The SUMO protease SENP6 is a direct regulator of PML nuclear bodies
- PMID: 21148299
- PMCID: PMC3016979
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E10-06-0504
The SUMO protease SENP6 is a direct regulator of PML nuclear bodies
Abstract
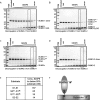
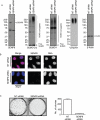
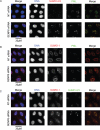
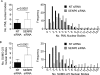
Promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML) is the core component of PML-nuclear bodies (PML NBs). The small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) system (and, in particular, SUMOylation of PML) is a critical component in the formation and regulation of PML NBs. SUMO protease SENP6 has been shown previously to be specific for SUMO-2/3-modified substrates and shows preference for SUMO polymers. Here, we further investigate the substrate specificity of SENP6 and show that it is also capable of cleaving mixed chains of SUMO-1 and SUMO-2/3. Depletion of SENP6 results in accumulation of endogenous SUMO-2/3 and SUMO-1 conjugates, and immunofluorescence analysis shows accumulation of SUMO and PML in an increased number of PML NBs. Although SENP6 depletion drastically increases the size of PML NBs, the organizational structure of the body is not affected. Mutation of the catalytic cysteine of SENP6 results in its accumulation in PML NBs, and biochemical analysis indicates that SUMO-modified PML is a substrate of SENP6.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stabilization of PML nuclear localization by conjugation and oligomerization of SUMO-3.Oncogene. 2005 Aug 18;24(35):5401-13. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208714. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 15940266
-
SUMOylation promotes PML degradation during encephalomyocarditis virus infection.J Virol. 2010 Nov;84(22):11634-45. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01321-10. Epub 2010 Sep 8. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20826694 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation regulates the number and size of promyelocytic leukemia-nuclear bodies (PML-NBs) and arsenic perturbs SUMO dynamics on PML by insolubilizing PML in THP-1 cells.Arch Toxicol. 2022 Feb;96(2):545-558. doi: 10.1007/s00204-021-03195-w. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Arch Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35001170
-
A manually curated network of the PML nuclear body interactome reveals an important role for PML-NBs in SUMOylation dynamics.Int J Biol Sci. 2010 Jan 12;6(1):51-67. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.6.51. Int J Biol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20087442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unravelling the molecular interplay: SUMOylation, PML nuclear bodies and vascular cell activity in health and disease.Cell Signal. 2024 Jul;119:111156. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111156. Epub 2024 Apr 2. Cell Signal. 2024. PMID: 38574938 Review.
Cited by
-
SUMO, a small, but powerful, regulator of double-strand break repair.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017 Oct 5;372(1731):20160281. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0281. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28847818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the tumor suppressor PML by sequential post-translational modifications.Front Oncol. 2012 Dec 31;2:204. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2012.00204. eCollection 2012. Front Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23293771 Free PMC article.
-
The role of SUMOylation in biomolecular condensate dynamics and protein localization.Cell Insight. 2024 Sep 10;3(6):100199. doi: 10.1016/j.cellin.2024.100199. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cell Insight. 2024. PMID: 39399482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and functions of SUMOylation in health and disease: a review focusing on immune cells.J Biomed Sci. 2024 Jan 27;31(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01003-y. J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 38280996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SUMO-specific Isopeptidases Tuning Cardiac SUMOylation in Health and Disease.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Nov 19;8:786136. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.786136. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34869605 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bailey D, O’Hare P. Herpes simplex virus 1 ICP0 co-localizes with a SUMO-specific protease. J Gen Virol. 2002;83:2951–2964. - PubMed
-
- Bailey D, O’Hare P. Characterization of the localization and proteolytic activity of the SUMO-specific protease, SENP1. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:692–703. - PubMed
-
- Bernardi R, Pandolfi PP. Structure, dynamics and functions of promyelocytic leukaemia nuclear bodies. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:1006–1016. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

