HLA-DM captures partially empty HLA-DR molecules for catalyzed removal of peptide
- PMID: 21131964
- PMCID: PMC3018327
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1967
HLA-DM captures partially empty HLA-DR molecules for catalyzed removal of peptide
Abstract
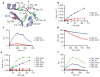
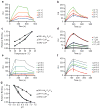
The mechanisms of HLA-DM-catalyzed peptide exchange remain uncertain. Here we found that all stages of the interaction of HLA-DM with HLA-DR were dependent on the occupancy state of the peptide-binding groove. High-affinity peptides were protected from removal by HLA-DM through two mechanisms: peptide binding induced the dissociation of a long-lived complex of empty HLA-DR and HLA-DM, and high-affinity HLA-DR-peptide complexes bound HLA-DM only very slowly. Nonbinding covalent HLA-DR-peptide complexes were converted into efficient HLA-DM binders after truncation of an N-terminal peptide segment that emptied the P1 pocket and disrupted conserved hydrogen bonds to HLA-DR. HLA-DM thus binds only to HLA-DR conformers in which a critical part of the binding site is already vacant because of spontaneous peptide motion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
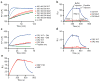
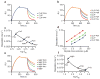
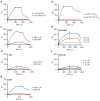
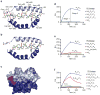
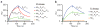
Similar articles
-
Formation of two peptide/MHC II isomers is catalyzed differentially by HLA-DM.Biochemistry. 2003 Jan 28;42(3):838-47. doi: 10.1021/bi020466p. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12534297
-
Kinetic analysis of peptide loading onto HLA-DR molecules mediated by HLA-DM.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Sep 3;93(18):9724-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.18.9724. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8790398 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the HLA-DM-HLA-DR1 complex defines mechanisms for rapid peptide selection.Cell. 2012 Dec 21;151(7):1557-68. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.025. Cell. 2012. PMID: 23260142 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of HLA-DM induced peptide exchange in the MHC class II antigen presentation pathway.Curr Opin Immunol. 2012 Feb;24(1):105-11. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2011.11.004. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Curr Opin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22138314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of the non-classical MHC proteins HLA-DM and HLA-DO on loading of MHC class II molecules.Immunol Rev. 1999 Dec;172:267-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1999.tb01371.x. Immunol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10631952 Review.
Cited by
-
Re-Directing CD4(+) T Cell Responses with the Flanking Residues of MHC Class II-Bound Peptides: The Core is Not Enough.Front Immunol. 2013 Jul 1;4:172. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00172. eCollection 2013. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23847615 Free PMC article.
-
The peptide-receptive transition state of MHC class I molecules: insight from structure and molecular dynamics.J Immunol. 2012 Aug 1;189(3):1391-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200831. Epub 2012 Jun 29. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22753930 Free PMC article.
-
HLA-DM catalytically enhances peptide dissociation by sensing peptide-MHC class II interactions throughout the peptide-binding cleft.J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 6;295(10):2959-2973. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010645. Epub 2020 Jan 22. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31969393 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Characteristics of HLA-DQ that May Impact DM Editing and Susceptibility to Type-1 Diabetes.Front Immunol. 2013 Aug 29;4:262. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00262. eCollection 2013. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24009614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Insights Into HLA-DM Mediated MHC II Peptide Exchange.Curr Top Biochem Res. 2011;13(2):39-55. Curr Top Biochem Res. 2011. PMID: 25264402 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lanzavecchia A, Reid PA, Watts C. Irreversible association of peptides with class II MHC molecules in living cells. Nature. 1992;357:249–252. - PubMed
-
- Stern LJ, et al. Crystal structure of the human class II MHC protein HLA-DR1 complexed with an influenza virus peptide. Nature. 1994;368:215–221. - PubMed
-
- Brown JH, et al. Three-dimensional structure of the human class II histocompatibility antigen HLA-DR1. Nature. 1993;364:33–39. - PubMed
-
- Germain RN, Rinker AG., Jr Peptide binding inhibits protein aggregation of invariant-chain free class II dimers and promotes surface expression of occupied molecules. Nature. 1993;363:725–728. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 AI045757-13/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI045757-10S1/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI045757-12/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI057493-04/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS044914-04/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI045757/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI057493-01/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS044914-05A1/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS044914/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS044914/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS044914-06/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI045757-08/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI045757-11/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI057493/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI057493-03/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI045757-09/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI057493-05/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI045757-10/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS044914-07/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS044914-08/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI057493-02/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

