Wide-ranging functions of E2F4 in transcriptional activation and repression revealed by genome-wide analysis
- PMID: 21247883
- PMCID: PMC3089461
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq1313
Wide-ranging functions of E2F4 in transcriptional activation and repression revealed by genome-wide analysis
Abstract
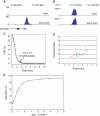
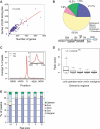
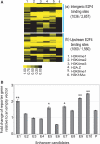
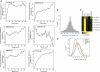
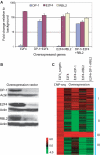
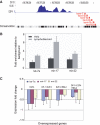
The E2F family of transcription factors has important roles in cell cycle progression. E2F4 is an E2F family member that has been proposed to be primarily a repressor of transcription, but the scope of its binding activity and functions in transcriptional regulation is not fully known. We used ChIP sequencing (ChIP-seq) to identify around 16,000 E2F4 binding sites which potentially regulate 7346 downstream target genes with wide-ranging functions in DNA repair, cell cycle regulation, apoptosis, and other processes. While half of all E2F4 binding sites (56%) occurred near transcription start sites (TSSs), ∼20% of sites occurred more than 20 kb away from any annotated TSS. These distal sites showed histone modifications suggesting that E2F4 may function as a long-range regulator, which we confirmed by functional experimental assays on a subset. Overexpression of E2F4 and its transcriptional cofactors of the retinoblastoma (Rb) family and its binding partner DP-1 revealed that E2F4 acts as an activator as well as a repressor. E2F4 binding sites also occurred near regulatory elements for miRNAs such as let-7a and mir-17, suggestive of regulation of miRNAs by E2F4. Taken together, our genome-wide analysis provided evidence of versatile roles of E2F4 and insights into its functions.
© The Author(s) 2011. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
E2F4-RB and E2F4-p107 complexes suppress gene expression by transforming growth factor beta through E2F binding sites.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 May 13;94(10):4948-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.10.4948. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9144170 Free PMC article.
-
E2F4 regulates transcriptional activation in mouse embryonic stem cells independently of the RB family.Nat Commun. 2019 Jul 3;10(1):2939. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10901-x. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31270324 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive ChIP-chip analysis of E2F1, E2F4, and E2F6 in normal and tumor cells reveals interchangeable roles of E2F family members.Genome Res. 2007 Nov;17(11):1550-61. doi: 10.1101/gr.6783507. Epub 2007 Oct 1. Genome Res. 2007. PMID: 17908821 Free PMC article.
-
Novel functions for the transcription factor E2F4 in development and disease.Cell Cycle. 2016 Dec;15(23):3183-3190. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1234551. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27753528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo genome-wide binding of Id2 to E2F4 target genes as part of a reversible program in mice liver.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Sep;71(18):3583-97. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1588-1. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24573694 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
E2F7 and E2F8 promote angiogenesis through transcriptional activation of VEGFA in cooperation with HIF1.EMBO J. 2012 Oct 3;31(19):3871-84. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.231. Epub 2012 Aug 17. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22903062 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic and distinct histone modifications facilitate human trophoblast lineage differentiation.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 24;14(1):4505. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55189-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38402275 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient motif search in ranked lists and applications to variable gap motifs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jul;40(13):5832-47. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks206. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22416066 Free PMC article.
-
E2F7 represses a network of oscillating cell cycle genes to control S-phase progression.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Apr;40(8):3511-23. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1203. Epub 2011 Dec 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22180533 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-type specific and combinatorial usage of diverse transcription factors revealed by genome-wide binding studies in multiple human cells.Genome Res. 2012 Jan;22(1):9-24. doi: 10.1101/gr.127597.111. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Genome Res. 2012. PMID: 22090374 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rowland BD, Bernards R. Re-evaluating cell-cycle regulation by E2Fs. Cell. 2006;127:871–874. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

