Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases PARP1 and PARP2 modulate topoisomerase II beta (TOP2B) function during chromatin condensation in mouse spermiogenesis
- PMID: 21228215
- PMCID: PMC3080419
- DOI: 10.1095/biolreprod.110.090035
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases PARP1 and PARP2 modulate topoisomerase II beta (TOP2B) function during chromatin condensation in mouse spermiogenesis
Abstract
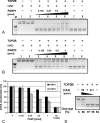
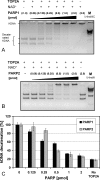
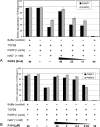
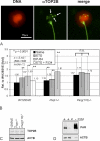
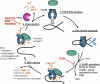
To achieve the specialized nuclear structure in sperm necessary for fertilization, dramatic chromatin reorganization steps in developing spermatids are required where histones are largely replaced first by transition proteins and then by protamines. This entails the transient formation of DNA strand breaks to allow for, first, DNA relaxation and then chromatin compaction. However, the nature and origin of these breaks are not well understood. We previously reported that these DNA strand breaks trigger the activation of poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) polymerases PARP1 and PARP2 and that interference with PARP activation causes poor chromatin integrity with abnormal retention of histones in mature sperm and impaired embryonic survival. Here we show that the activity of topoisomerase II beta (TOP2B), an enzyme involved in DNA strand break formation in elongating spermatids, is strongly inhibited by the activity of PARP1 and PARP2 in vitro, and this is in turn counteracted by the PAR-degrading activity of PAR glycohydrolase. Moreover, genetic and pharmacological PARP inhibition both lead to increased TOP2B activity in murine spermatids in vivo as measured by covalent binding of TOP2B to the DNA. In summary, the available data suggest a functional relationship between the DNA strand break-generating activity of TOP2B and the DNA strand break-dependent activation of PARP enzymes that in turn inhibit TOP2B. Because PARP activity also facilitates histone H1 linker removal and local chromatin decondensation, cycles of PAR formation and degradation may be necessary to coordinate TOP2B-dependent DNA relaxation with histone-to-protamine exchange necessary for spermatid chromatin remodeling.
Figures

Comment in
-
Regulating DNA supercoiling: sperm points the way.Biol Reprod. 2011 May;84(5):841-3. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.111.090951. Epub 2011 Jan 19. Biol Reprod. 2011. PMID: 21248288 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation during chromatin remodeling steps in rat spermiogenesis.Chromosoma. 2005 May;114(1):67-74. doi: 10.1007/s00412-005-0344-6. Epub 2005 Apr 19. Chromosoma. 2005. PMID: 15838619
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) metabolism is essential for proper nucleoprotein exchange during mouse spermiogenesis.Biol Reprod. 2011 Feb;84(2):218-28. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.110.087361. Epub 2010 Sep 29. Biol Reprod. 2011. PMID: 20881315 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of poly(ADP-ribose) homeostasis affects spermiogenesis and sperm chromatin integrity in mice.Biol Reprod. 2009 Jul;81(1):46-55. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.108.075390. Epub 2009 Mar 4. Biol Reprod. 2009. PMID: 19264700 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic insight into the role of Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation in DNA topology modulation and response to DNA damage.Mutagenesis. 2020 Feb 13;35(1):107-118. doi: 10.1093/mutage/gez045. Mutagenesis. 2020. PMID: 31782485 Review.
-
Relation between carcinogenesis, chromatin structure and poly(ADP-ribosylation) (review).Anticancer Res. 1991 Mar-Apr;11(2):489-527. Anticancer Res. 1991. PMID: 1905900 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of chromatin structure by poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation.Front Genet. 2012 Sep 3;3:169. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2012.00169. eCollection 2012. Front Genet. 2012. PMID: 22969794 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Post-Translational Modifications and CircRNAs in Mouse and Human Spermatozoa: Potential Epigenetic Marks to Assess Human Sperm Quality.J Clin Med. 2020 Feb 27;9(3):640. doi: 10.3390/jcm9030640. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32121034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Untangling the roles of TOP2A and TOP2B in transcription and cancer.Sci Adv. 2022 Nov 4;8(44):eadd4920. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.add4920. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36322662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and clinical correlates of sperm DNA damage.Asian J Androl. 2012 Jan;14(1):24-31. doi: 10.1038/aja.2011.59. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Asian J Androl. 2012. PMID: 22138903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Breaking news" from spermatids.Basic Clin Androl. 2013 Nov 7;23:11. doi: 10.1186/2051-4190-23-11. eCollection 2013. Basic Clin Androl. 2013. PMID: 25780573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao M, Shirley CR, Hayashi S, Marcon L, Mohapatra B, Suganuma R, Behringer RR, Boissonneault G, Yanagimachi R, Meistrich ML. Transition nuclear proteins are required for normal chromatin condensation and functional sperm development. Genesis 2004; 38: 200 213 - PubMed
-
- Brykczynska U, Hisano M, Erkek S, Ramos L, Oakeley EJ, Roloff TC, Beisel C, Schubeler D, Stadler MB, Peters AH. Repressive and active histone methylation mark distinct promoters in human and mouse spermatozoa. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2010; 17: 679 687 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

