A glimpse of various pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 21261520
- PMCID: PMC3700379
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.pathol.4.110807.092150
A glimpse of various pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
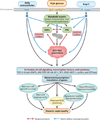
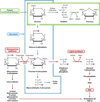
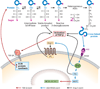
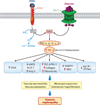
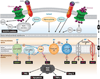
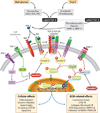
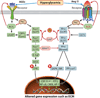
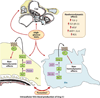
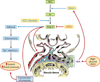
Diabetic nephropathy is a well-known complication of diabetes and is a leading cause of chronic renal failure in the Western world. It is characterized by the accumulation of extracellular matrix in the glomerular and tubulointerstitial compartments and by the thickening and hyalinization of intrarenal vasculature. The various cellular events and signaling pathways activated during diabetic nephropathy may be similar in different cell types. Such cellular events include excessive channeling of glucose intermediaries into various metabolic pathways with generation of advanced glycation products, activation of protein kinase C, increased expression of transforming growth factor β and GTP-binding proteins, and generation of reactive oxygen species. In addition to these metabolic and biochemical derangements, changes in the intraglomerular hemodynamics, modulated in part by local activation of the renin-angiotensin system, compound the hyperglycemia-induced injury. Events involving various intersecting pathways occur in most cell types of the kidney.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diabetic nephropathy: mechanisms of renal disease progression.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2008 Jan;233(1):4-11. doi: 10.3181/0705-MR-134. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2008. PMID: 18156300 Review.
-
Cell biology of diabetic kidney disease.Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2005;101(3):e100-10. doi: 10.1159/000087339. Epub 2005 Aug 8. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2005. PMID: 16088221 Review.
-
Pathophysiology of the diabetic kidney.Compr Physiol. 2011 Jul;1(3):1175-232. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c100049. Compr Physiol. 2011. PMID: 23733640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress in diabetic nephropathy.Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(34):4256-69. doi: 10.2174/092986710793348581. Curr Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20939814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetic nephropathy and transforming growth factor-beta: transforming our view of glomerulosclerosis and fibrosis build-up.Semin Nephrol. 2003 Nov;23(6):532-43. doi: 10.1053/s0270-9295(03)00132-3. Semin Nephrol. 2003. PMID: 14631561 Review.
Cited by
-
Nox4 and diabetic nephropathy: with a friend like this, who needs enemies?Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Aug;61:130-42. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.03.014. Epub 2013 Mar 23. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23528476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on the Mechanisms of Tubular Cell Injury in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Mar 30;8:661076. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.661076. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33859992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sappanone a prevents diabetic kidney disease by inhibiting kidney inflammation and fibrosis via the NF-κB signaling pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 16;13:953004. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.953004. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36052141 Free PMC article.
-
The serum 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D concentration, a marker of vitamin D catabolism, is reduced in chronic kidney disease.Kidney Int. 2012 Sep;82(6):693-700. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.193. Epub 2012 May 30. Kidney Int. 2012. PMID: 22648296 Free PMC article.
-
Recent developments in epigenetics of acute and chronic kidney diseases.Kidney Int. 2015 Aug;88(2):250-61. doi: 10.1038/ki.2015.148. Epub 2015 May 20. Kidney Int. 2015. PMID: 25993323 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- LeRoith D, Taylor SI, Olefsky JM. Diabetes Mellitus: A Fundamental and Clinical Text. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott William & Wilkins; 2004. p. 1,540.
-
- Reddy AS. Diabetic Nephropathy: Theory and Practice. East Hanover, NJ: College Book Publ; 2004. p. 563.
-
- Wolf G. New insights into the pathophysiology of diabetic nephropathy: from hemodynamics to molecular pathology. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2004;34:785–796. - PubMed
-
- Schena FP, Gesualdo L. Pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005;16:S30–S33. - PubMed
-
- Susztak K, Bottinger EP. Diabetic nephropathy: a frontier for personalized medicine. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006;17:361–367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

