SOD2-mediated effects induced by WR1065 and low-dose ionizing radiation on micronucleus formation in RKO human colon carcinoma cells
- PMID: 21175348
- PMCID: PMC3071890
- DOI: 10.1667/RR2349.1
SOD2-mediated effects induced by WR1065 and low-dose ionizing radiation on micronucleus formation in RKO human colon carcinoma cells
Abstract
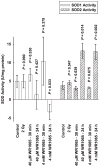
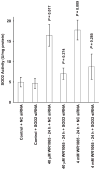
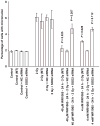
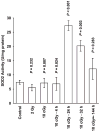
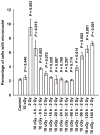
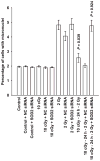
RKO36 cells exposed to either WR1065 or 10 cGy X rays show elevated SOD2 gene expression and SOD2 enzymatic activity. Cells challenged at this time with 2 Gy exhibit enhanced radiation resistance. This phenomenon has been identified as a delayed radioprotective effect or an adaptive response when induced by thiols or low-dose radiation, respectively. In this study we investigated the relative effectiveness of both WR1065 and low-dose radiation in reducing the incidence of radiation-induced micronucleus formation in binucleated RKO36 human colon carcinoma cells. The role of SOD2 in this process was assessed by measuring changes in enzymatic activity as a function of the inducing agent used, the level of protection afforded, and the inhibitory effects of short interfering RNA (SOD2 siRNA). Both WR1065 and 10 cGy X rays effectively induced a greater than threefold elevation in SOD2 activity 24 h after exposure. Cells irradiated at this time with 2 Gy exhibited a significant resistance to micronucleus formation (P < 0.05; Student's two-tailed t test). This protective effect was significantly inhibited in cells transfected with SOD2 siRNA. SOD2 played an important role in the adaptive/delayed radioprotective response by inhibiting the initiation of a superoxide anion-induced ROS cascade leading to enhanced mitochondrial and nuclear damages.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Notification: Dr. David J. Grdina is a paid consultant to Pinnacle Biologics on potential novel uses of amifostine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SOD2-mediated adaptive responses induced by low-dose ionizing radiation via TNF signaling and amifostine.Free Radic Biol Med. 2011 Nov 15;51(10):1918-25. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.08.032. Epub 2011 Sep 3. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011. PMID: 21945096 Free PMC article.
-
Maintenance of manganese superoxide dismutase (SOD2)-mediated delayed radioprotection induced by repeated administration of the free thiol form of amifostine.Radiat Res. 2008 May;169(5):495-505. doi: 10.1667/RR1194.1. Radiat Res. 2008. PMID: 18439041 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed radioprotection by nuclear transcription factor kappaB -mediated induction of manganese superoxide dismutase in human microvascular endothelial cells after exposure to the free radical scavenger WR1065.Free Radic Biol Med. 2006 Mar 15;40(6):1004-16. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.10.060. Epub 2005 Nov 21. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006. PMID: 16540396 Free PMC article.
-
Manganese superoxide dismutase (SOD2)-mediated delayed radioprotection induced by the free thiol form of amifostine and tumor necrosis factor alpha.Radiat Res. 2007 Apr;167(4):465-74. doi: 10.1667/RR0758.1. Radiat Res. 2007. PMID: 17388698
-
Modulation of the clastogenic activity of ionizing radiation and bleomycin by the aminothiol WR-1065.Environ Mol Mutagen. 1993;22(4):225-30. doi: 10.1002/em.2850220408. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1993. PMID: 7693458 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Neuroprotective Role of Selected Antioxidant Agents in Preventing Cisplatin-Induced Damage of Human Neurons In Vitro.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Jul;39(5):619-636. doi: 10.1007/s10571-019-00667-7. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30874981 Free PMC article.
-
A survivin-associated adaptive response in radiation therapy.Cancer Res. 2013 Jul 15;73(14):4418-28. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4640. Epub 2013 May 7. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23651635 Free PMC article.
-
SOD2-mediated adaptive responses induced by low-dose ionizing radiation via TNF signaling and amifostine.Free Radic Biol Med. 2011 Nov 15;51(10):1918-25. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.08.032. Epub 2011 Sep 3. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011. PMID: 21945096 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of free radicals in breast cancer.Springerplus. 2013 Aug 27;2:404. doi: 10.1186/2193-1801-2-404. Springerplus. 2013. PMID: 24024092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gamma Low-Dose-Rate Ionizing Radiation Stimulates Adaptive Functional and Molecular Response in Human Aortic Endothelial Cells in a Threshold-, Dose-, and Dose Rate-Dependent Manner.Dose Response. 2018 Mar 4;16(1):1559325818755238. doi: 10.1177/1559325818755238. eCollection 2018 Jan-Mar. Dose Response. 2018. PMID: 29531508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roots R, Okada S. Protection of DNA molecules of cultured mammalian cells from radiation induced single strand scissions by various alcohols and SH compounds. Int J Radiat Biol. 1972;21:329–342. - PubMed
-
- Ward JF. DNA damage as the cause of ionizing radiation-induced gene activation. Radiat Res. 1994;138(Suppl):S85–S88. - PubMed
-
- Leach KJ, Van Tuyle G, Lin PS, Schmidt-Ullrich R, Mikkelsen RB. Ionizing radiation-induced, mitochondria-dependent generation of reactive oxygen/nitrogen. Cancer Res. 2001;61:3894–3901. - PubMed
-
- Mikkelsen RB, Wardman P. Biological chemistry of reactive oxygen and nitrogen and radiation-induced signal transduction mechanisms. Oncogene. 2003;22:5734–5754. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

