Modulation of TRAIL resistance in colon carcinoma cells: different contributions of DR4 and DR5
- PMID: 21272366
- PMCID: PMC3045356
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-39
Modulation of TRAIL resistance in colon carcinoma cells: different contributions of DR4 and DR5
Abstract
Background: rhTRAIL is a therapeutic agent, derived from the TRAIL cytokine, which induces apoptosis in cancer cells by activating the membrane death receptors 4 and 5 (DR4 and DR5). Here, we investigated each receptor's contribution to rhTRAIL sensitivity and rhTRAIL resistance. We assessed whether agonistic DR4 or DR5 antibodies could be used to circumvent rhTRAIL resistance, alone or in combination with various chemotherapies.
Methods: Our study was performed in an isogenic model comprised of the SW948 human colon carcinoma cell line and its rhTRAIL resistant sub-line SW948-TR. Effects of rhTRAIL and agonistic DR4/DR5 antibodies on cell viability were measured using MTT assays and identification of morphological changes characteristic of apoptosis, after acridine orange staining. Sensitivity to the different death receptor ligands was stimulated using pretreatment with the cytokine IFN-gamma and the proteasome inhibitor MG-132. To investigate the mechanisms underlying the changes in rhTRAIL sensitivity, alterations in expression levels of targets of interest were measured by Western blot analysis. Co-immunoprecipitation was used to determine the composition of the death-inducing signalling complex at the cell membrane.
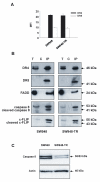
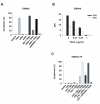
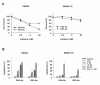
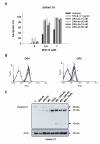
Results: SW948 cells were sensitive to all three of the DR-targeting agents tested, although the agonistic DR5 antibody induced only weak caspase 8 cleavage and limited apoptosis. Surprisingly, agonistic DR4 and DR5 antibodies induced equivalent DISC formation and caspase 8 cleavage at the level of their individual receptors, suggesting impairment of further caspase 8 processing upon DR5 stimulation. SW948-TR cells were cross-resistant to all DR-targeting agents as a result of decreased caspase 8 expression levels. Caspase 8 protein expression was restored by MG-132 and IFN-gamma pretreatment, which also re-established sensitivity to rhTRAIL and agonistic DR4 antibody in SW948-TR. Surprisingly, MG-132 but not IFN-gamma could also increase DR5-mediated apoptosis in SW948-TR.
Conclusions: These results highlight a critical difference between DR4- and DR5-mediated apoptotic signaling modulation, with possible implications for future combinatorial regimens.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Downregulation of active caspase 8 as a mechanism of acquired TRAIL resistance in mismatch repair-proficient colon carcinoma cell lines.Int J Oncol. 2010 Oct;37(4):1031-41. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000755. Int J Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20811726
-
Inhibition of IGF-1R-dependent PI3K activation sensitizes colon cancer cells specifically to DR5-mediated apoptosis but not to rhTRAIL.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2011 Jun;34(3):245-59. doi: 10.1007/s13402-011-0033-9. Epub 2011 Apr 30. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2011. PMID: 21538027
-
Inhibition of IGF-1R-dependent PI3K activation sensitizes colon cancer cells specifically to DR5-mediated apoptosis but not to rhTRAIL.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2010;33(5):229-44. doi: 10.3233/ACP-CLO-2010-0549. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2010. PMID: 20978316 Free PMC article.
-
TRAIL receptor signalling and modulation: Are we on the right TRAIL?Cancer Treat Rev. 2009 May;35(3):280-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2008.11.006. Epub 2008 Dec 30. Cancer Treat Rev. 2009. PMID: 19117685 Review.
-
TRAIL death receptors and cancer therapeutics.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2007 Nov 1;224(3):284-9. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2006.12.007. Epub 2006 Dec 15. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17240413 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of never in mitosis A (NIMA)-related kinase-4 reduces survivin expression and sensitizes cancer cells to TRAIL-induced cell death.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 4;7(40):65957-65967. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11781. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27602754 Free PMC article.
-
Oxaliplatin Enhances the Apoptotic Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Delivering Soluble TRAIL in Chemoresistant Colorectal Cancer.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Oct 12;16(10):1448. doi: 10.3390/ph16101448. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895919 Free PMC article.
-
Thermotherapy enhances oxaliplatin-induced cytotoxicity in human colon carcinoma cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Feb 21;18(7):646-53. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i7.646. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22363135 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus casei Exerts Anti-Proliferative Effects Accompanied by Apoptotic Cell Death and Up-Regulation of TRAIL in Colon Carcinoma Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 5;11(2):e0147960. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147960. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26849051 Free PMC article.
-
Down-Regulation of Survivin by Nemadipine-A Sensitizes Cancer Cells to TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2013 Jan;21(1):29-34. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2012.088. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2013. PMID: 24009855 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

