The SoxRS response of Escherichia coli is directly activated by redox-cycling drugs rather than by superoxide
- PMID: 21226770
- PMCID: PMC3071027
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07520.x
The SoxRS response of Escherichia coli is directly activated by redox-cycling drugs rather than by superoxide
Abstract
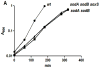
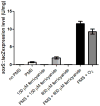
When Escherichia coli is exposed to redox-cycling drugs, its SoxR transcription factor is activated by oxidation of its [2Fe-2S] cluster. In aerobic cells these drugs generate superoxide, and because superoxide dismutase (SOD) is a member of the SoxRS regulon, superoxide was initially thought to be the activator of SoxR. Its many-gene regulon was therefore believed to comprise a defence against superoxide stress. However, we found that abundant superoxide did not effectively activate SoxR in an SOD⁻ mutant, that overproduced SOD could not suppress activation by redox-cycling drugs, and that redox-cycling drugs were able to activate SoxR in anaerobic cells as long as alternative respiratory acceptors were provided. Thus superoxide is not the signal that SoxR senses. Indeed, redox-cycling drugs directly oxidized the cluster of purified SoxR in vitro, while superoxide did not. Redox-cycling drugs are excreted by both bacteria and plants. Their toxicity does not require superoxide, as they poisoned E. coli under anaerobic conditions, in part by oxidizing dehydratase iron-sulfur clusters. Under these conditions SoxRS induction was protective. Thus it is physiologically appropriate that the SoxR protein directly senses redox-cycling drugs rather than superoxide.
© 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
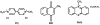


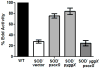




Comment in
-
A shared mechanism of SoxR activation by redox-cycling compounds.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Mar;79(5):1119-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07552.x. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21338412
Similar articles
-
A shared mechanism of SoxR activation by redox-cycling compounds.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Mar;79(5):1119-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07552.x. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21338412
-
Comparative study of SoxR activation by redox-active compounds.Mol Microbiol. 2013 Dec;90(5):983-96. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12410. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Mol Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24112649 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of the soxRS genes of Escherichia coli: two genes control a superoxide stress regulon.Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4479-84. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4479. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991. PMID: 1653416 Free PMC article.
-
Sensing and protecting against superoxide stress in Escherichia coli--how many ways are there to trigger soxRS response?Redox Rep. 2000;5(5):287-93. doi: 10.1179/135100000101535825. Redox Rep. 2000. PMID: 11145103 Review.
-
Redox signaling and gene control in the Escherichia coli soxRS oxidative stress regulon--a review.Gene. 1996 Nov 7;179(1):53-7. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(96)00329-0. Gene. 1996. PMID: 8955629 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and phylogenetic analysis of Rhodobacter capsulatus NifF: uncovering general features of nitrogen-fixation (nif)-flavodoxins.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jan 9;14(1):1152-63. doi: 10.3390/ijms14011152. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23303276 Free PMC article.
-
The Pseudomonas aeruginosa efflux pump MexGHI-OpmD transports a natural phenazine that controls gene expression and biofilm development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jun 21;113(25):E3538-47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1600424113. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27274079 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin C Maintenance against Cell Growth Arrest and Reactive Oxygen Species Accumulation in the Presence of Redox Molecular Chaperone hslO Gene.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 24;23(21):12786. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112786. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361576 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of ROS-Induced Damage of TCA Cycle Enzymes on Metabolism and Virulence of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Front Microbiol. 2019 Apr 24;10:762. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00762. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31105651 Free PMC article.
-
Catechol-Based Capacitor for Redox-Linked Bioelectronics.ACS Appl Electron Mater. 2019 Aug 27;1(8):1337-1347. doi: 10.1021/acsaelm.9b00272. Epub 2019 Jul 3. ACS Appl Electron Mater. 2019. PMID: 32090203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bolton JL, Trush MA, Penning TM, Dryhurst G, Monks TJ. Role of quinones in toxicology. Chem Res Toxicol. 2000;13:135–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

