Identification of residues in the N-terminal PAS domains important for dimerization of Arnt and AhR
- PMID: 21245039
- PMCID: PMC3089468
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq1336
Identification of residues in the N-terminal PAS domains important for dimerization of Arnt and AhR
Abstract
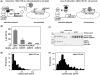
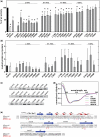
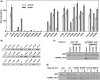
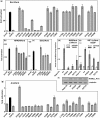
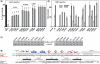
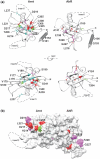
The basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH).PAS dimeric transcription factors have crucial roles in development, stress response, oxygen homeostasis and neurogenesis. Their target gene specificity depends in part on partner protein choices, where dimerization with common partner Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (Arnt) is an essential step towards forming active, DNA binding complexes. Using a new bacterial two-hybrid system that selects for loss of protein interactions, we have identified 22 amino acids in the N-terminal PAS domain of Arnt that are involved in heterodimerization with aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR). Of these, Arnt E163 and Arnt S190 were selective for the AhR/Arnt interaction, since mutations at these positions had little effect on Arnt dimerization with other bHLH.PAS partners, while substitution of Arnt D217 affected the interaction with both AhR and hypoxia inducible factor-1α but not with single minded 1 and 2 or neuronal PAS4. Arnt uses the same face of the N-terminal PAS domain for homo- and heterodimerization and mutational analysis of AhR demonstrated that the equivalent region is used by AhR when dimerizing with Arnt. These interfaces differ from the PAS β-scaffold surfaces used for dimerization between the C-terminal PAS domains of hypoxia inducible factor-2α and Arnt, commonly used for PAS domain interactions.
© The Author(s) 2011. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heterodimers of bHLH-PAS protein fragments derived from AhR, AhRR, and Arnt prepared by co-expression in Escherichia coli: characterization of their DNA binding activity and preparation of a DNA complex.J Biochem. 2003 Jul;134(1):83-90. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvg115. J Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12944374
-
Functional analysis of aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator interactions with aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the yeast two-hybrid system.Biochem Pharmacol. 1995 Oct 12;50(8):1295-302. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(95)02016-6. Biochem Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 7488247
-
Structural modeling of the AhR:ARNT complex in the bHLH-PASA-PASB region elucidates the key determinants of dimerization.Mol Biosyst. 2017 May 2;13(5):981-990. doi: 10.1039/c7mb00005g. Mol Biosyst. 2017. PMID: 28393157 Free PMC article.
-
The evolution and structure/function of bHLH-PAS transcription factor family.Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Jun 30;50(3):1227-1243. doi: 10.1042/BST20211225. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022. PMID: 35695677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA binding and protein interactions of the AHR/ARNT heterodimer that facilitate gene activation.Chem Biol Interact. 2002 Sep 20;141(1-2):63-76. doi: 10.1016/s0009-2797(02)00066-2. Chem Biol Interact. 2002. PMID: 12213385 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure and dimerization properties of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor PAS-A domain.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Nov;33(21):4346-56. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00698-13. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24001774 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the functional residues in a flavin-binding fluorescent protein using deep mutational scanning.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 2;9(6):e97817. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097817. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24887409 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of HIF-2α PAS-B domain contributes to physiological responses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 26;115(52):13240-13245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1810897115. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30523118 Free PMC article.
-
bHLH-PAS proteins in cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2013 Dec;13(12):827-41. doi: 10.1038/nrc3621. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24263188 Review.
-
Human variants in the neuronal basic helix-loop-helix/Per-Arnt-Sim (bHLH/PAS) transcription factor complex NPAS4/ARNT2 disrupt function.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 17;9(1):e85768. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085768. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McIntosh BE, Hogenesch JB, Bradfield CA. Mammalian Per-Arnt-Sim proteins in environmental adaptation. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010;72:625–645. - PubMed
-
- Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, Lim M, Hilton DA, Zagzag D, Buechler P, Isaacs WB, Semenza GL, Simons JW. Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in common human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res. 1999;59:5830–5835. - PubMed
-
- Kewley RJ, Whitelaw ML, Chapman-Smith A. The mammalian basic helix-loop-helix/PAS family of transcriptional regulators. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004;36:189–204. - PubMed
-
- Arpiainen S, Lamsa V, Pelkonen O, Yim SH, Gonzalez FJ, Hakkola J. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator and upstream stimulatory factor regulate Cytochrome P450 2a5 transcription through a common E-box site. J. Mol. Biol. 2007;369:640–652. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

