RAB-5- and RAB-11-dependent vesicle-trafficking pathways are required for plasma membrane repair after attack by bacterial pore-forming toxin
- PMID: 21320697
- PMCID: PMC3057397
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2011.01.005
RAB-5- and RAB-11-dependent vesicle-trafficking pathways are required for plasma membrane repair after attack by bacterial pore-forming toxin
Abstract
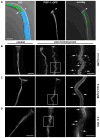
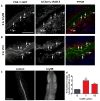
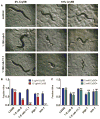
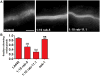
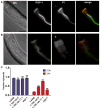
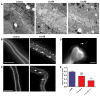
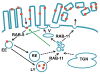
Pore-forming toxins (PFTs) secreted by pathogenic bacteria are the most common bacterial protein toxins and are important virulence factors for infection. PFTs punch holes in host cell plasma membranes, and although cells can counteract the resulting membrane damage, the underlying mechanisms at play remain unclear. Using Caenorhabditis elegans as a model, we demonstrate in vivo and in an intact epithelium that intestinal cells respond to PFTs by increasing levels of endocytosis, dependent upon RAB-5 and RAB-11, which are master regulators of endocytic and exocytic events. Furthermore, we find that RAB-5 and RAB-11 are required for protection against PFT and to restore integrity to the plasma membrane. One physical mechanism involved is the RAB-11-dependent expulsion of microvilli from the apical side of the intestinal epithelial cells. Specific vesicle-trafficking pathways thus protect cells against an attack by PFTs on plasma membrane integrity, via altered plasma membrane dynamics.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PRMT-7/PRMT7 activates HLH-30/TFEB to guard plasma membrane integrity compromised by bacterial pore-forming toxins.Autophagy. 2024 Jun;20(6):1335-1358. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2024.2306655. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Autophagy. 2024. PMID: 38261662 Free PMC article.
-
Global functional analyses of cellular responses to pore-forming toxins.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Mar;7(3):e1001314. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001314. Epub 2011 Mar 3. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21408619 Free PMC article.
-
EHBP-1 functions with RAB-10 during endocytic recycling in Caenorhabditis elegans.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Aug 15;21(16):2930-43. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-02-0149. Epub 2010 Jun 23. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20573983 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Basis of the Pore-Forming Toxin/Membrane Interaction.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Feb 9;13(2):128. doi: 10.3390/toxins13020128. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33572271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pore worms: using Caenorhabditis elegans to study how bacterial toxins interact with their target host.Int J Med Microbiol. 2004 Apr;293(7-8):599-607. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00303. Int J Med Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15149037 Review.
Cited by
-
Vegetative Insecticidal Protein (Vip): A Potential Contender From Bacillus thuringiensis for Efficient Management of Various Detrimental Agricultural Pests.Front Microbiol. 2021 May 13;12:659736. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.659736. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34054756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New role for DCR-1/dicer in Caenorhabditis elegans innate immunity against the highly virulent bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis DB27.Infect Immun. 2013 Oct;81(10):3942-57. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00700-13. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 23918784 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane Repair Mechanisms against Permeabilization by Pore-Forming Toxins.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Jun 9;10(6):234. doi: 10.3390/toxins10060234. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29890730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A study of wound repair in Dictyostelium cells by using novel laserporation.Sci Rep. 2018 May 22;8(1):7969. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26337-0. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29789591 Free PMC article.
-
PRMT-7/PRMT7 activates HLH-30/TFEB to guard plasma membrane integrity compromised by bacterial pore-forming toxins.Autophagy. 2024 Jun;20(6):1335-1358. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2024.2306655. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Autophagy. 2024. PMID: 38261662 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alegado RA, Campbell MC, Chen WC, Slutz SS, Tan MW. Characterization of mediators of microbial virulence and innate immunity using the Caenorhabditis elegans host-pathogen model. Cell Microbiol. 2003;5:435–444. - PubMed
-
- Alouf JE. Molecular features of the cytolytic pore-forming bacterial protein toxins. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 2003;48:5–16. - PubMed
-
- Aroian R, van der Goot FG. Pore-forming toxins and cellular non-immune defenses (CNIDs) Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007;10:57–61. - PubMed
-
- Babiychuk EB, Monastyrskaya K, Potez S, Draeger A. Intracellular Ca(2+) operates a switch between repair and lysis of streptolysin O-perforated cells. Cell Death Differ. 2009;16:1126–1134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM071603-03/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI056189-06A1/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI056189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM071603/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071603-01A2/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 2R01AI056189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI056189-07/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071603-04S2/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071603-04S1/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071603-03S1/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071603-04/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071603/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071603-02/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

