Haploinsufficiency of the murine Col3a1 locus causes aortic dissection: a novel model of the vascular type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- PMID: 21071432
- PMCID: PMC3058731
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvq356
Haploinsufficiency of the murine Col3a1 locus causes aortic dissection: a novel model of the vascular type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Abstract
Aims: The vascular type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS IV) is an autosomal-dominant disorder characterized by thin translucent skin and extensive bruising. Patients with EDS IV have reduced life expectancy (median 45-50 years) due to spontaneous rupture of arteries (particularly large arteries) or bowel. EDS IV results from mutation of the COL3A1 gene, which encodes the pro-α(1) chains of type III collagen that is secreted into the extracellular matrix, e.g. by smooth muscle cells. A mouse model of EDS IV produced by targeted ablation of Col3a1 has been of limited use as only 10% of homozygous animals survive to adulthood, whereas heterozygous animals do not die from arterial rupture. We report a novel, exploitable model of EDS IV in a spontaneously generated mouse line.
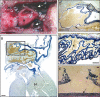
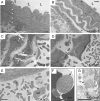
Methods and results: Mice were identified by predisposition to sudden, unexpected death from dissection of the thoracic aorta. Aortic dissection inheritance was autosomal-dominant, presented at an early age (median, 6 weeks) with incomplete penetrance, and had a similar sex ratio bias as EDS IV (2:1, male:female). Molecular genetic analysis demonstrated that the causal mutation is a spontaneous 185 kb deletion, including the promoter region and exons 1-39, of the Col3a1 gene. As in EDS IV, aortic dissection was not associated with elevated blood pressure, aneurysm formation, or infection, but may result from aberrant collagen fibrillogenesis within the aortic wall.
Conclusion: This novel, exploitable mouse line that faithfully models the vascular aspects of human EDS IV provides an important new tool for advancing understanding of EDS IV and of aortic dissection in general.
Figures
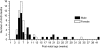

Similar articles
-
Angiotensin II promotes thoracic aortic dissections and ruptures in Col3a1 haploinsufficient mice.Hypertension. 2013 Jul;62(1):203-8. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.00974. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Hypertension. 2013. PMID: 23630948
-
Haploinsufficiency for one COL3A1 allele of type III procollagen results in a phenotype similar to the vascular form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV.Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Nov;69(5):989-1001. doi: 10.1086/324123. Epub 2001 Sep 27. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11577371 Free PMC article.
-
Cervical artery dissections and type A aortic dissection in a family with a novel missense COL3A1 mutation of vascular type Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.Eur J Med Genet. 2015 Nov;58(11):634-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2015.10.009. Epub 2015 Oct 21. Eur J Med Genet. 2015. PMID: 26497932
-
Type III collagen (COL3A1): Gene and protein structure, tissue distribution, and associated diseases.Gene. 2019 Jul 30;707:151-171. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.05.003. Epub 2019 May 7. Gene. 2019. PMID: 31075413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heritable diseases of the blood vessels.Cardiovasc Pathol. 2005 Jul-Aug;14(4):185-8. doi: 10.1016/j.carpath.2005.04.003. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2005. PMID: 16009316 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanisms of thoracic aortic dissection.J Surg Res. 2013 Oct;184(2):907-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jun 29. J Surg Res. 2013. PMID: 23856125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges in thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Nov;10(Suppl 33):S4140-S4143. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.10.69. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 30631576 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Involved in Aortic Wall Aneurysm Development.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jan 10;13(2):253. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13020253. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36673063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genes Associated with Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm and Dissection: 2018 Update and Clinical Implications.Aorta (Stamford). 2018 Feb;6(1):13-20. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1639612. Epub 2018 Jul 27. Aorta (Stamford). 2018. PMID: 30079932 Free PMC article.
-
Four decades in the making: Collagen III and mechanisms of vascular Ehlers Danlos Syndrome.Matrix Biol Plus. 2021 Nov 9;12:100090. doi: 10.1016/j.mbplus.2021.100090. eCollection 2021 Dec. Matrix Biol Plus. 2021. PMID: 34849481 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Prockop DJ, Kivirikko KI. Heritable diseases of collagen. N Engl J Med. 1984;311:376–386. doi:10.1056/NEJM198408093110606. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kontusaari S, Tromp G, Kuivaniemi H, Romanic AM, Prockop DJ. A mutation in the gene for type-III procollagen (Col3A1) in a family with aortic-aneurysms. J Clin Invest. 1990;86:1465–1473. doi:10.1172/JCI114863. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kuivaniemi H, Tromp G, Bergfeld WF, Kay M, Helm TN. Ehlers–Danlos-syndrome type-IV—a single-base substitution of the last nucleotide of exon-34 in Col3A1 leads to exon skipping. J Invest Dermatol. 1995;105:352–356. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12320704. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Burke JM, Balian G, Ross R, Bornstein P. Synthesis of Type-1 and Type-3 procollagen and collagen by monkey aortic smooth-muscle cells in vitro. Biochemistry. 1977;16:3243–3249. doi:10.1021/bi00633a031. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mccullagh KA, Balian G. Collagen characterization and cell transformation in human atherosclerosis. Nature. 1975;258:73–75. doi:10.1038/258073a0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

