Human saliva, plasma and breast milk exosomes contain RNA: uptake by macrophages
- PMID: 21235781
- PMCID: PMC3033821
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-9
Human saliva, plasma and breast milk exosomes contain RNA: uptake by macrophages
Abstract
Background: Exosomes are 30-100 nm membrane vesicles of endocytic origin produced by numerous cells. They can mediate diverse biological functions, including antigen presentation. Exosomes have recently been shown to contain functional RNA, which can be delivered to other cells. Exosomes may thus mediate biological functions either by surface-to-surface interactions with cells, or by the delivery of functional RNA to cells. Our aim was therefore to determine the presence of RNA in exosomes from human saliva, plasma and breast milk and whether these exosomes can be taken up by macrophages.
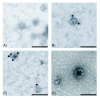
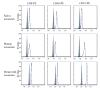
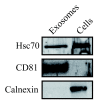
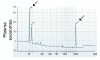
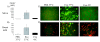
Method: Exosomes were purified from human saliva, plasma and breast milk using ultracentrifugation and filtration steps. Exosomes were detected by electron microscopy and examined by flow cytometry. Flow cytometry was performed by capturing the exosomes on anti-MHC class II coated beads, and further stain with anti-CD9, anti-CD63 or anti-CD81. Breast milk exosomes were further analysed for the presence of Hsc70, CD81 and calnexin by Western blot. Total RNA was detected with a Bioanalyzer and mRNA was identified by the synthesis of cDNA using an oligo (dT) primer and analysed with a Bioanalyzer. The uptake of PKH67-labelled saliva and breast milk exosomes by macrophages was examined by measuring fluorescence using flow cytometry and fluorescence microscopy.
Results: RNA was detected in exosomes from all three body fluids. A portion of the detected RNA in plasma exosomes was characterised as mRNA. Our result extends the characterisation of exosomes in healthy humans and confirms the presence of RNA in human saliva and plasma exosomes and reports for the first time the presence of RNA in breast milk exosomes. Our results also show that the saliva and breast milk exosomes can be taken up by human macrophages.
Conclusions: Exosomes in saliva, plasma and breast milk all contain RNA, confirming previous findings that exosomes from several sources contain RNA. Furthermore, exosomes are readily taken up by macrophages, supporting the notion that exosomal RNA can be shuttled between cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RNA-containing exosomes in human nasal secretions.Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2011 Mar-Apr;25(2):89-93. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2011.25.3573. Epub 2010 Dec 17. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2011. PMID: 21172122
-
Isolation and characterization of RNA-containing exosomes.J Vis Exp. 2012 Jan 9;(59):e3037. doi: 10.3791/3037. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 22257828 Free PMC article.
-
Nanostructural and transcriptomic analyses of human saliva derived exosomes.PLoS One. 2010 Jan 5;5(1):e8577. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008577. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20052414 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes: proteomic insights and diagnostic potential.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2009 Jun;6(3):267-83. doi: 10.1586/epr.09.17. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2009. PMID: 19489699 Review.
-
Tumor-derived exosomes in cancer progression and treatment failure.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 10;6(35):37151-68. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6022. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26452221 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomal miRNAs from Peritoneum Lavage Fluid as Potential Prognostic Biomarkers of Peritoneal Metastasis in Gastric Cancer.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 24;10(7):e0130472. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130472. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26208314 Free PMC article.
-
Advances of engineered extracellular vesicles-based therapeutics strategy.Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2022 Oct 20;23(1):655-681. doi: 10.1080/14686996.2022.2133342. eCollection 2022. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2022. PMID: 36277506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Echinococcus granulosus Protoscoleces-Derived Exosome-like Vesicles and Egr-miR-277a-3p Promote Dendritic Cell Maturation and Differentiation.Cells. 2022 Oct 14;11(20):3220. doi: 10.3390/cells11203220. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36291088 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Proteomic Analysis of Human Milk-derived Extracellular Vesicles Unveils a Novel Functional Proteome Distinct from Other Milk Components.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016 Nov;15(11):3412-3423. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M116.060426. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27601599 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Study of Extracellular Vesicles from the Urine of Healthy Individuals and Prostate Cancer Patients.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 15;11(6):e0157566. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157566. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27305142 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Théry C, Zitvogel L, Amigorena S. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:569–579. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard N, Lankar D, Faure F, Regnault A, Dumont C, Raposo G, Hivroz C. TCR Activation of Human T Cells Induces the Production of Exosomes Bearing the TCR/CD3/ζ Complex. J Immunol. 2002;168:3235–3241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

