The SUMO pathway: emerging mechanisms that shape specificity, conjugation and recognition
- PMID: 21102611
- PMCID: PMC3079294
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm3011
The SUMO pathway: emerging mechanisms that shape specificity, conjugation and recognition
Abstract
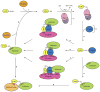
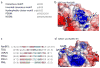
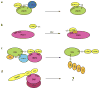
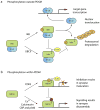
Proteins of the small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) family are conjugated to proteins to regulate such cellular processes as nuclear transport, transcription, chromosome segregation and DNA repair. Recently, numerous insights into regulatory mechanisms of the SUMO modification pathway have emerged. Although SUMO-conjugating enzymes can discriminate between SUMO targets, many substrates possess characteristics that facilitate their modification. Other post-translational modifications also regulate SUMO conjugation, suggesting that SUMO signalling is integrated with other signal transduction pathways. A better understanding of SUMO regulatory mechanisms will lead to improved approaches for analysing the function of SUMO and substrate conjugation in distinct cellular pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
E2-mediated small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) modification of thymine DNA glycosylase is efficient but not selective for the enzyme-product complex.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 30;289(22):15810-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.572081. Epub 2014 Apr 21. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24753249 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms in SUMO conjugation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Feb 28;48(1):123-135. doi: 10.1042/BST20190357. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 31872228 Review.
-
Identification of small ubiquitin-like modifier substrates with diverse functions using the Xenopus egg extract system.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014 Jul;13(7):1659-75. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M113.035626. Epub 2014 May 5. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24797264 Free PMC article.
-
Site-specific inhibition of the small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO)-conjugating enzyme Ubc9 selectively impairs SUMO chain formation.J Biol Chem. 2017 Sep 15;292(37):15340-15351. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.794255. Epub 2017 Aug 7. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28784659 Free PMC article.
-
Protein modification by SUMO.Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:355-82. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.074118. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15189146 Review.
Cited by
-
SUMOylation is developmentally regulated and required for cell pairing during conjugation in Tetrahymena thermophila.Eukaryot Cell. 2015 Feb;14(2):170-81. doi: 10.1128/EC.00252-14. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Eukaryot Cell. 2015. PMID: 25527524 Free PMC article.
-
Current perspectives of ubiquitination and SUMOylation in abiotic stress tolerance in plants.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Sep 20;13:993194. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.993194. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36212351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small ubiquitin-like modifier 2 (SUMO2) is critical for memory processes in mice.FASEB J. 2020 Nov;34(11):14750-14767. doi: 10.1096/fj.202000850RR. Epub 2020 Sep 10. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32910521 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Smoothened Trafficking and Hedgehog Signaling by the SUMO Pathway.Dev Cell. 2016 Nov 21;39(4):438-451. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2016.09.014. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Dev Cell. 2016. PMID: 27746045 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation of the small GTPase ARL-13 promotes ciliary targeting of sensory receptors.J Cell Biol. 2012 Nov 12;199(4):589-98. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201203150. Epub 2012 Nov 5. J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 23128241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnson ES. Protein modification by SUMO. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:355–382. - PubMed
-
- Geiss-Friedlander R, Melchior F. Concepts in sumoylation: a decade on. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:947–956. - PubMed
-
- Kerscher O, Felberbaum R, Hochstrasser M. Modification of proteins by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:159–180. - PubMed
-
- Guo D, et al. A functional variant of SUMO4, a new I kappa B alpha modifier, is associated with type 1 diabetes. Nat Genet. 2004;36:837–841. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

