The melanocortin 3 receptor: a novel mediator of exercise-induced inflammation reduction in postmenopausal women?
- PMID: 21253483
- PMCID: PMC3022199
- DOI: 10.4061/2011/512593
The melanocortin 3 receptor: a novel mediator of exercise-induced inflammation reduction in postmenopausal women?
Abstract
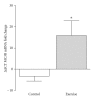
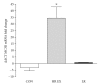
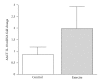
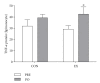
The purpose of this study was to determine whether resistance exercise training-induced reductions in inflammation are mediated via melanocortin 3 receptor expression in obese (BMI 32.7 ± 3.7) women (65.6 ± 2.8 yrs) randomized to either a control (N = 11) or resistance training group (N = 12). The resistance trained group performed resistance training 3 days/week for 12 weeks. Resting blood samples were collected before and after the training intervention in both resistance trained and control groups. Resistance training upregulated melanocortin 3 receptor mRNA by 16-fold (P = .035) and decreased monocyte count, without changing leukocyte number, body composition, or body weight. Resistance trained individuals exhibited increased sensitivity to inflammatory stimuli, whereas control individuals exhibited no change. While there was no change in whole blood tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA between the groups, whole blood interleukin 10 mRNA was higher in the resistance trained group following the intervention period. In summary, it appears that resistance training may modulate melanocortin 3 receptor expression, providing a possible mechanism for the anti-inflammatory effects of exercise training.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resistance training reduces subclinical inflammation in obese, postmenopausal women.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012 Nov;44(11):2099-110. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e3182644984. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012. PMID: 22874536 Clinical Trial.
-
Melanocortin receptor expression is associated with reduced CRP in response to resistance training.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012 Aug;113(3):393-400. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00107.2012. Epub 2012 Jun 7. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012. PMID: 22678961 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Adipose tissue inflammation in breast cancer survivors: effects of a 16-week combined aerobic and resistance exercise training intervention.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Feb;168(1):147-157. doi: 10.1007/s10549-017-4576-y. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 29168064 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Toll-like receptor 4 and CD14 mRNA expression are lower in resistive exercise-trained elderly women.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2003 Nov;95(5):1833-42. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00359.2003. Epub 2003 Jun 27. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2003. PMID: 12832426
-
The impact of exercise training on inflammatory markers in postmenopausal women: A systemic review and meta-analysis.Exp Gerontol. 2021 Jul 15;150:111398. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2021.111398. Epub 2021 May 7. Exp Gerontol. 2021. PMID: 33965553 Review.
Cited by
-
Associations of the melanocortin 3 receptor C17A + G241A haplotype with body composition and inflammation in African-American adults.Ann Hum Genet. 2019 Sep;83(5):355-360. doi: 10.1111/ahg.12315. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Ann Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 30937899 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of resistance training on body weight and body composition in older adults: An inter-individual response difference meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Sci Prog. 2023 Apr-Jun;106(2):368504231179062. doi: 10.1177/00368504231179062. Sci Prog. 2023. PMID: 37302150 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Exercise on the Body Composition and Lipid Profile of Individuals with Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Obes Metab Syndr. 2019 Dec;28(4):278-294. doi: 10.7570/jomes.2019.28.4.278. Epub 2019 Dec 30. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2019. PMID: 31909371 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of real-time PCR Melanocortin 3 (MC3R) gene expression to identify new biomarkers inflammation in tuberculosis.Egypt J Med Hum Genet. 2022;23(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s43042-022-00323-8. Epub 2022 Jul 18. Egypt J Med Hum Genet. 2022. PMID: 37521838 Free PMC article.
-
Linking Physical Activity to Breast Cancer Risk via Inflammation, Part 1: The Effect of Physical Activity on Inflammation.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2023 May 1;32(5):588-596. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-22-0928. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2023. PMID: 36867865 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rizzo M, Corrado E, Coppola G, Muratori I, Novo G, Novo S. Markers of inflammation are strong predictors of subclinical and clinical atherosclerosis in women with hypertension. Coronary Artery Disease. 2009;20(1):15–20. - PubMed
-
- Pedersen BK. Exercise and cytokines. Immunology and Cell Biology. 2000;78(5):532–535. - PubMed
-
- Plaisance EP, Grandjean PW. Physical activity and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein. Sports Medicine. 2006;36(5):443–458. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

