Transcription initiation patterns indicate divergent strategies for gene regulation at the chromatin level
- PMID: 21249180
- PMCID: PMC3020932
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001274
Transcription initiation patterns indicate divergent strategies for gene regulation at the chromatin level
Abstract
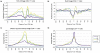
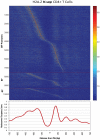
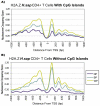
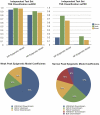
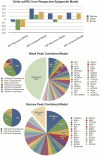
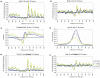
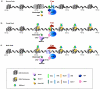
The application of deep sequencing to map 5' capped transcripts has confirmed the existence of at least two distinct promoter classes in metazoans: "focused" promoters with transcription start sites (TSSs) that occur in a narrowly defined genomic span and "dispersed" promoters with TSSs that are spread over a larger window. Previous studies have explored the presence of genomic features, such as CpG islands and sequence motifs, in these promoter classes, but virtually no studies have directly investigated the relationship with chromatin features. Here, we show that promoter classes are significantly differentiated by nucleosome organization and chromatin structure. Dispersed promoters display higher associations with well-positioned nucleosomes downstream of the TSS and a more clearly defined nucleosome free region upstream, while focused promoters have a less organized nucleosome structure, yet higher presence of RNA polymerase II. These differences extend to histone variants (H2A.Z) and marks (H3K4 methylation), as well as insulator binding (such as CTCF), independent of the expression levels of affected genes. Notably, differences are conserved across mammals and flies, and they provide for a clearer separation of promoter architectures than the presence and absence of CpG islands or the occurrence of stalled RNA polymerase. Computational models support the stronger contribution of chromatin features to the definition of dispersed promoters compared to focused start sites. Our results show that promoter classes defined from 5' capped transcripts not only reflect differences in the initiation process at the core promoter but also are indicative of divergent transcriptional programs established within gene-proximal nucleosome organization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metazoan promoters: emerging characteristics and insights into transcriptional regulation.Nat Rev Genet. 2012 Mar 6;13(4):233-45. doi: 10.1038/nrg3163. Nat Rev Genet. 2012. PMID: 22392219 Review.
-
Human genes with CpG island promoters have a distinct transcription-associated chromatin organization.Genome Biol. 2012 Nov 27;13(11):R110. doi: 10.1186/gb-2012-13-11-r110. Genome Biol. 2012. PMID: 23186133 Free PMC article.
-
An unmethylated 3' promoter-proximal region is required for efficient transcription initiation.PLoS Genet. 2007 Feb 16;3(2):e27. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030027. Epub 2007 Jan 2. PLoS Genet. 2007. PMID: 17305432 Free PMC article.
-
Downstream Antisense Transcription Predicts Genomic Features That Define the Specific Chromatin Environment at Mammalian Promoters.PLoS Genet. 2016 Aug 3;12(8):e1006224. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006224. eCollection 2016 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27487356 Free PMC article.
-
Promoter architectures and developmental gene regulation.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016 Sep;57:11-23. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.01.014. Epub 2016 Jan 16. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 26783721 Review.
Cited by
-
A global change in RNA polymerase II pausing during the Drosophila midblastula transition.Elife. 2013 Aug 13;2:e00861. doi: 10.7554/eLife.00861. Elife. 2013. PMID: 23951546 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin analysis of adult pluripotent stem cells reveals a unique stemness maintenance strategy.Sci Adv. 2023 Oct 6;9(40):eadh4887. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adh4887. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37801496 Free PMC article.
-
CAST-ChIP maps cell-type-specific chromatin states in the Drosophila central nervous system.Cell Rep. 2013 Oct 17;5(1):271-82. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.09.001. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Cell Rep. 2013. PMID: 24095734 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative promoters in CpG depleted regions are prevalently associated with epigenetic misregulation of liver cancer transcriptomes.Nat Commun. 2023 May 11;14(1):2712. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38272-4. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37169774 Free PMC article.
-
Metazoan promoters: emerging characteristics and insights into transcriptional regulation.Nat Rev Genet. 2012 Mar 6;13(4):233-45. doi: 10.1038/nrg3163. Nat Rev Genet. 2012. PMID: 22392219 Review.
References
-
- Carninci P, Sandelin A, Lenhard B, Katayama S, Shimokawa K, et al. Genome-wide analysis of mammalian promoter architecture and evolution. Nat Genet. 2006;38:626–635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

