Quantitative studies of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs provide novel insights into their regulation
- PMID: 21068248
- PMCID: PMC3020024
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01528-10
Quantitative studies of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs provide novel insights into their regulation
Abstract
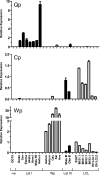
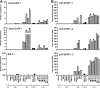
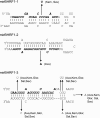
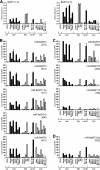
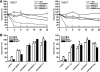
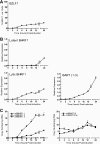
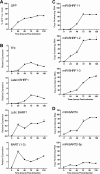
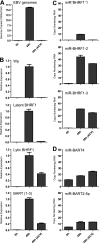
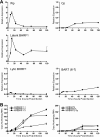
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) has been shown to encode at least 40 microRNAs (miRNAs), an important class of molecules that negatively regulate the expression of many genes through posttranscriptional mechanisms. Here, we have used real-time PCR assays to quantify the levels of EBV-encoded BHRF1 and BART miRNAs in latently infected cells and in cells induced into the lytic cycle. During latency, BHRF1 miRNAs were seen only in cells with detectable Cp- and/or Wp-initiated EBNA transcripts, while the BART miRNAs were expressed in all forms of latent infection. Surprisingly, levels of different BART miRNAs were found to vary up to 50-fold within a cell line. However, this variation could not be explained by differential miRNA turnover, as all EBV miRNAs appeared to be remarkably stable. Following entry into the virus lytic cycle, miR-BHRF1-2 and -1-3 were rapidly induced, coincident with the onset of lytic BHRF1 transcripts, while miR-BHRF1-1 expression was delayed until 48 h and correlated with the appearance of Cp/Wp-initiated EBNA transcripts. In contrast, levels of BART miRNAs were relatively unchanged during virus replication, despite dramatic increases in BART transcription. Finally, we show that BHRF1 and BART miRNAs were delayed relative to the induction of BHRF1 and BART transcripts in freshly infected primary B cell cultures. In summary, our data show that changes in BHRF1 and BART transcription are not necessarily reflected in altered miRNA levels, suggesting that miRNA maturation is a key step in regulating steady-state levels of EBV miRNAs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The members of an Epstein-Barr virus microRNA cluster cooperate to transform B lymphocytes.J Virol. 2011 Oct;85(19):9801-10. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05100-11. Epub 2011 Jul 13. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21752900 Free PMC article.
-
The role of promoter methylation in Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) microRNA expression in EBV-infected B cell lines.Exp Mol Med. 2011 Jul 30;43(7):401-10. doi: 10.3858/emm.2011.43.7.044. Exp Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21628990 Free PMC article.
-
A viral microRNA cluster strongly potentiates the transforming properties of a human herpesvirus.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Feb;7(2):e1001294. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001294. Epub 2011 Feb 17. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21379335 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Viral and Host microRNAs in Immune Regulation of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Diseases.Front Immunol. 2020 Mar 3;11:367. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00367. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32194570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathobiologic Roles of Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded MicroRNAs in Human Lymphomas.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Apr 12;19(4):1168. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041168. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29649101 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Implication of viral microRNAs in the genesis and diagnosis of Epstein-Barr virus-associated tumors.Oncol Lett. 2019 Oct;18(4):3433-3442. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10713. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31516561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Manipulation of Type I Interferon Signaling by HIV and AIDS-Associated Viruses.J Immunol Res. 2019 Apr 4;2019:8685312. doi: 10.1155/2019/8685312. eCollection 2019. J Immunol Res. 2019. PMID: 31089479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of small Epstein-Barr virus derived non-coding RNAs in epithelial malignancy.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Aug 23;14(9):17378-409. doi: 10.3390/ijms140917378. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23979421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Interplay Between Viral-Derived miRNAs and Host Immunity During Infection.Front Immunol. 2020 Jan 23;10:3079. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03079. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32038626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of microRNAs in Epstein-Barr virus latency and lytic reactivation.Microbes Infect. 2011 Dec;13(14-15):1156-67. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2011.07.007. Epub 2011 Jul 28. Microbes Infect. 2011. PMID: 21835261 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alfieri, C., M. Birkenbach, and E. Kieff. 1991. Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection of human B lymphocytes. Virology 181:595-608. - PubMed
-
- Allday, M. J., D. H. Crawford, and B. E. Griffin. 1989. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression during the initiation of B cell immortalization. J. Gen. Virol. 70:1755-1764. - PubMed
-
- Al-Mozaini, M., et al. 2009. Epstein-Barr virus BART gene expression. J. Gen. Virol. 90:307-316. - PubMed
-
- Anderton, E., J. Yee, P. Smith, T. Crook, R. E. White, and M. J. Allday. 2008. Two Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) oncoproteins cooperate to repress expression of the proapoptotic tumour-suppressor Bim: clues to the pathogenesis of Burkitt's lymphoma. Oncogene 27:421-433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

