Receptor-mediated T cell absorption of antigen presenting cell-derived molecules
- PMID: 21196178
- PMCID: PMC3057749
- DOI: 10.2741/3695
Receptor-mediated T cell absorption of antigen presenting cell-derived molecules
Abstract
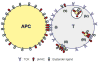
T cells tend to acquire a variety of cell surface molecules derived from antigen presenting cells (APCs). The molecule uptake occurs mainly during direct T/APC contact and is instigated by specific receptor/ligand interactions, such as T cell receptor (TCR) with a cognate peptide/MHC complex (pMHC) or CD28 with B7. The acquired molecules are targeted for internalization and degradation in the lysosome. Nevertheless, those molecules are expressed on the surface of T cells for a period of time. The presentation of APC-derived ligands by T cells exhibited a multitude of immunological effects via antigen-specific T/T interaction upon recognition of the absorbed antigens by contact with other T cells. Ligand uptake also occurs via absorption of membrane vesicles shed from APCs prior to contact (e.g., exosomes and plasma membrane-derived vesicles). As in ligand absorption via direct T/APC interaction, the absorption of pre-formed membrane vesicles is also dependent on specific receptor/ligand interactions. In this review, biological mechanisms underlying the ligand absorption process as well as the biological significance and application of the event will be discussed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
T cells can use either T cell receptor or CD28 receptors to absorb and internalize cell surface molecules derived from antigen-presenting cells.J Exp Med. 2000 Apr 3;191(7):1137-48. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.7.1137. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 10748232 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the actin cytoskeleton in T cell absorption and internalization of ligands from APC.J Immunol. 2001 Apr 15;166(8):5099-107. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.8.5099. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11290791
-
T-cell receptor triggering is critically dependent on the dimensions of its peptide-MHC ligand.Nature. 2005 Jul 28;436(7050):578-82. doi: 10.1038/nature03843. Nature. 2005. PMID: 16049493
-
Intercellular transfer of antigen-presenting cell determinants onto T cells: molecular mechanisms and biological significance.FASEB J. 2002 Apr;16(6):477-86. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0933rev. FASEB J. 2002. PMID: 11919150 Review.
-
Synthetic surfaces as artificial antigen presenting cells in the study of T cell receptor triggering and immunological synapse formation.Semin Immunol. 2007 Aug;19(4):245-54. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2007.02.011. Epub 2007 Mar 29. Semin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17398113 Review.
Cited by
-
Parapharyngeal liposarcoma: a case report.Diagn Pathol. 2013 Mar 7;8:42. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-8-42. Diagn Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23497351 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Analysis of Tumor-Derived Exosomes.Curr Protoc Immunol. 2019 Dec;127(1):e91. doi: 10.1002/cpim.91. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31763776 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid raft-dependent plasma membrane repair interferes with the activation of B lymphocytes.J Cell Biol. 2015 Dec 21;211(6):1193-205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201505030. J Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26694840 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of biologically active and morphologically intact exosomes from plasma of patients with cancer.J Extracell Vesicles. 2016 Mar 24;5:29289. doi: 10.3402/jev.v5.29289. eCollection 2016. J Extracell Vesicles. 2016. PMID: 27018366 Free PMC article.
-
A review of therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell secretions and induction of secretory modification by different culture methods.J Transl Med. 2014 Oct 11;12:260. doi: 10.1186/s12967-014-0260-8. J Transl Med. 2014. PMID: 25304688 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beutler B. Innate immune responses to microbial poisons: discovery and function of the Toll-like receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2003;43:609–28. - PubMed
-
- Taylor PR, Martinez-Pomares L, Stacey M, Lin HH, Brown GD, Gordon S. Macrophage receptors and immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:901–44. - PubMed
-
- Cambier JC, Pleiman CM, Clark MR. Signal transduction by the B cell antigen receptor and its coreceptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:457–86. - PubMed
-
- Cantrell D. T cell antigen receptor signal transduction pathways. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:259–74. - PubMed
-
- Guermonprez P, Valladeau J, Zitvogel L, Thery C, Amigorena S. Antigen presentation and T cell stimulation by dendritic cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:621–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

