A distinct trans-Golgi network subcompartment for sorting of synaptic and granule proteins in neurons and neuroendocrine cells
- PMID: 21321327
- PMCID: PMC3039018
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.076372
A distinct trans-Golgi network subcompartment for sorting of synaptic and granule proteins in neurons and neuroendocrine cells
Abstract
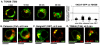
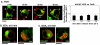
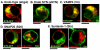
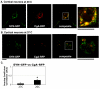
Golgi-to-plasma-membrane trafficking of synaptic-like microvesicle (SLMV) proteins, vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT) and synaptophysin (SYN), and a large dense-core vesicle (LDCV) protein, chromogranin A (CgA), was investigated in undifferentiated neuroendocrine PC12 cells. Live cell imaging and 20°C block-release experiments showed that VAChT-GFP, SYN-GFP and CgA-RFP specifically and transiently cohabitated in a distinct sorting compartment during cold block and then separated into synaptic protein transport vesicles (SPTVs) and LDCVs, after release from temperature block. We found that in this trans-Golgi subcompartment there was colocalization of SPTV and LDCV proteins, most significantly with VAMP4 and Golgin97, and to some degree with TGN46, but not at all with TGN38. Moreover, some SNAP25 and VAMP2, two subunits of the exocytic machinery, were also recruited onto this compartment. Thus, in neuroendocrine cells, synaptic vesicle and LDCV proteins converge briefly in a distinct trans-Golgi network subcompartment before sorting into SPTVs and LDCVs, ultimately for delivery to the plasma membrane. This specialized sorting compartment from which SPTVs and LDCVs bud might facilitate the acquisition of common exocytic machinery needed on the membranes of these vesicles.
Figures
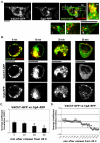
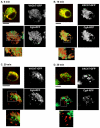
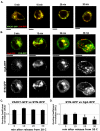
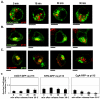
Similar articles
-
Assembly of active zone precursor vesicles: obligatory trafficking of presynaptic cytomatrix proteins Bassoon and Piccolo via a trans-Golgi compartment.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 3;281(9):6038-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M508784200. Epub 2005 Dec 21. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16373352
-
Local protein dynamics during microvesicle exocytosis in neuroendocrine cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2018 Aug 1;29(15):1891-1903. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-12-0716. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29874123 Free PMC article.
-
Differential localization of vesicular acetylcholine and monoamine transporters in PC12 cells but not CHO cells.J Cell Biol. 1997 Nov 17;139(4):907-16. doi: 10.1083/jcb.139.4.907. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9362509 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin granule biogenesis, trafficking and exocytosis.Vitam Horm. 2009;80:473-506. doi: 10.1016/S0083-6729(08)00616-X. Vitam Horm. 2009. PMID: 19251047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRP Channel Trafficking.In: Liedtke WB, Heller S, editors. TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2007. Chapter 23. In: Liedtke WB, Heller S, editors. TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2007. Chapter 23. PMID: 21204515 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Commonly used trafficking blocks disrupt ARF1 activation and the localization and function of specific Golgi proteins.Mol Biol Cell. 2018 Apr 15;29(8):937-947. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-11-0622. Epub 2018 Mar 30. Mol Biol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29467256 Free PMC article.
-
The Conserved VPS-50 Protein Functions in Dense-Core Vesicle Maturation and Acidification and Controls Animal Behavior.Curr Biol. 2016 Apr 4;26(7):862-71. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.01.049. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Curr Biol. 2016. PMID: 26948874 Free PMC article.
-
The redistribution of Drosophila vesicular monoamine transporter mutants from synaptic vesicles to large dense-core vesicles impairs amine-dependent behaviors.J Neurosci. 2014 May 14;34(20):6924-37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0694-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24828646 Free PMC article.
-
Chromogranin B regulates early-stage insulin granule trafficking from the Golgi in pancreatic islet β-cells.J Cell Sci. 2019 Jul 1;132(13):jcs231373. doi: 10.1242/jcs.231373. J Cell Sci. 2019. PMID: 31182646 Free PMC article.
-
UNC-16/JIP3 regulates early events in synaptic vesicle protein trafficking via LRK-1/LRRK2 and AP complexes.PLoS Genet. 2017 Nov 16;13(11):e1007100. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007100. eCollection 2017 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 29145394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams L. A., Ang L. C., Munoz D. G. (1993). Chromogranin A, a soluble synaptic vesicle protein, is found in cortical neurons other than previously defined peptidergic neurons in the human neocortex. Brain Res. 602, 336-341 - PubMed
-
- Agoston D. V., Whittaker V. P. (1989). Characterization, by size, density, osmotic fragility, and immunoaffinity, of acetylcholine- and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-containing storage particles from myenteric neurones of the guinea-pig. J. Neurochem. 52, 1474-1480 - PubMed
-
- Bauerfeind R., Regnier-Vigouroux A., Flatmark T., Huttner W. B. (1993). Selective storage of acetylcholine, but not catecholamines, in neuroendocrine synaptic-like microvesicles of early endosomal origin. Neuron 11, 105-121 - PubMed
-
- Blusztajn J. K., Berse B. (2000). The cholinergic neuronal phenotype in Alzheimer's disease. Metab. Brain Dis. 15, 45-64 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

