The activator protein 1 binding motifs within the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early enhancer are functionally redundant and act in a cooperative manner with the NF-{kappa}B sites during acute infection
- PMID: 21106746
- PMCID: PMC3028895
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01713-10
The activator protein 1 binding motifs within the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early enhancer are functionally redundant and act in a cooperative manner with the NF-{kappa}B sites during acute infection
Abstract
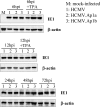
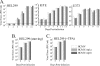
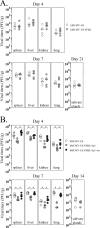
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection causes a rapid induction of c-Fos and c-Jun, the major subunits of activator protein 1 (AP-1), which in turn have been postulated to activate the viral immediate-early (IE) genes. Accordingly, the major IE promoter (MIEP) enhancer, a critical control region for initiating lytic HCMV infection and reactivation from the latent state, contains one well-characterized AP-1 site and a second candidate interaction site. In this study we explored the role of these AP-1 elements in the context of the infection. We first show that the distal candidate AP-1 motif binds c-Fos/c-Jun heterodimers (AP-1 complex) and confers c-Fos/c-Jun-mediated activity to a core promoter. Site-directed mutagenesis studies indicate that both AP-1 response elements are critical for 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-enhanced MIEP activity in transient-transfection assays. In marked contrast to the results obtained with the isolated promoter, disruption of the AP-1 recognition sites of the MIEP in the context of the infectious HCMV genome has no significant influence on the expression of the MIE protein IE1 or viral replication in different cell types. Moreover, a chimeric murine CMV driven by the HCMV MIEP (hMCMV-ES) with the two AP-1 binding sites mutated is not compromised in virulence, is able to grow and disseminate to different organs of the newborn mice as efficiently as the parental virus, and is competent in reactivation. We show, however, that combined inactivation of the enhancer AP-1 and NF-κB recognition sites leads to an attenuation of the hMCMV-ES in the neonatal murine infection model, not observed when each single element is abolished. Altogether, these results underline the functional redundancy of the MIEP elements, highlighting the plasticity of this region, which probably evolved to ensure maximal transcriptional performance across many diverse environments.
Figures

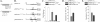




Similar articles
-
Repression of the major immediate early promoter of human cytomegalovirus allows transcription from an alternate promoter.J Gen Virol. 2023 Sep;104(9). doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001894. J Gen Virol. 2023. PMID: 37702591
-
Phorbol ester-induced human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early (MIE) enhancer activation through PKC-delta, CREB, and NF-kappaB desilences MIE gene expression in quiescently infected human pluripotent NTera2 cells.J Virol. 2010 Sep;84(17):8495-508. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00416-10. Epub 2010 May 26. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20504934 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Cell Fusion Induced by a Fusion-Active Form of Human Cytomegalovirus Glycoprotein B (gB) Is Inhibited by Antibodies Directed at Antigenic Domain 5 in the Ectodomain of gB.J Virol. 2020 Aug 31;94(18):e01276-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01276-20. Print 2020 Aug 31. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32641474 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Surgical and Nonsurgical Aesthetic Procedures: A 14-Year Analysis of the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery-ISAPS.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Oct;48(20):4217-4227. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04260-2. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 39103642 Review.
Cited by
-
Multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells are fully permissive for human cytomegalovirus infection.Virol Sin. 2016 Jun;31(3):219-28. doi: 10.1007/s12250-016-3754-0. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Virol Sin. 2016. PMID: 27105639 Free PMC article.
-
Infection of vascular endothelial cells with human cytomegalovirus under fluid shear stress reveals preferential entry and spread of virus in flow conditions simulating atheroprone regions of the artery.J Virol. 2012 Dec;86(24):13745-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02244-12. Epub 2012 Oct 10. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 23055562 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic editing of the HIV-1 coreceptor CCR5 in adult hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells using zinc finger nucleases.Mol Ther. 2013 Jun;21(6):1259-69. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.65. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Mol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23587921 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus major immediate early transcripts arise predominantly from the canonical major immediate early promoter in reactivating progenitor-derived dendritic cells.J Gen Virol. 2020 Jun;101(6):635-644. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001419. J Gen Virol. 2020. PMID: 32375946 Free PMC article.
-
Activator protein-1 transactivation of the major immediate early locus is a determinant of cytomegalovirus reactivation from latency.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Aug 25;117(34):20860-20867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2009420117. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32788362 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angel, P., and M. Karin. 1991. The role of Jun, Fos, and the AP-1 complex in cell proliferation and transformation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1072:129-157. - PubMed
-
- Angel, P., et al. 1987. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell 49:729-739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

