A computationally optimized broadly reactive antigen (COBRA) based H5N1 VLP vaccine elicits broadly reactive antibodies in mice and ferrets
- PMID: 21320540
- PMCID: PMC3090662
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.01.100
A computationally optimized broadly reactive antigen (COBRA) based H5N1 VLP vaccine elicits broadly reactive antibodies in mice and ferrets
Abstract
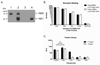
Pandemic outbreaks of influenza are caused by the emergence of a pathogenic and transmissible virus to which the human population is immunologically naïve. Recent outbreaks of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) of the H5N1 subtype are of particular concern because of the high mortality rate (60% case fatality rate) and novel subtype. In order to develop a vaccine that elicits broadly reactive antibody responses against emerging H5N1 isolates, we utilized a novel antigen design technique termed computationally optimized broadly reactive antigen (COBRA). The COBRA HA sequence was based upon HA amino acid sequences from clade 2 H5N1 human infections and the expressed protein retained the ability to bind the receptor, as well as mediate particle fusion. Non-infectious recombinant VLP vaccines using the COBRA HA were purified from a mammalian expression system. Mice and ferrets vaccinated with COBRA HA H5N1 VLPs had protective levels of HAI antibodies to a representative isolates from each subclade of clade 2. Furthermore, VLP vaccinated animals were completely protected from a lethal challenge of the clade 2.2 H5N1 virus A/Whooper Swan/Mongolia/244/2005. This is the first report describing the use of COBRA-based antigen design. The COBRA HA H5N1 VLP vaccine elicited broadly reactive antibodies and is an effective influenza vaccine against HPAI virus.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Antibody breadth and protective efficacy are increased by vaccination with computationally optimized hemagglutinin but not with polyvalent hemagglutinin-based H5N1 virus-like particle vaccines.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012 Feb;19(2):128-39. doi: 10.1128/CVI.05533-11. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22190399 Free PMC article.
-
Cocktail of H5N1 COBRA HA vaccines elicit protective antibodies against H5N1 viruses from multiple clades.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015;11(3):572-83. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1012013. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015. PMID: 25671661 Free PMC article.
-
A computationally optimized hemagglutinin virus-like particle vaccine elicits broadly reactive antibodies that protect nonhuman primates from H5N1 infection.J Infect Dis. 2012 May 15;205(10):1562-70. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis232. Epub 2012 Mar 23. J Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22448011 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Characterization of a Computationally Optimized Broadly Reactive Hemagglutinin Vaccine for H1N1 Influenza Viruses.J Virol. 2016 Apr 14;90(9):4720-4734. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03152-15. Print 2016 May. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26912624 Free PMC article.
-
Elicitation of Protective Antibodies against a Broad Panel of H1N1 Viruses in Ferrets Preimmune to Historical H1N1 Influenza Viruses.J Virol. 2017 Nov 30;91(24):e01283-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01283-17. Print 2017 Dec 15. J Virol. 2017. Retraction in: J Virol. 2024 Jul 23;98(7):e0183223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01832-23 PMID: 28978709 Free PMC article. Retracted.
Cited by
-
An H1N1 Computationally Optimized Broadly Reactive Antigen Elicits a Neutralizing Antibody Response against an Emerging Human-Infecting Eurasian Avian-Like Swine Influenza Virus.J Virol. 2021 Jun 10;95(13):e0242120. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02421-20. Epub 2021 Jun 10. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33853960 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Strategies Targeting Hemagglutinin as a Universal Influenza Vaccine.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Mar 13;9(3):257. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9030257. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Avoiding Regions Symptomatic of Conformational and Functional Flexibility to Identify Antiviral Targets in Current and Future Coronaviruses.Genome Biol Evol. 2016 Dec 31;8(11):3471-3484. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evw246. Genome Biol Evol. 2016. PMID: 27797946 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody breadth and protective efficacy are increased by vaccination with computationally optimized hemagglutinin but not with polyvalent hemagglutinin-based H5N1 virus-like particle vaccines.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012 Feb;19(2):128-39. doi: 10.1128/CVI.05533-11. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22190399 Free PMC article.
-
Very Broadly Effective Hemagglutinin-Directed Influenza Vaccines with Anti-Herpetic Activity.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 May 14;12(5):537. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12050537. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38793788 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Avian influenza: assessing the pandemic threat. 2005 [cited; Available from http://www.who.int/csr/disease/influenza/WHO_CDS_2005_29/en/index.html.
-
- World Health Organization. Cumulative Number of Confirmed Human Cases of Avian Influenza A/(H5N1) Reported to WHO. 2008 [cited; Available from: http://www.who.int/csr/disease/avian_influenza/country/cases_table_2008_....
-
- Li KS, Guan Y, Wang J, Smith GJD, Xu KM, Duan L, et al. Genesis of a highly pathogenic and potentially pandemic H5N1 influenza virus in eastern Asia. Nature. 2004;430(6996):209–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

