AAV2-mediated in vivo immune gene therapy of solid tumours
- PMID: 21172020
- PMCID: PMC3016353
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-0556-8-8
AAV2-mediated in vivo immune gene therapy of solid tumours
Abstract
Background: Many strategies have been adopted to unleash the potential of gene therapy for cancer, involving a wide range of therapeutic genes delivered by various methods. Immune therapy has become one of the major strategies adopted for cancer gene therapy and seeks to stimulate the immune system to target tumour antigens. In this study, the feasibility of AAV2 mediated immunotherapy of growing tumours was examined, in isolation and combined with anti-angiogenic therapy.
Methods: Immune-competent Balb/C or C57 mice bearing subcutaneous JBS fibrosarcoma or Lewis Lung Carcinoma (LLC) tumour xenografts respectively were treated by intra-tumoural administration of AAV2 vector encoding the immune up-regulating cytokine granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and the co-stimulatory molecule B7-1 to subcutaneous tumours, either alone or in combination with intra-muscular (IM) delivery of AAV2 vector encoding Nk4 14 days prior to tumour induction. Tumour growth and survival was monitored for all animals. Cured animals were re-challenged with tumourigenic doses of the original tumour type. In vivo cytotoxicity assays were used to investigate establishment of cell-mediated responses in treated animals.
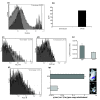
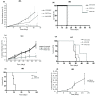
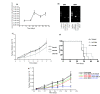
Results: AAV2-mediated GM-CSF, B7-1 treatment resulted in a significant reduction in tumour growth and an increase in survival in both tumour models. Cured animals were resistant to re-challenge, and induction of T cell mediated anti-tumour responses were demonstrated. Adoptive transfer of splenocytes to naïve animals prevented tumour establishment. Systemic production of Nk4 induced by intra-muscular (IM) delivery of Nk4 significantly reduced subcutaneous tumour growth. However, combination of Nk4 treatment with GM-CSF, B7-1 therapy reduced the efficacy of the immune therapy.
Conclusions: Overall, this study demonstrates the potential for in vivo AAV2 mediated immune gene therapy, and provides data on the inter-relationship between tumour vasculature and immune cell recruitment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-metastatic effects of viral and non-viral mediated Nk4 delivery to tumours.Genet Vaccines Ther. 2009 Mar 9;7:5. doi: 10.1186/1479-0556-7-5. Genet Vaccines Ther. 2009. PMID: 19272140 Free PMC article.
-
Therapy of established tumour with a hybrid cellular vaccine generated by using granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor genetically modified dendritic cells.Immunology. 1999 Aug;97(4):616-25. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00823.x. Immunology. 1999. PMID: 10457215 Free PMC article.
-
Effective immunotherapy of weakly immunogenic solid tumours using a combined immunogene therapy and regulatory T-cell inactivation.Cancer Gene Ther. 2010 Jul;17(7):501-11. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2010.8. Epub 2010 Feb 26. Cancer Gene Ther. 2010. PMID: 20186173
-
GM-CSF and B7-1 (CD80) co-stimulatory signals co-operate in the induction of effective anti-tumor immunity in syngeneic mice.Int J Cancer. 1997 Nov 14;73(4):556-61. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19971114)73:4<556::aid-ijc17>3.0.co;2-7. Int J Cancer. 1997. PMID: 9389572
-
Non-viral in vivo immune gene therapy of cancer: combined strategies for treatment of systemic disease.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2006 Nov;55(11):1443-50. doi: 10.1007/s00262-006-0169-z. Epub 2006 Apr 13. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2006. PMID: 16612593 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Atp6v1c1 Prevents Inflammation and Bone Erosion Caused by Periodontitis and Reveals Its Critical Function in Osteoimmunology.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 14;10(8):e0134903. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134903. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26274612 Free PMC article.
-
Bicistronic vector for combined expression of the HSVtk killer gene and cytokine GM-CSF gene in cancer cells.Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2011 Jul-Aug;439:174-7. doi: 10.1134/S1607672911040065. Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2011. PMID: 21928138 No abstract available.
-
Adeno-associated virus type 2-mediated gene transfer of a short hairpin-RNA targeting human IGFBP-2 suppresses the proliferation and invasion of MDA-MB-468 cells.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Mar;17(3):4383-4391. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8434. Epub 2018 Jan 16. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29344663 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kurnick JT, Ramirez-Montagut T, Boyle LA, Andrews DM, Pandolfi F, Durda PJ, Butera D, Dunn IS, Benson EM, Gobin SJ, van den Elsen PJ. A novel autocrine pathway of tumor escape from immune recognition: melanoma cell lines produce a soluble protein that diminishes expression of the gene encoding the melanocyte lineage melan-A/MART-1 antigen through down-modulation of its promoter. J Immunol. 2001;167:1204–1211. - PubMed
-
- Cabrera CM, Jimenez P, Cabrera T, Esparza C, Ruiz-Cabello F, Garrido F. Total loss of MHC class I in colorectal tumors can be explained by two molecular pathways: beta2-microglobulin inactivation in MSI-positive tumors and LMP7/TAP2 downregulation in MSI-negative tumors. Tissue Antigens. 2003;61:211–219. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0039.2003.00020.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

