Anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-19 inhibits smooth muscle cell migration and activation of cytoskeletal regulators of VSMC motility
- PMID: 21209363
- PMCID: PMC3074623
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00439.2010
Anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-19 inhibits smooth muscle cell migration and activation of cytoskeletal regulators of VSMC motility
Abstract
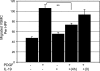
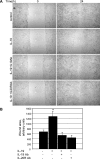
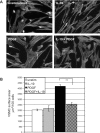
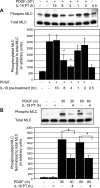
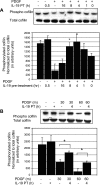
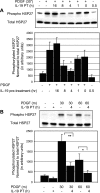
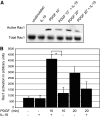
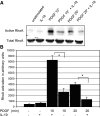
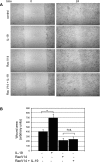
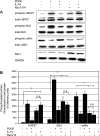
Vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) migration is an important cellular event in multiple vascular diseases, including atherosclerosis, restenosis, and transplant vasculopathy. Little is known regarding the effects of anti-inflammatory interleukins on VSMC migration. This study tested the hypothesis that an anti-inflammatory Th2 interleukin, interleukin-19 (IL-19), could decrease VSMC motility. IL-19 significantly decreased platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-stimulated VSMC chemotaxis in Boyden chambers and migration in scratch wound assays. IL-19 significantly decreased VSMC spreading in response to PDGF. To determine the molecular mechanism(s) for these cellular effects, we examined the effect of IL-19 on activation of proteins that regulate VSMC cytoskeletal dynamics and locomotion. IL-19 decreased PDGF-driven activation of several cytoskeletal regulatory proteins that play an important role in smooth muscle cell motility, including heat shock protein-27 (HSP27), myosin light chain (MLC), and cofilin. IL-19 decreased PDGF activation of the Rac1 and RhoA GTPases, important integrators of migratory signals. IL-19 was unable to inhibit VSMC migration nor was able to inhibit activation of cytoskeletal regulatory proteins in VSMC transduced with a constitutively active Rac1 mutant (RacV14), suggesting that IL-19 inhibits events proximal to Rac1 activation. Together, these data are the first to indicate that IL-19 can have important inhibitory effects on VSMC motility and activation of cytoskeletal regulatory proteins. This has important implications for the use of anti-inflammatory cytokines in the treatment of vascular occlusive disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 attenuates PDGF-induced vascular smooth muscle cell migration via the cyclic adenosine monophosphate/protein kinase A (cAMP/PKA) pathway.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 31;12(3):e0174936. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174936. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28362840 Free PMC article.
-
Protein disulfide isomerase is required for platelet-derived growth factor-induced vascular smooth muscle cell migration, Nox1 NADPH oxidase expression, and RhoGTPase activation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 24;287(35):29290-300. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.394551. Epub 2012 Jul 6. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22773830 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol inhibits migration and Rac1 activation in EGF- but not PDGF-activated vascular smooth muscle cells.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011 Aug;55(8):1230-6. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201100309. Epub 2011 Jul 5. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011. PMID: 21732534 Free PMC article.
-
RhoA phosphorylation induces Rac1 release from guanine dissociation inhibitor alpha and stimulation of vascular smooth muscle cell migration.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Oct;30(20):4786-96. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00381-10. Epub 2010 Aug 9. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20696841 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria spatially and temporally modulate VSMC phenotypes via interacting with cytoskeleton in cardiovascular diseases.Redox Biol. 2023 Aug;64:102778. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102778. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Redox Biol. 2023. PMID: 37321061 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-19 mediates tissue damage in murine ischemic acute kidney injury.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56028. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056028. Epub 2013 Feb 26. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23468852 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Deletion of IL-19 (Interleukin-19) Exacerbates Atherogenesis in Il19-/-×Ldlr-/- Double Knockout Mice by Dysregulation of mRNA Stability Protein HuR (Human Antigen R).Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Jun;38(6):1297-1308. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.310929. Epub 2018 Apr 19. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29674474 Free PMC article.
-
IL-19 reduces ligation-mediated neointimal hyperplasia by reducing vascular smooth muscle cell activation.Am J Pathol. 2014 Jul;184(7):2134-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.04.001. Epub 2014 May 9. Am J Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24814101 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of pro- and anti-atherogenic cytokines.Cytokine. 2019 Oct;122:154175. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.09.031. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Cytokine. 2019. PMID: 29221669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-19 decreases leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions by reduction in endothelial cell adhesion molecule mRNA stability.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 Aug 1;305(3):C255-65. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00069.2013. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23596173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An SS, Fabry B, Mellema M, Bursac P, Gerthoffer WT, Kayyali US, Gaestel M, Shore SA, Fredberg JJ. Role of heat shock protein 27 in cytoskeletal remodeling of the airway smooth muscle cell. J Appl Physiol 96: 1701–1713, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Autieri MV, Kelemen SE, Wendt KW. AIF-1 is an actin-polymerizing and Rac1-activating protein that promotes vascular smooth muscle cell migration. Circ Res 92: 1107–1114, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Banyard J, Anand-Apte B, Symons M, Zetter BR. Motility and invasion are differentially modulated by Rho family GTPases. Oncogene 19: 580–91, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

