Decreased clearance of CNS beta-amyloid in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 21148344
- PMCID: PMC3073454
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1197623
Decreased clearance of CNS beta-amyloid in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
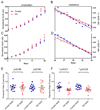
Alzheimer's disease is hypothesized to be caused by an imbalance between β-amyloid (Aβ) production and clearance that leads to Aβ accumulation in the central nervous system (CNS). Aβ production and clearance are key targets in the development of disease-modifying therapeutic agents for Alzheimer's disease. However, there has not been direct evidence of altered Aβ production or clearance in Alzheimer's disease. By using metabolic labeling, we measured Aβ42 and Aβ40 production and clearance rates in the CNS of participants with Alzheimer's disease and cognitively normal controls. Clearance rates for both Aβ42 and Aβ40 were impaired in Alzheimer's disease compared with controls. On average, there were no differences in Aβ40 or Aβ42 production rates. Thus, the common late-onset form of Alzheimer's disease is characterized by an overall impairment in Aβ clearance.
Figures
Comment in
-
It is all about clearance.Biomark Med. 2011 Apr;5(2):202. Biomark Med. 2011. PMID: 21614802 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The amyloid-β degradation intermediate Aβ34 is pericyte-associated and reduced in brain capillaries of patients with Alzheimer's disease.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019 Dec 3;7(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s40478-019-0846-8. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019. PMID: 31796114 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal Predictive Relationships between Amyloid and Tau Biomarkers in Alzheimer's Disease Progression: An Empirical Model.J Neurosci. 2019 Sep 11;39(37):7428-7437. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1056-19.2019. Epub 2019 Jul 26. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31350262 Free PMC article.
-
Clusterin levels are increased in Alzheimer's disease and influence the regional distribution of Aβ.Brain Pathol. 2017 May;27(3):305-313. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12392. Epub 2016 Jul 8. Brain Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27248362 Free PMC article.
-
Fluid and PET biomarkers for amyloid pathology in Alzheimer's disease.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2019 Jun;97:3-17. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2018.12.004. Epub 2018 Dec 8. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30537535 Review.
-
P-glycoprotein: a role in the export of amyloid-β in Alzheimer's disease?FEBS J. 2020 Feb;287(4):612-625. doi: 10.1111/febs.15148. Epub 2019 Dec 9. FEBS J. 2020. PMID: 31750987 Review.
Cited by
-
Meningeal lymphatics affect microglia responses and anti-Aβ immunotherapy.Nature. 2021 May;593(7858):255-260. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03489-0. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Nature. 2021. PMID: 33911285 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Novel Therapeutics Targeting the Blood-Brain Barrier: From Barrier to Carrier.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Aug;8(16):e2101090. doi: 10.1002/advs.202101090. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34085418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal models of Alzheimer's disease: Applications, evaluation, and perspectives.Zool Res. 2022 Nov 18;43(6):1026-1040. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2022.289. Zool Res. 2022. PMID: 36317468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Longitudinal clinical, cognitive and biomarker profiles in dominantly inherited versus sporadic early-onset Alzheimer's disease.Brain Commun. 2023 Oct 18;5(6):fcad280. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcad280. eCollection 2023. Brain Commun. 2023. PMID: 37942088 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular indicators of Alzheimer's: exploring disease in the retina.Acta Neuropathol. 2016 Dec;132(6):767-787. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1613-6. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Acta Neuropathol. 2016. PMID: 27645291 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 AG05681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020579-31/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AG027091-03/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG030946/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR000954-34/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AG027091/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R24 GM136766/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS065667/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991-28/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681-28/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG03991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103422/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG030946-04/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341-10/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS065667-03/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992-05/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR000954/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

