Counter-regulation of opioid analgesia by glial-derived bioactive sphingolipids
- PMID: 21084596
- PMCID: PMC3000610
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2391-10.2010
Counter-regulation of opioid analgesia by glial-derived bioactive sphingolipids
Abstract
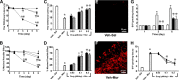
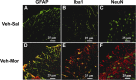
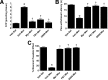
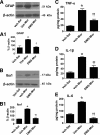
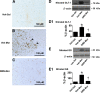
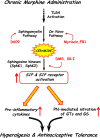
The clinical efficacy of opiates for pain control is severely limited by analgesic tolerance and hyperalgesia. Herein we show that chronic morphine upregulates both the sphingolipid ceramide in spinal astrocytes and microglia, but not neurons, and spinal sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), the end-product of ceramide metabolism. Coadministering morphine with intrathecal administration of pharmacological inhibitors of ceramide and S1P blocked formation of spinal S1P and development of hyperalgesia and tolerance in rats. Our results show that spinally formed S1P signals at least in part by (1) modulating glial function because inhibiting S1P formation blocked increased formation of glial-related proinflammatory cytokines, in particular tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1βα, and interleukin-6, which are known modulators of neuronal excitability, and (2) peroxynitrite-mediated posttranslational nitration and inactivation of glial-related enzymes (glutamine synthetase and the glutamate transporter) known to play critical roles in glutamate neurotransmission. Inhibitors of the ceramide metabolic pathway may have therapeutic potential as adjuncts to opiates in relieving suffering from chronic pain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Analgesia: lipid linked to improved opiate therapy.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011 Jan;10(1):20-1. doi: 10.1038/nrd3344. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011. PMID: 21193864 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Lipoxin A4 analog attenuates morphine antinociceptive tolerance, withdrawal-induced hyperalgesia, and glial reaction and cytokine expression in the spinal cord of rat.Neuroscience. 2012 Apr 19;208:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.02.009. Epub 2012 Feb 14. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22366510
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate acting via the S1P₁ receptor is a downstream signaling pathway in ceramide-induced hyperalgesia.Neurosci Lett. 2011 Jul 15;499(1):4-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2011.05.018. Epub 2011 May 13. Neurosci Lett. 2011. PMID: 21605625 Free PMC article.
-
Proinflammatory cytokines oppose opioid-induced acute and chronic analgesia.Brain Behav Immun. 2008 Nov;22(8):1178-89. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2008.05.004. Epub 2008 Jul 2. Brain Behav Immun. 2008. PMID: 18599265 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of bioactive sphingolipids in cancer biology and therapeutics.Subcell Biochem. 2008;49:413-40. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4020-8831-5_16. Subcell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 18751921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is autophagy the key mechanism by which the sphingolipid rheostat controls the cell fate decision?Autophagy. 2007 Jan-Feb;3(1):45-7. doi: 10.4161/auto.3416. Epub 2007 Jan 18. Autophagy. 2007. PMID: 17035732 Review.
Cited by
-
Pain after discontinuation of morphine treatment is associated with synaptic increase of GluA4-containing AMPAR in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Jul;38(8):1472-84. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.46. Epub 2013 Feb 12. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23403695 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 activation in the central nervous system drives cisplatin-induced cognitive impairment.J Clin Invest. 2022 Sep 1;132(17):e157738. doi: 10.1172/JCI157738. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 36047496 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate enhances the excitability of rat sensory neurons through activation of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors 1 and/or 3.J Neuroinflammation. 2015 Apr 12;12:70. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0286-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 25880547 Free PMC article.
-
Opioid-Induced Tolerance and Hyperalgesia.CNS Drugs. 2019 Oct;33(10):943-955. doi: 10.1007/s40263-019-00660-0. CNS Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31578704 Review.
-
Activation of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor subtype 1 in the central nervous system contributes to morphine-induced hyperalgesia and antinociceptive tolerance in rodents.Pain. 2020 Sep 1;161(9):2107-2118. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001888. Pain. 2020. PMID: 32301840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnér S, Rawal N, Gustafsson LL. Clinical experience of long-term treatment with epidural and intrathecal opioids: a nationwide survey. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1988;32:253–259. - PubMed
-
- Claus RA, Bunck AC, Bockmeyer CL, Brunkhorst FM, Lösche W, Kinscherf R, Deigner HP. Role of increased sphingomyelinase activity in apoptosis and organ failure of patients with severe sepsis. FASEB J. 2005;19:1719–1721. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
