Functional architecture of olfactory ionotropic glutamate receptors
- PMID: 21220098
- PMCID: PMC3050028
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.11.042
Functional architecture of olfactory ionotropic glutamate receptors
Abstract
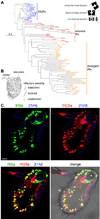
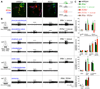
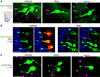
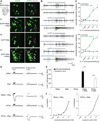
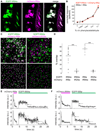
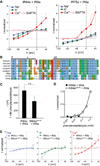
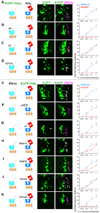
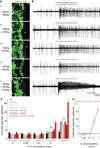
Ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGluRs) are ligand-gated ion channels that mediate chemical communication between neurons at synapses. A variant iGluR subfamily, the Ionotropic Receptors (IRs), was recently proposed to detect environmental volatile chemicals in olfactory cilia. Here, we elucidate how these peripheral chemosensors have evolved mechanistically from their iGluR ancestors. Using a Drosophila model, we demonstrate that IRs act in combinations of up to three subunits, comprising individual odor-specific receptors and one or two broadly expressed coreceptors. Heteromeric IR complex formation is necessary and sufficient for trafficking to cilia and mediating odor-evoked electrophysiological responses in vivo and in vitro. IRs display heterogeneous ion conduction specificities related to their variable pore sequences, and divergent ligand-binding domains function in odor recognition and cilia localization. Our results provide insights into the conserved and distinct architecture of these olfactory and synaptic ion channels and offer perspectives into the use of IRs as genetically encoded chemical sensors.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ionotropic receptors (IRs): chemosensory ionotropic glutamate receptors in Drosophila and beyond.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Sep;43(9):888-97. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2013.02.007. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23459169 Review.
-
In vivo assembly and trafficking of olfactory Ionotropic Receptors.BMC Biol. 2019 Apr 17;17(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12915-019-0651-7. BMC Biol. 2019. PMID: 30995910 Free PMC article.
-
Insect odorant response sensitivity is tuned by metabotropically autoregulated olfactory receptors.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58889. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058889. Epub 2013 Mar 12. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23554952 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory Ionotropic Receptors in Mosquito Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae).J Med Entomol. 2017 Sep 1;54(5):1229-1235. doi: 10.1093/jme/tjx063. J Med Entomol. 2017. PMID: 28399284
-
Functional properties of insect olfactory receptors: ionotropic receptors and odorant receptors.Cell Tissue Res. 2021 Jan;383(1):7-19. doi: 10.1007/s00441-020-03363-x. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Cell Tissue Res. 2021. PMID: 33502604 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The genetic analysis of functional connectomics in Drosophila.Adv Genet. 2012;80:99-151. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-404742-6.00003-X. Adv Genet. 2012. PMID: 23084874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Olfactory receptor coexpression and co-option in the dengue mosquito.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 22:2024.08.21.608847. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.21.608847. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39229077 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
High-throughput behavioral phenotyping of tiny arthropods: Chemosensory traits in a mesostigmatic hematophagous mite.J Exp Zool A Ecol Integr Physiol. 2023 Jan;339(1):46-62. doi: 10.1002/jez.2651. Epub 2022 Sep 2. J Exp Zool A Ecol Integr Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36052497 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of candidate chemosensory receptors in the antennal transcriptome of Tropidothorax elegans.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Apr;48(4):3127-3143. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06327-8. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33871783
-
Olfaction in Anopheles mosquitoes.Chem Senses. 2021 Jan 1;46:bjab021. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjab021. Chem Senses. 2021. PMID: 33885760 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ache BW, Young JM. Olfaction: diverse species, conserved principles. Neuron. 2005;48:417–430. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong N, Gouaux E. Mechanisms for activation and antagonism of an AMPA-sensitive glutamate receptor: crystal structures of the GluR2 ligand binding core. Neuron. 2000;28:165–181. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong N, Sun Y, Chen GQ, Gouaux E. Structure of a glutamate-receptor ligand-binding core in complex with kainate. Nature. 1998;395:913–917. - PubMed
-
- Avidor-Reiss T, Maer AM, Koundakjian E, Polyanovsky A, Keil T, Subramaniam S, Zuker CS. Decoding cilia function: defining specialized genes required for compartmentalized cilia biogenesis. Cell. 2004;117:527–539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

