Altered immune response in mice deficient for the G protein-coupled receptor GPR34
- PMID: 21097509
- PMCID: PMC3023507
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.196659
Altered immune response in mice deficient for the G protein-coupled receptor GPR34
Abstract
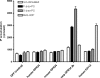
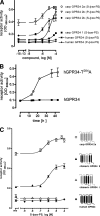
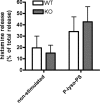
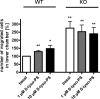
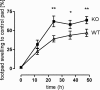
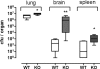
The X-chromosomal GPR34 gene encodes an orphan G(i) protein-coupled receptor that is highly conserved among vertebrates. To evaluate the physiological relevance of GPR34, we generated a GPR34-deficient mouse line. GPR34-deficient mice were vital, reproduced normally, and showed no gross abnormalities in anatomical, histological, laboratory chemistry, or behavioral investigations under standard housing. Because GPR34 is highly expressed in mononuclear cells of the immune system, mice were specifically tested for altered functions of these cell types. Following immunization with methylated BSA, the number of granulocytes and macrophages in spleens was significantly lower in GPR34-deficient mice as in wild-type mice. GPR34-deficient mice showed significantly increased paw swelling in the delayed type hypersensitivity test and higher pathogen burden in extrapulmonary tissues after pulmonary infection with Cryptococcus neoformans compared with wild-type mice. The findings in delayed type hypersensitivity and infection tests were accompanied by significantly different basal and stimulated TNF-α, GM-CSF, and IFN-γ levels in GPR34-deficient animals. Our data point toward a functional role of GPR34 in the cellular response to immunological challenges.
Figures
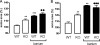
Similar articles
-
Dendritic Cells Regulate GPR34 through Mitogenic Signals and Undergo Apoptosis in Its Absence.J Immunol. 2016 Mar 15;196(6):2504-13. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501326. Epub 2016 Feb 5. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26851221
-
Altered microglial phagocytosis in GPR34-deficient mice.Glia. 2015 Feb;63(2):206-15. doi: 10.1002/glia.22744. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Glia. 2015. PMID: 25142016
-
GPR34 in spinal microglia exacerbates neuropathic pain in mice.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Apr 11;16(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1458-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 30975169 Free PMC article.
-
The G protein-coupled receptor GPR34 - The past 20 years of a grownup.Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Sep;189:71-88. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.04.008. Epub 2018 Apr 22. Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29684466 Review.
-
Cryptococcal immunity and immunostimulation.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1992;319:225-30. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3434-1_23. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1992. PMID: 1414597 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
GPR34 senses demyelination to promote neuroinflammation and pathologies.Cell Mol Immunol. 2024 Oct;21(10):1131-1144. doi: 10.1038/s41423-024-01204-3. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Cell Mol Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39030423
-
Lysophosphatidylserine induces necrosis in pressure overloaded male mouse hearts via G protein coupled receptor 34.Nat Commun. 2023 Jul 31;14(1):4494. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40201-4. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37524709 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced B cell frequencies in cord blood of HIV-exposed uninfected infants: an immunological and transcriptomic analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 4;15:1445239. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1445239. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39295873 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophospholipid receptor nomenclature review: IUPHAR Review 8.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Aug;171(15):3575-94. doi: 10.1111/bph.12678. Epub 2014 Jul 12. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24602016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles for lysophosphatidylserine in resolution of inflammation.Prog Lipid Res. 2012 Jul;51(3):199-207. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2012.03.001. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Prog Lipid Res. 2012. PMID: 22465125 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

