammatory mediator release associated with LPS and improve survival in sepsis models. While early clinical results are promising, its efficacy and safety for treating patients with sepsis are currently under investigation. Even if the ongoing Phase III clinical trial enrolling patients with severe sepsis and increased risk of death shows benefit from eritoran, questions remain and confirmatory studies would be necessary to define its clinical usage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare intramural funding from the National Institutes of Health
Figures


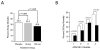
Similar articles
-
In vivo Toll-like receptor 4 antagonism restores cardiac function during endotoxemia.Shock. 2011 Dec;36(6):613-20. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e318235805f. Shock. 2011. PMID: 22089127
-
Phase 2 trial of eritoran tetrasodium (E5564), a toll-like receptor 4 antagonist, in patients with severe sepsis.Crit Care Med. 2010 Jan;38(1):72-83. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181b07b78. Crit Care Med. 2010. PMID: 19661804 Clinical Trial.
-
Influence of severity of illness on the effects of eritoran tetrasodium (E5564) and on other therapies for severe sepsis.Shock. 2011 Oct;36(4):327-31. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e318227980e. Shock. 2011. PMID: 21701421 Clinical Trial.
-
Toll-like receptor-4 antagonist eritoran tetrasodium for severe sepsis.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2011 May;9(5):507-20. doi: 10.1586/eri.11.27. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2011. PMID: 21609262 Review.
-
Targeting myeloid differentiation 2 for treatment of sepsis.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014 Jun 1;19(6):904-15. doi: 10.2741/4256. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014. PMID: 24896325 Review.
Cited by
-
Morphine activates neuroinflammation in a manner parallel to endotoxin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Apr 17;109(16):6325-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1200130109. Epub 2012 Apr 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22474354 Free PMC article.
-
Is Toll-like receptor 4 involved in the severity of COVID-19 pathology in patients with cardiometabolic comorbidities?Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021 Apr;58:102-110. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.09.002. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021. PMID: 32988728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ablation of Myeloid Cell MRP8 Ameliorates Nephrotoxic Serum-induced Glomerulonephritis by Affecting Macrophage Characterization through Intraglomerular Crosstalk.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 20;10(1):3056. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59970-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32080297 Free PMC article.
-
Like Cures Like: Pharmacological Activity of Anti-Inflammatory Lipopolysaccharides From Gut Microbiome.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Apr 30;11:554. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00554. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32425790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) antagonist eritoran tetrasodium attenuates liver ischemia and reperfusion injury through inhibition of high-mobility group box protein B1 (HMGB1) signaling.Mol Med. 2015 Mar 13;20(1):639-48. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2014.00076. Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25375408 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aderem A, Ulevitch RJ. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature. 2000 Aug 17;406(6797):782–7. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Takeda K, Kaisho T. Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat Immunol. 2001 Aug;2(8):675–80. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Hemmi H. Recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns by TLR family. Immunol Lett. 2003 Jan 22;85(2):85–95. - PubMed
-
- Janeway CA, Jr, Medzhitov R. Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:197–216. - PubMed
-
- Park BS, Song DH, Kim HM, et al. The structural basis of lipopolysaccharide recognition by the TLR4-MD-2 complex. Nature. 2009 Apr 30;458(7242):1191–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
