Probiotics for treating acute infectious diarrhoea
- PMID: 21069673
- PMCID: PMC6532699
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003048.pub3
Probiotics for treating acute infectious diarrhoea
Update in
-
Probiotics for treating acute infectious diarrhoea.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Dec 8;12(12):CD003048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003048.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33295643 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Probiotics may offer a safe intervention in acute infectious diarrhoea to reduce the duration and severity of the illness.
Objectives: To assess the effects of probiotics in proven or presumed acute infectious diarrhoea.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Infectious Diseases Group's trials register (July 2010), the Cochrane Controlled Trials Register (The Cochrane Library Issue 2, 2010), MEDLINE (1966 to July 2010), EMBASE (1988 to July 2010), and reference lists from studies and reviews. We also contacted organizations and individuals working in the field, and pharmaceutical companies manufacturing probiotic agents.
Selection criteria: Randomized and quasi-randomized controlled trials comparing a specified probiotic agent with a placebo or no probiotic in people with acute diarrhoea that is proven or presumed to be caused by an infectious agent.
Data collection and analysis: Two reviewers independently assessed the methodological quality of the trial and extracted data. Primary outcomes were the mean duration of diarrhoea, stool frequency on day 2 after intervention and ongoing diarrhoea on day 4. A random-effects model was used.
Main results: Sixty-three studies met the inclusion criteria with a total of 8014 participants. Of these, 56 trials recruited infants and young children. The trials varied in the definition used for acute diarrhoea and the end of the diarrhoeal illness, as well as in the risk of bias. The trials were undertaken in a wide range of different settings and also varied greatly in organisms tested, dosage, and participants' characteristics. No adverse events were attributed to the probiotic intervention.Probiotics reduced the duration of diarrhoea, although the size of the effect varied considerably between studies.The average of the effect was significant for mean duration of diarrhoea (mean difference 24.76 hours; 95% confidence interval 15.9 to 33.6 hours; n=4555, trials=35) diarrhoea lasting ≥4 days (risk ratio 0.41; 0.32 to 0.53; n=2853, trials=29) and stool frequency on day 2 (mean difference 0.80; 0.45 to 1.14; n=2751, trials=20).The differences in effect size between studies was not explained by study quality, probiotic strain, the number of different strains, the viability of the organisms, dosage of organisms, the causes of diarrhoea, or the severity of the diarrhoea, or whether the studies were done in developed or developing countries.
Authors' conclusions: Used alongside rehydration therapy, probiotics appear to be safe and have clear beneficial effects in shortening the duration and reducing stool frequency in acute infectious diarrhoea. However, more research is needed to guide the use of particular probiotic regimens in specific patient groups.
Conflict of interest statement
Stephen Allen is participating in ongoing research studies of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria provided by Cultech Ltd, UK, in the prevention of atopic disorders in infants and antibiotic‐associated diarrhoea in older people. In previous research, Scientific Hospital Supplies, UK, and Valio Ltd, Finland, have provided
Figures
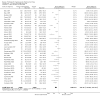
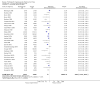
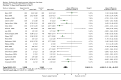
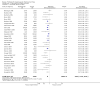
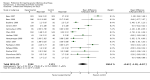



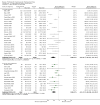
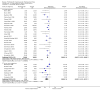

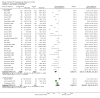
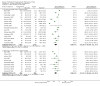
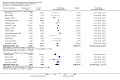



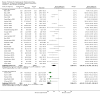

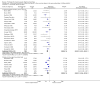

Update of
-
Probiotics for treating infectious diarrhoea.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(2):CD003048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Nov 10;(11):CD003048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003048.pub3. PMID: 15106189 Updated. Review.
Comment in
-
Cochrane column.Int J Epidemiol. 2012 Apr;41(2):390-2. doi: 10.1093/ije/dys013. Epub 2012 Mar 19. Int J Epidemiol. 2012. PMID: 22434863 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Probiotics for treating acute infectious diarrhoea.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Dec 8;12(12):CD003048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003048.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33295643 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotics for treating infectious diarrhoea.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(2):CD003048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Nov 10;(11):CD003048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003048.pub3. PMID: 15106189 Updated. Review.
-
Probiotics for the prevention of pediatric antibiotic-associated diarrhea.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Nov 9;(11):CD004827. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004827.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Dec 22;(12):CD004827. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004827.pub4. PMID: 22071814 Updated. Review.
-
Probiotics for treating persistent diarrhoea in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Nov 10;(11):CD007401. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007401.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Aug 20;(8):CD007401. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007401.pub3. PMID: 21069693 Updated. Review.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the safety, tolerance and efficacy of 1-year consumption of infant formula supplemented with Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 Lc40 or Bifidobacterium breve CECT7263: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Pediatr. 2019 Oct 21;19(1):361. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1753-7. BMC Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31630683 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Biosensing in Smart Engineered Probiotics.Biotechnol J. 2020 Oct;15(10):e1900319. doi: 10.1002/biot.201900319. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 31860168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of an Oral Rehydration Solution Enriched with Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 and Zinc in the Management of Acute Diarrhoea in Infants: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.Nutrients. 2018 Sep 1;10(9):1189. doi: 10.3390/nu10091189. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30200394 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The intestinal microbiota and viral susceptibility.Front Microbiol. 2011 Apr 27;2:92. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2011.00092. eCollection 2011. Front Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21833331 Free PMC article.
-
Successful treatment of asymptomatic or clinically terminal bovine Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis infection (Johne's disease) with the bacterium Dietzia used as a probiotic alone or in combination with dexamethasone: Adaption to chronic human diarrheal diseases.Virulence. 2011 Mar-Apr;2(2):131-43. doi: 10.4161/viru.2.2.15647. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Virulence. 2011. PMID: 21460639 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
References to studies included in this review
Basu 2007 {published data only}
-
- Basu S, Chatterjee M, Ganguly S, Chandra P.K. Efficacy of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in acute watery diarrhoea of Indian children: a randomised controlled trial. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 2007;43(12):837‐42. - PubMed
Basu 2009 {published data only}
-
- Basu S, Paul DK, Ganguly S, Chatterjee M, Chandra PK. Efficacy of high‐dose Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in controlling acute watery diarrhea in Indian children: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 2009;43(3):208‐13. - PubMed
Bhatnagar 1998 {published data only}
-
- Bhatnagar S, Singh KD, Sazawal S, Saxena SK, Bhan MK. Efficacy of milk versus yogurt offered as part of a mixed diet in acute noncholera diarrhea among malnourished children. Journal of Pediatrics 1998;132(6):999‐1004. - PubMed
Billoo 2006 {published data only}
Boudraa 2001 {published data only}
-
- Boudraa G, Benbouabdellah M, Hachelaf W, Boisset M, Desjeux JF, Touhami M. Effect of feeding yogurt versus milk in children with acute diarrhea and carbohydrate malabsorption. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2001;33(3):307‐13. - PubMed
Boulloche 1994 {published data only}
-
- Boulloche J, Mouterde O, Mallet E. Management of acute diarrhoea in infants and young children. Controlled study of the anti‐diarrheal efficacy of killed L. acidophilus (LB strain) versus a placebo and a reference drug (loperamide). Annales de Pediatrie 1994;41(7):457‐63.
Bruno 1981 {published data only}
-
- Bruno F, Frigerio G. A new therapeutic alternative for the treatment of enteritis ‐‐ controlled double‐blind tests with the strain SF 68 [Eine neuartige möglichkeit zur behandlung der enteritis ‐ kontrollierte doppel‐blindversuche mit dem Stamm SF 68]. Schweizerische Rundschau fur Medizin Praxis 1981;70(39):1717‐20. - PubMed
Bruno 1983 {published data only}
-
- Bruno F, Nastasi A, Bruno M. Double‐blind controlled study of the effect of the lactogenic enterococcus SF68 strain on various enterocolitis associated manifestations and on salmonella infections [Studio controllato dopio‐cieco sull'effecto dell'enterococco lattoproduttore ceppo SF 68 su manifestazione associate a forme enterocolitiche variee a salmonellosi]. La Clinica Terapeutica 1983;105(3):203‐7. - PubMed
Buydens 1996 {published data only}
-
- Buydens P, Debeuckelaere S. Efficacy of SF68 in the treatment of acute diarrhea. A placebo‐controlled trial. Scandanavian Journal of Gastroenterology 1996;31(9):887‐91. - PubMed
Canani 2007 {published data only}
Carague‐Orendain {unpublished data only}
-
- Carrague‐Orendain A. Randomized, double blind placebo‐controlled trial on the efficacy and safety of lactobacillus (Infloran Berna capsules) in the treatment of acute non‐bloody diarrhoea in children two to five years of age.
Cetina‐Sauri 1994 {published data only}
-
- Cetina‐Sauri G, Sierra Basto G. Evaluation of Saccharomyces boulardii in children with acute diarrhea [Evaluation therapeutique de Saccharomyces boulardii chez des enfants souffrant de diarrhee aigue]. Annales de Pediatrie 1994;41(6):397‐400.
Chapoy 1985 {published data only}
-
- Chapoy P. Treatment of acute infantile diarrhea: controlled trial of Saccharomyces boulardii [Traitement des diarrhées aiguës infantiles]. Annales de Pediatrie 1985;32(6):561‐3. - PubMed
Chen 2010 {published data only}
-
- Chen CC, Kong MS, Lai MW, Chao HC, Chang KW, Chen SY, et al. Probiotics have clinical, microbiologic, and immunologic efficacy in acute infectious diarrhea. The Pediatric Infectious Diseases Journal 2010;29(2):135‐8. - PubMed
Costa‐Ribeiro 2003 {published data only}
-
- Costa‐Ribeiro H, Ribeiro TC, Mattos AP, Valois SS, Neri DA, Almeida P, et al. Limitations of probiotic therapy in acute, severe dehydrating diarrhea. Journal of Pediatric Gastroentology and Nutrition 2003;36(1):112‐5. - PubMed
Czerwionka 2009 {published data only}
-
- Czerwionka‐Szaflarska M, Murawska S, Swincow G. Evaluation of influence of oral treatment with probiotic and/or oral rehydration solution on course of acute diarrhoea in children. Przeglad Gastroenterologiczny 2009;4(3):166‐72.
D'Apuzzo 1982 {published data only}
-
- D'Apuzzo V, Salzberg R. The treatment of acute diarrhoea in paediatrics using Streptococcus faecium: results of a double blind trial [Die Behandlung der akuten Diarrho in der Padiatrie mit Streptococcus faecium: Resultae einer doppleblindstudie]. Therapeutische Umschau 1982;39(12):1033‐5. - PubMed
Dubey 2008 {published data only}
-
- Dubey AP, Rajeshwari K, Chakravarty A, Famularo G. Use of VSL#3 in the treatment of rotavirus diarrhea in children: preliminary results. Journal of Clinincal Gastroenterology 2008;42 Suppl 3 Pt 1:S126‐9. - PubMed
Frigerio 1986 {published data only}
-
- Frigerio G. A lactic acid producer enterococcus in the prevention of antibiotic‐associated diarrhoea and in the treatment of acute diarrhoeal disorders: a double‐blind multicentre placebo‐controlled clinical trial (Abstract). Digestive Diseases and Sciences 1986;31 Suppl:496.
Grandi 2009 {published data only}
Guandalini 2000 {published data only}
-
- Guandalini S, Pensabene L, Zikri MA, Dias JA, Casali LB, Hoekstra H, et al. Lactobacillus GG administered in oral rehydration solution to children with acute diarrhoea: a multicenter European trial. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2000;30(1):54‐60. - PubMed
Guarino 1997 {published data only}
-
- Canani RB, Albano F, Spagnuolo MI, Benedetto L, Stabile A, Guarino A. Effect of oral administration of Lactobacillus GG on the duration of diarrhea and on rotavirus excretion in ambulatory children (Abstract). Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 1997;24(4):469.
-
- Guarino A, Canani RB, Spagnuolo MI, Albano F, Benedetto L. Oral bacterial therapy reduces the duration of symptoms and viral excretion in children with mild diarrhoea. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 1997;25(5):516‐9. - PubMed
Hafeez 2002 {published data only}
-
- Hafeez A, Tariq P, Ali S, Kundi ZU, Khan A, Hassan M. The efficacy of Saccharomyces boulardii in the treatment of acute watery diarrhoea in children: a multicentre randomized controlled trial. Journal of College of Physicians and Surgeons Pakistan 2002;12(7):432‐4.
Henker 2007a {published data only}
Henker 2008 {published data only}
-
- Henker J, Laass MW, Blokhin BM, Maydannik VG, Bolbot YK, Elze M, et al. Probiotic E.Coli Nissle 1917 versus placebo for treating diarrhea of greater than 4 days duration in infants and toddlers. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2008;27(6):494‐99. - PubMed
Hernandez 1998 {published data only}
-
- Hernandez CL, Pineda EE, Jimenez MIR, Lucena MS. Clinical therapeutic affect of Saccharomyces boulardii on children with acute diarrhea. Revista de Enfermedades Infecciosas en Pediatria March 1998;11(43):87‐9.
Hochter 1990 {published data only}
-
- Höchter W, Chase D, Hagenhoff G. Saccharomyces boulardii in the treatment of acute adult diarrhoea. [Saccharomyces boulardii bei acuter Erwachsenendiarrhoea]. Münchener medizinische Wochenschrift 1990;132(12):188‐92.
Htwe 2008 {published data only}
-
- Htwe K, Yee K.S, Tin M, Vandenplas Y. Effect of Saccharomyces boulardii in the treatment of acute watery diarrhea in Myanmar children: a randomized control study. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2008;78(2):214‐16. - PubMed
Isolauri 1994 {published data only}
-
- Isolauri E, Kaila M, Mykkanen H, Ling WH, Salminen S. Oral bacteriotherapy for viral gastroenteritis. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 1994;39(12):2595‐600. - PubMed
Jasinski 2002 {published data only}
-
- Jasinski C, Tanzi MN, Schelotto F, Varela G, Zanetta E, Acuna AM, et al. Efficacy of Lactobacillus GG in oral rehydration solution [Efectop del Lactobacillus casei administrado en el suero de rehidratacion oral, en el tratamiento de la enfermedad diarreica aguda]. Pediatrika 2002;22(7):231‐43.
Khanna 2005 {published data only}
-
- Khanna V, Seema A, Ashraf M, Abida M. Efficacy of tyndalized lactobacillus acidophilus in acute diarrhoea. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 2005;72(11):935‐8. - PubMed
Kianifar 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kianifar HR, Farid R, Ahanchian H, Jabbari F, Moghiman T, Sistanian A. Probiotics in the treatment of acute diarrhea in young children. Iranian Journal of Medical Sciences 2009;34(3):204‐7.
Kowalska‐Duplaga 1999 {published data only}
-
- Kowalska‐Duplaga K, Strus M, Heczko P, Krobicka B, Kurowska‐Baran D, Mrukowicz JZ. Lactobif, a marketed probiotic product containing Bifidobacterium ruminantium, was not effective in the treatment of acute rotavirus diarrhoea in infants. Gut 1999;44:17‐25.
Kowalska‐Duplaga 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kowalska‐Duplaga K, Krzysztof F, Szajewska H, Janiak R. Efficacy of Trilac® in the treatment of acute diarrhoea in infants and young children ‐ a multicentre, randomised, double blind placebo‐controlled study. Pediatria Wspolczesna, Gastroenterologia, Hepatologia i Zywienie Dziecka 2004;6(3):295‐9.
Kurugol 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kurugol Z, Koturoglu G. Effects of Saccharomyces boulardii in children with acute diarrhoea. Acta Paediatrica 2005;94(1):44‐7. - PubMed
Lee 2001 {published data only}
-
- Lee M‐C, Lin L‐H, Hung K‐L, Wu H‐Y. Oral bacterial therapy promotes recovery from acute diarrhoea in children. Acta Paediatrica Taiwan 2001;42(5):301‐5. - PubMed
Lievin Le‐Maol 2007 {published data only}
-
- Lievin‐Le Maol V, Sarrazin‐Davilla L.E, Servin A.L. An experimental study and a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled clinical trial to evaluate the antisecretory activity of Lactobacillus acidophilus strain LB against non‐rotavirus diarrhea. Pediatrics 2007;120(4):795‐803. - PubMed
Mao 2008 {published data only}
-
- Mao M, Yu T, Xiong Y, Wang Z, Liu H, Gotteland M, et al. Effect of a lactose‐free milk formula supplemented with bifidobacteria and streptococci on the recovery from acute diarrhoea. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2008;17(1):30‐4. - PubMed
Misra 2009 {published data only}
-
- Misra S, Sabui TK, Pal NK. A randomized controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy of Lactobacillus GG in infantile diarrhea. The Journal of Pediatrics 2009;155(1):129‐32. - PubMed
Narayanappa 2008 {published data only}
-
- Narayanappa D. Randomized double blinded controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Bifilac in patients with acute viral diarrhea. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 2008;75(7):709‐13. - PubMed
Oandasan 1999 {unpublished data only}
-
- Oandasan M, Gatcheco F, Kapahmgan S. Randomized, double blind placebo‐controlled clinical trial on the efficacy and safety of Infloran berna capsules in the treatment of acute non‐bloody diarrhea in infants.
Ozkan 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ozkan TB, Sahin E, Erdemir G, Budak F. Effect of Saccharomyces boulardii in children with acute gastroenteritis and its relationship to the immune response. The Journal of International Medical Research 2007;35(2):201‐12. - PubMed
Pant 1996 {published data only}
-
- Pant AR, Graham SM, Allen SJ, Harikul S, Sabchareon A, Cuevas L, et al. Lactobacillus GG and acute diarrhoea in young children in the tropics. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 1996;42(3):162‐5. - PubMed
Pashapour 2006 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Pashapour N, Iou SG. Evaluation of yogurt effect on acute diarrhea in 6‐24‐month‐old hospitalized infants. Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2006;48(2):115‐18. - PubMed
Rafeey 2008a {published data only}
-
- Rafeey M, Ostadrahimi A, Boniadi M, Ghorashi Z, Alizadeh MM, Hadafey V. Lactobacillus acidophilus yogurt and supplement in children with acute diarrhea: a clinical trial. Research Journal of Medical Sciences 2008;2(1):13‐18.
Raza 1995 {published data only}
-
- Raza S, Graham SM, Allen SJ, Sultana S, Cuevas L, Hart CA. Lactobacillus GG promotes recovery from acute nonbloody diarrhoea in Pakistan. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1995;14(2):107‐11. - PubMed
Ritchie 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ritchie BK, Brewster DR, Tran CD, Davidson GP, McNeil Y, Butler RN. Efficacy of Lactobacillus GG in Aboriginal children with acute diarrhoeal disease: a randomised clinical trial. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2010;50(6):619‐24. - PubMed
Rosenfeldt 2002a {published data only}
-
- Rosenfeldt V, Michaelsen KF, Jakobsen M, Larsen CN, Moller PL, Pedersen P. Effect of probiotic Lactobacillus strains in young children hospitalized with acute diarrhea. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2002;21(5):411‐6. - PubMed
Rosenfeldt 2002b {published data only}
-
- Rosenfeldt V, Michaelsen KF, Jakobsen M, Larsen CN, Moller PL, Tvede M, et al. Effect of probiotic Lactobacillus strains on acute diarrhea in a cohort of nonhospitalized children attending day‐care centers. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2002;21(5):417‐9. - PubMed
Sarkar 2005 {published data only}
-
- Sarker SA, Sultana S, Fuchs GJ, Alam NH, Azim T, Brűssow H, et al. Lactobacillus paracasei strain ST11 has no effect on rotavirus but ameliorates the outcome of nonrotavirus diarrhea in children from Bangladesh. Pediatrics 2005;116(2):e221‐8. - PubMed
Sepp 1995 {published data only}
-
- Sepp E, Tamm E, Torm S, Lutsar I, Mikelsaar M, Salminen S. Impact of a Lactobacillus probiotic on the faecal microflora in children with shigellosis. Microecology and Therapy 1995;23(1):74‐80.
Shornikova 1997a {published data only}
-
- Shornikova AV, Isolauri E, Burkanova L, Lukovnikova S, Vesikari T. A trial in the Karelian Republic of oral rehydration and Lactobacillus GG for treatment of acute diarrhoea. Acta Paediatrica 1997;86(5):460‐5. - PubMed
Shornikova 1997b {published data only}
-
- Shornikova AV, Casas IA, Mykkanen H, Salo E, Vesikari T. Bacteriotherapy with Lactobacillus reuteri in rotavirus gastroenteritis. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1997;16(12):1103‐7. - PubMed
Shornikova 1997c {published data only}
-
- Shornikova AV, Casas IA, Isolauri E, Mykkanen H, Vesikari T. Lactobacillus reuteri as a therapeutic agent in acute diarrhea in young children. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 1997;24(4):399‐404. - PubMed
Simakachorn 2000 {published data only}
-
- Simakachorn N, Pichaipat V, Rithipornpaisarn P, Kongkaew C, Tongpradit P, Varavithya W. Clinical evaluation of the addition of lyophilized, heat‐killed Lactobacillus acidophilus LB to oral rehydration therapy in the treatment of acute diarrhoea in children. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2000;30(1):68‐72. - PubMed
-
- Simakachorn N, Pichaipat V, Rithipornpaisarn P, Kongkaew C, Tongpradit P, Varavithya W. Erratum. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology 2000;30(2):228. - PubMed
Sugita 1994 {published data only}
-
- Sugita T, Togawa M. Efficacy of Lactobacillus preparation bioloactis powder in children with rotavirus enteritis. Japan Journal of Pediatrics 1994;47:2755‐62.
Szymanski 2006 {published data only}
-
- Szymanski H, Pejcz J, Jawien M, Chmielarczyk A, Strus M, Heczko PB. Treatment of acute infectious diarrhoea in infants and children with a mixture of three Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains ‐‐ a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2006;23(2):247‐53. - PubMed
Teran 2009 {published data only}
-
- Teran CG, Teran‐Escalera CN, Villarroel P. Nitazoxanide vs. probiotics for the treatment of acute rotavirus diarrhea in children: a randomized, single‐blind, controlled trial in Bolivian children. International Journal of Infectiouos Diseases 2009;13(4):518—23. - PubMed
Táborská 1997 {published data only}
-
- Táborská J, Pazdiora P. Smecta and Lactobacillus acidophilus ND in the treatment of acute diarrhoea in children [Smecta a Lactobacillus acidophilus ND v lécbe akutních detských prujmu]. Ceskoslovenská pediatrie 1997;52(1):29‐33.
Urganci 2001 {published data only}
-
- Urganci N, Polat T, Uysalol M, Cetinkaya F. Evaluation of the efficacy of Saccharomyces boulardii in children with acute diarrhoea. Archives of Gastroenterohepatology 2001;20(3‐4):81‐3.
Villarruel 2007 {published data only}
-
- Villarruel G, Rubio DM, Lopez F, Cintioni J, Gurevech R, Romero G, et al. Saccharomyces boulardii in acute childhood diarrhea: a randomised placebo controlled study. Acta Paediatrica 2007;96(4):538‐41. - PubMed
Vivatvakin 2006 {published data only}
-
- Vivatvakin B, Kowitdamrong E. Randomized control trial of live Lactobacillus acidophilus plus Bifidobacterium infantis in treatment of infantile acute watery diarrhea. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 2006;89:Suppl 3:S126‐33. - PubMed
Wunderlich 1989 {published data only}
-
- Wunderlich PF, Braun L, Fumagalli I, D'Apuzzo V, Heim F, Karly M, et al. Double‐blind report of the efficacy of lactic acid‐producing Enterococcus SF68 in the prevention of antibiotic‐associated diarrhoea and in the treatment of acute diarrhoea. The Journal of International Medical Research 1989;17(4):333‐8. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Agarwal 2001 {published data only}
-
- Agarwal KN, Bhasin SK, Faridi MMA, Mathur M, Gupta S. Lactobacillus casei in the control of acute diarrhoea ‐ a pilot study. Indian Pediatrics 2001;38(8):905‐10. - PubMed
Agarwal 2002 {published data only}
-
- Agarwal KN, Bhasin SK. Feasibility studies to control acute diarrhoea in children by feeding fermented milk preparations Actimel and Indian Dahi. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2002;56(Suppl. 4):S56‐9. - PubMed
Alexander 1971 {published data only}
Alvisi 1982 {published data only}
-
- Alvisi V, Tralli M, Loponte A, Pavani F, Massari M. Double‐blind study of treatment with SF 68 or with antibiotics in acute enteritis in adults [Studio in doppio cieco sul trattamento con SF68 o con antibiotici nelle enteritis acute dell'adulto]. La Clinica Terapeutica 1982;101(6):581‐6. - PubMed
Barone 2000 {published data only}
-
- Barone C, Pettinato R, Avola E, Alberti A, Greco D, Failla P, et al. Comparison of three probiotics in the treatment of acute diarrhea in mentally retarded children. Minerva Pediatrica 2000;52(3):161‐5. - PubMed
Beck 1961 {published data only}
-
- Beck C, Necheles H. Beneficial effects of administration of Lactobacillus acidophilus in diarrheal and other intestinal disorders. The American Journal of Gastroenterology 1961;35:522‐30. - PubMed
Bellomo 1979 {published data only}
-
- Bellomo G, Finocchiaro C, Frigerio G. A new approach for the treatment of enteritides in paediatrics [Une novelle approche pour le traitement des entérites en pédiatrie]. Médecine et Hygiène 1979;37:3781‐4.
Bellomo 1980 {published data only}
-
- Bellomo G, Mangiagle A, Nicastro L, Frigeria G. A controlled double‐blind study of SF68 strain as a new biological preparation for the treatment of diarrhoea in pediatrics. Current Therapeutic Research: Clinical and Experimental 1980;28(6):927‐35.
Bellomo 1982 {published data only}
-
- Bellomo G, Finocchiaro C, Frigerio G, Mangiagli A, Nicastro L. Controlled study ofEnterococcus LAB strain SF68 in acute enteritis in children with concomitant respiratory infection [Studio controllato sull'enterococco L.A.B. ceppo SF 68 nelle enteriti acute del bambino concomitanti ad infezioni delle vie respiratorie]. Clinica Pediatrica 1982;64:219‐27.
Bin Li Xie 1995 {published data only}
-
- Bin Li Xie. Controlled clinical trial of Lacteol Fort Sachet versus furazolidone or berberine in treatment of acute diarrhoea in children [Étude contrôlée du Lactéol Fort sachets versus furazolidone ou berbérine dans le traitement des diarrhées aiguës de l'enfant]. Annales de Pediatrie 1995;42(6):396‐401.
Brewster 2004 {published data only}
-
- Brewster DR, Ritchie B, McNeil Y, Davidson G, Butler R. Efficacy of probiotic therapy in Aboriginal children with acute diarrheal disease. Poster presentation 2004.
Camarri 1981 {published data only}
-
- Camarri E, Belvisi A, Guidoni G, Marini G, Frigerio G. A double‐blind comparison of two different treatments for acute enteritis in adults. Chemotherapy 1981;27(6):466‐70. - PubMed
Cetina Sauri 1990 {published data only}
-
- Cetina‐Sauri G, Basto GS. Therapeutic evaluation of children with acute diarrhea. Tribuna Medica 1990;81(3):141‐4.
Chandra 2002 {published data only}
-
- Chandra RK. Effect of Lactobacillus on the incidence and severity of acute rotavirus diarrhoea in infants. A prospective placebo‐controlled double‐blind study. Nutrition Research 2002;22(1):65‐9.
Chicoine 1973 {published data only}
-
- Chicoine L, Joncas JH. Use of lactic enzymes in non‐bacterial gastroenteritis [Emploi des ferments lactiques dans la gastro‐entérite non bactérienne]. L'Union Médicale du Canada 1973;102(5):1114‐5. - PubMed
Costa‐Ribeiro 2000a {published data only}
-
- Costa‐Ribeiro H, Ribeiro TCM, Mattos AP, Almeida PS, Valois SS, Vanderhoof JA. Use of Lactobacillus GG in the treatment of severe, acute diarrhoea in adverse environmental conditions.. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2000;31 Suppl 2:251‐2.
Costa‐Ribeiro 2000b {published data only}
-
- Costa‐Ribeiro H, Ribeiro TCM, Mattos AP, Lins EV, Neri DA, Valois SS, Vanderhoof JA. Prophylactic administration of Lactobacillus GG to children in a daycare center. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2000;31 Suppl 2:252.
Cui 2004 {published data only}
-
- Cui Y‐L, Wan F‐C, Tang D‐L, Wu S‐H. Efficacy of Bacillus coagulans tablets in the treatment of acute and chronic diarrhoea. International Journal of Immunotherapy 2004;20(1):17‐22.
de dios Pozo‐O 1978 {published data only}
-
- dios Pozo‐Olano J, Warram JH Jr, Gomez RG, Cavazos MG. Effect of a lactobacilli preparation on traveler's diarrhoea. A randomised, double blind clinical trial. Gastroenterology 1978;74(5 Pt 1):829‐30. - PubMed
Eren 2010 {published data only}
Fang 2009 {published data only}
-
- Fang S B, Lee H‐C, Hu J‐J, Hou S‐Y, Liu H‐L, Fang H‐W. Dose‐dependent effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus on quantitative reduction of faecal rotavirus shedding in children. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 2009;55(5):297‐301. - PubMed
Fourrier 1968 {published data only}
-
- Fourrier A, Lequien P. The treatment of infantile gastroenteritis by the use solely of a combination of colibacillus and lactobacillus. Apropos of 56 cases. Annales de Pediatrie 1968;15:491‐5. - PubMed
Girola 1995 {published data only}
-
- Girola M, Ventura P. Efficacy of probiotic preparation with living, freeze‐dried lactic acid bacteria and yeast on child diarrhoea [Efficacia di un prodotto probiotico a base di fermenti lattici e lievito vitali liofilizzati nel trattamento della diarrea del bambino]. Archivio di Medicina Interna 1995;47(2‐3):61‐72.
Gracheva 1996 {published data only}
-
- Gracheva NM, Gavrilov AF, Solov'eva AI, Smirnov VV, Sorokulova IB, Reznik SR, et al. The efficacy of the new bacterial preparation biosporin in treating acute intestinal infections. Zhurnal Mikrobiologii, Epidemiologii, i Immunobiologii 1996;1(1):75‐7. - PubMed
Henker 2007b {published data only}
-
- Henker J, Blokhin BM, Bolbot YK, Maydannik VG. Acute diarrhoea in infants and small children. Successful adjuvant therapy with the probiotic Mutaflor [Akute diarrhő bei säuglingen und kleinkindern. Erfolgreiche adjuvante therapie mit dem probiotikum Mutaflor]. Pädiat. Prax 2007;71:605‐10.
Heydarian 2010 {published data only}
-
- Heydarian F, Kianifar HR, Ahanchian H, Khakshure A, Seyedi J, Moshirian D. A comparison between traditional yogurt and probiotic yogurt in non‐inflammatory acute gastroenteritis. Saudi Med J 2010;31(3):280‐3. - PubMed
Isolauri 1991 {published data only}
-
- Isolauri E, Juntunen M, Rautanen T, Sillanaukee P, Koivula T. A human Lactobacillus strain (Lactobacillus casei GG) promotes recovery from acute diarrhea in children. Pediatrics 1991;88(1):90‐7. - PubMed
Kaila 1992 {published data only}
-
- Kaila M, Isolauri E, Soppi E, Virtanen E, Laine S, Arvilommi H. Enhancement of the circulating antibody secreting cell response in human diarrhea by a human Lactobacillus strain. Pediatric Research 1992;32(2):141‐4. - PubMed
Kaila 1995 {published data only}
Korviakova 2000 {published data only}
-
- Korviakova EP. Use of loading doses of Bifidumbacterin forte for the treatment of patients with acute enteric infections. Zhurnal Mikrobiologii, Epidemiologii, i Immunobiologii 2000;6:58‐61. - PubMed
Le Leyur 2010 {published data only}
-
- Luyer B, Makhoul G, Duhamel JF. A multicentric study of a lactose free formula supplemented with Saccharomyces boulardii in children with acute diarrhea. Archives de Pédiatrie 2010;17(5):459‐65. - PubMed
Lei 2006 {published data only}
-
- Lei V, Friis H, Michaelsen KF. Spontaneously fermented millet product as a natural probiotic treatment for diarrhea in young children: an intervention study Northern Ghana. International Journal of Food Microbiology 2006;110(3):246‐53. - PubMed
Lin 2009 {published data only}
-
- Lin JS, Chiu YH, Lin NT, Chu CH, Huang KC, Liao KW, et al. Different effects of probiotic species/strains on infections in preschool children: a double‐blind, randomized, controlled study. Vaccine 2009;27(7):1073‐9. - PubMed
Magreiter 2006 {published data only}
-
- Margreiter M, Ludl K, Phleps W, Kaehler ST. Therapeutic value of a Lactobacillus gasseri and Bifdobacterium longum fixed bacterium combination in acute diarrhea: a randomized, double‐blind, controlled clinical trial. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics May 2006;44(5):207‐15. - PubMed
Majamaa 1995 {published data only}
-
- Majamaa H, Isolauri E, Saxelin M, Vesikari T. Lactic acid bacteria in the treatment of acute rotavirus gastroenteritis. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 1995;20(3):333‐8. - PubMed
Mazo 2006 {published data only}
-
- Mazo SA, Arias SA. Efficacy and safety of milk fermented by lactobacillus (kumis) in nutritional recovery of undernourished children and control of their diarrhoea episodes. Revista Facultad Nacional de Salud Pública 2006;24(2):83‐97.
Michielutti 1995 {published data only}
-
- Michielutti F, Bertini M, Presciuttini B, Andreotti G. Clinical assessment of a new oral bacterial treatment for children with acute diarrhea [Valutazione clinica di un nuovo batterioterapico orale in pazienti di eta pediatrica con diarrea acuta]. Minerva Medica 1996;87(11):545‐50. - PubMed
Mitra 1990 {published data only}
-
- Mitra AK, Rabbini GH. A double‐blind, controlled trial of bioflorin (Streptococcus faecium SF68) in adults with acute diarrhea due to Vibrio chlolerae and entertoxigenic Escherichia coli. Gastroenterology 1990;99(4):1149‐52. - PubMed
Moraes 2001 {published data only}
-
- Moraes E, Chinzon D, Coelho LG, Fernandes TF, Haddad MT, et al. A multicentric, randomised, investigator‐blind, parallel group study to assess the efficacy, safety and tolerability of Racecadotril versus Saccharomyces boulardii in the treatment of acute diarrhoea in adults [Estudo multicêntrico de grupos paralelos, randomizado, cego para o investigador, para avaliar a eficácia, segurança e tolerabilidade do racecadotril versus Saccharomyces boulardii no tratamento da diarréia aguda em adultos]. Revista Brasileira de Medicina 2001;58(1‐2):65‐74.
Niv 1963 {published data only}
-
- Niv M, Levy W, Greenstein NM. Yogurt in the treatment of infantile diarrhea. Clinical Pediatrics 1963;2(7):407‐11.
Ortlieb 1974 {published data only}
-
- Ortlieb R. Randomized comparative testing of a new drug in intestinal disorders in a child. Therapie der Gegenwart 1974;113(1):76‐8. - PubMed
Pearce 1974 {published data only}
-
- Pearce JL, Hamilton JR. Controlled trial of orally administered lactobacilli in acute infantile diarrhea. The Journal of Pediatrics 1974;84(2):261‐2. - PubMed
Pedone 1999 {published data only}
-
- Pedone CA, Bernabeu AO, Postaire ER, Bouley CF, Reinert P. The effect of supplementation with milk fermented by Lactobacillus casei (strain DN‐114 001) on acute diarrhoea in children attending day care centres. International Journal of Clinical Practice 1999;53(3):179‐84. - PubMed
Pedone 2000 {published data only}
-
- Pedone CA, Arnaud CC, Postaire ER, Bouley CF, Reinert P. Multicentric study of the effect of milk fermented by Lactobacillus casei on the incidence of diarrhoea. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2000;54(9):568‐71. - PubMed
Pene 1966 {published data only}
-
- Pene P, Linhard J, Bernou JC. The colibacillus‐lactobacillus combination in the treatment of diarrhea in adults, children and infants [L'association colibacilles‐lactobacilles dans le traitement des diarrhées de l'adulte, de l'enfant et du nourrisson]. La Semaine Des Hopitaux 1966;42(4):241‐4. - PubMed
Rafeey 2008b {published data only}
-
- Rafeey M, Ghojazadeh M, Hadari V. Probiotics in children with acute diarrhea. WCPGHAN 3: World Congress of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition 2008:129‐35.
Rautanen 1998 {published data only}
Saint‐Marc 1991 {published data only}
-
- Saint‐Marc T, Rossello‐Prats L, Touraine JL. Efficacy of Saccharomyces boulardii in the treatment of diarrhea in AIDS [Efficacite de Saccharomyces boulardii dans le traitement des diarrhees du SIDA]. Annales de Médecine Interne 1991;142(1):64‐5. - PubMed
Salazar‐Lindo 2004 {published data only}
-
- Salazar‐Lindo E, Miranda‐Langschwager P, Campos‐Sanchez M, Chea‐Woo E, Bradley Sack R. Lactobacillus casei strain GG in the treatment of infants with acute watery diarrhoea: a randomised, double‐blind, placebo controlled clinical trial. BMC Pediatrics 2004; Vol. 4, issue 18. [http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471‐2431/4/18] - PMC - PubMed
Salazar‐Lindo 2007 {published data only}
-
- Salazar‐Lindo E, Figueroa‐Quintanilla D, Caciano MI, Reto‐Valiente V, Chauviere G, Colin P, et al. Effectiveness and safety of Lactobacillus LB in the treatment of mild acute darrhea in children. Journal of Paediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2006;44(5):571‐6. - PubMed
Satoh 1984 {published data only}
-
- Satoh Y, Iwata S, Iwata Y, Yamashita N, Oikawa T, Osano M, et al. Effect of Bifidobacterium breve administration on clinical course and intestinal flora in children with acute diarrhea [Abstract]. Nippon Shonikagakkai Zasshi 1984;88:2178‐9.
Savas‐Erdeve 2009 {published data only}
-
- Savas‐Erdeve S, Gökay S, Dallar Y. Efficacy and safety of Saccharomyces boulardii in amebiasis‐associated diarrhea in children. The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2009;51(3):220‐4. - PubMed
Schrezenmeir 2004 {published data only}
-
- Schrezenmeir J, Heller K, McCue M, Llamas C, Lam W, Burrow H, et al. Benefits of oral supplementation with and without synbiotics in young children. Clinical Paediatrics 2004;43:239‐49. - PubMed
Singh 1987 {published data only}
-
- Singh T. Yoghurt feeding during acute diarrhea. Indian Pediatrics 1987;24(6):530. - PubMed
Sudarmo 2003 {published data only}
-
- Sudarmo SM, Ranuh RG, Rochim A, Soeparto P. Management of infant diarrhea with high‐lactose probiotic‐containing formula. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 2003;34(4):845‐8. - PubMed
Szymanski 2005 {published data only}
-
- Szymanski H, Pejcz J, Jawien M, Kucharska A, Strus M, Heczko PB. Treatment of acute infectious diarrhoea in children with a mixture of three new Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains (573L/1,573L/2, 573L/3). A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2005;40(5):652.
Tojo 1987 {published data only}
-
- Tojo M, Oikawa T, Morikawa Y, Yamashita N, Iwata S, Satoh Y, et al. The effects of Bifidobacterium breve administration on campylobacter enteritis. Acta Paediatrica Japonica 1987;29(1):160‐7. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Contreras 1983 {published data only}
-
- Contreras G. Compend Invest Clin Latinoam 1983;3:114‐6.
Salgado {published data only}
-
- Salgado AJ, Garcia Jara JA. Use of heat‐killedLactobacillus acidophilus, Lacteol strain in the treatment of acute diarrhoea. Open trial. Revista del Hospital de la Muyer 2.
References to ongoing studies
Freedman 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ongoing study Starting date of trial not provided. Contact author for more information.
Additional references
Allen 2003
-
- Allen SJ, Okoko B, Martinez EG, Gregorio GV, Dans LF. Probiotics for treating infectious diarrhoea. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2003, Issue 4. [Art. No.: CD003048. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003048.pub2] - PubMed
Anonymous 1988
Baqui 1991
-
- Baqui AH, Black RE, Yunus M, Hoque AR, Chowdhury HR, Sack RB. Methodological issues in diarrhoeal diseases epidemiology: definition of diarrhoeal episodes. International Journal of Epidemiology 1991;20(4):1057‐63. - PubMed
Black 1986
Bryce 2006
-
- Bryce J, Terreri N, Victora CG, Mason E, Daelmans B, Bhutta ZA, et al. Countdown to 2015: tracking intervention coverage for child survival. Lancet 2006;368(9541):1067‐76. - PubMed
Chmielewska 2008
-
- Chmielewska A, Ruszczyński M, Szajewska H. Lactobacillus reuteri strain ATCC 55730 for the treatment of acute infectious diarrhoea in children: a meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Metaanalysis 2008;10:32‐6.
Clarke 2003
-
- Clarke M, Oxman A, editors. Optimal search strategy. Cochrane Reviewers' Handbook 4.2 [updated March 2003]; Appendix 5c. In: The Cochrane Library. The Cochrane Collaboration. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.; 2003, Issue 3.
Cunliffe 1998
FAO/WHO 2001
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)/World Health Organization (WHO). Joint FAO/WHO expert consultation on evaluation of health and nutritional properties of probiotics in food including powder milk and live lactic acid bacteria. ftp://ftp.fao.es/esn/food/probio_report_en.pdf 2001.
Gadewar 2005
-
- Gadewar S, Fasano A. Current concepts in the evaluation, diagnosis and management of acute infectious diarrhea. Current Opinion in Pharmacology 2005;5(6):559‐65. - PubMed
Gismondo 1999
-
- Gismondo MR, Drago L, Lombardi A. Review of probiotics available to modify gastrointestinal flora. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 1999;12(4):287‐92. - PubMed
Goldin 1998
-
- Goldin BR. Health benefits of probiotics. The British Journal of Nutrition 1998;80 Suppl(4):203‐7. - PubMed
Guerrant 1990
Hata 1988
-
- Hata D, Yoshida A, Ohkubo H, Mochizuki Y, Hosoki Y, Tanaka R, et al. Meningitis caused by Bifidobacterium in an infant. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1988;7(9):669‐71. - PubMed
Huilan 1991
Juni 1999
-
- Juni P, Witschi A, Bloch R, Egger M. The hazards of scoring the quality of clinical trials for meta‐analysis. JAMA: the Journal of the American Medical Association 1999;282(11):1054‐60. - PubMed
Klein 1998
-
- Klein G, Pack A, Bonaparte C, Reuter G. Taxonomy and physiology of the probiotic lactic acid bacteria. International Journal of Food Microbiology 1998;41(2):103‐25. - PubMed
Lopez 2006
-
- Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT, Murray CJL. Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet 2006;367(9524):1747‐57. - PubMed
Naidu 1999
-
- Naidu AS, Bidlack WR, Clemens RA. Probiotic spectra of lactic acid bacteria (LAB). Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 1999;39(1):13‐126. - PubMed
O'Ryan 2005
-
- O'Ryan M, Prado V, Pickering LK. A millennium update on pediatric diarrhoeal illness in the developing world. Seminars in Pediatric Infectious Diseases 2005;16(2):125‐36. - PubMed
Piarroux 1999
-
- Piarroux R, Millon L, Bardonnet K, Vagner O, Koenig H. Are live saccharomyces yeasts harmful to patients?. Lancet 1999;353(9167):1851‐2. - PubMed
Rijkers 2010
-
- Rijkers GT, Bengmark S, Enck P, Haller D, Herz U, Kaolliomaki M, et al. Guidance for substantiating the evidence for beneficial effects of probiotics: current status and recommendations for future research. Journal of Nutrition 2010;140(3):671S‐6S. - PubMed
Salminen 1998
-
- Salminen S, Wright A, Morelli L, Marteau P, Brassart D, Vos WM, et al. Demonstration of safety of probiotics ‐‐ a review. International Journal of Food Microbiology 1998;44(1‐2):93‐106. - PubMed
Salminen 1999
-
- Salminen S, Ouwehand A, Benno Y, Lee YK. Probiotics: how should they be defined?. Trends in Food Science & Technology 1999;10:107‐10.
Savarino 1993
-
- Savarino SJ, Bourgeois AL. Diarrhoeal disease: current concepts and future challenges. Epidemiology of diarrhoeal diseases in developed countries. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1993;87 Suppl 3:7‐11. - PubMed
Saxelin 1996
-
- Saxelin M, Chuang NH, Chassy B, Rautelin H, Makela PH, Salminen S, et al. Lactobacilli and bacteremia in southern Finland, 1989‐1992. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1996;22(3):564‐6. - PubMed
Sussman 1986
-
- Sussman J, Baron E, Goldberg S, Kaplan M, Pizzarello R. Clinical manifestations and therapy of Lactobacillus endocarditis: report of a case and review of the literature. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1986;8(5):771‐6. - PubMed
Szajewska 2001
-
- Szajewska H, Mrukowicz JZ. Probiotics in the treatment and prevention of acute infectious diarrhoea in infants and children; a systematic review of published randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trials. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2001;33 Suppl 2:17‐25. - PubMed
Szajewska 2007a
-
- Szajewska H, Skorka A, Ruszczynski M, Gieruszczak‐Bialek D. Meta‐analysis: Lactobacillus GG for treating acute diarrhoea in children. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2007;25(8):871–81. - PubMed
Szajewska 2007b
-
- Szajewska H, Skórka A, Dylag M. Meta‐analysis: Saccharomyces boulardii for treating acute diarrhoea in children. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2007;25:257‐64. - PubMed
Szajewska 2009
-
- Szajewska H, Skórka A. Saccharomyces boulardii for treating acute gastroenteritis in children: updated meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2009;30:960‐1. - PubMed
Van Niel 2002
-
- Niel CW, Feudtner C, Garrison MM, Christakis DA. Lactobacillus therapy for acute infectious diarrhoea in children: a meta‐analysis. Pediatrics 2002;109(4):678‐84. - PubMed
Vanderhoof 1998
-
- Vanderhoof JA, Young RJ. Use of probiotics in childhood gastrointestinal disorders. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 1998;27(3):323‐32. - PubMed
Walker‐Smith 1993
-
- Walker‐Smith JA. Diarrhoeal disease: current concepts and future challenges. Malnutrition and infection. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine 1993;87 Suppl 3:13‐5. - PubMed
WHO 1990
-
- Division of Diarrhoeal and Acute Respiratory Disease Control. The treatment of diarrhoea. A manual for physicians and other senior health workers. Geneva: World Health Organization, 1990:20‐1.
WHO 2001
-
- World Health Organization. The world health report : 2001: mental health : new understanding, new hope. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2001.
Wolvers 2010
-
- Wolvers D, Antoine JM, Myllyluoma E, Schrezenmeir J, Szajewska H, Rijkers GT. Guidance for substantiating the evidence for beneficial effects of probiotics: prevention and management of infections by probiotics. Journal of Nutrition 2010;140(3):698S‐712S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

