Prognostic significance of nuclear survivin expression in resected adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck
- PMID: 21034499
- PMCID: PMC2988778
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-3284-2-30
Prognostic significance of nuclear survivin expression in resected adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck
Abstract
Objectives: The expression of survivin, an inhibitor of apoptosis, in tumor cells is associated with poor clinical outcome for various cancers. We conducted this study to determine survivin expression in patients with adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) of the head and neck and to identify its clinical significance as a prognostic factor.
Materials and methods: We performed immunohistochemical staining for survivin, p53, bcl-2 protein, and Ki-67 in formalin fixed, paraffin-embedded blocks from 37 cases of head and neck ACC. We also reviewed the patients' clinical records to determine the association of staining with clinical course.
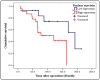
Results: Of the 37 cases of head and neck ACC, 31 (83.8%) were positive for cytoplasmic survivin expression, and 23 (62.2%) were positive for nuclear survivin expression. There was a significant association between nuclear survivin expression and bcl-2 (P = 0.031). A larger tumor was more commonly a survivin-positive tumor (cytoplasmic survivin, P = 0.043; nuclear survivin, P = 0.057). Median overall survival (OS) was significantly longer in patients not expressing nuclear survivin (P = 0.035). A multivariate analysis revealed that nuclear survivin expression significantly impacted OS (hazard ratio 8.567, P = 0.018) in addition to lymph node involvement (hazard ratio 7.704, P = 0.016).
Conclusions: The immunohistochemical expression of nuclear survivin has a prognostic impact in patients with head and neck ACC. These results suggest that nuclear survivin expression may be a useful biomarker for predicting prognosis in patients with head and neck ACC who were treated with surgical resection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the lacrimal gland: role of nuclear survivin (BIRC5) as a prognostic marker.Histopathology. 2013 May;62(6):840-6. doi: 10.1111/his.12073. Histopathology. 2013. PMID: 23611357
-
Survivin and pAkt as potential prognostic markers in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2014 Jun;117(6):733-42. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2014.02.005. Epub 2014 Feb 13. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24726415
-
Expression of beclin 1 in primary salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma and its relation to Bcl-2 and p53 and prognosis.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2014 Feb;47(3):252-8. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20133231. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2014. PMID: 24554038 Free PMC article.
-
New developments in the molecular pathogenesis of head and neck tumors: a review of tumor-specific fusion oncogenes in mucoepidermoid carcinoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma, and NUT midline carcinoma.Ann Diagn Pathol. 2011 Feb;15(1):69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2010.12.001. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21238915 Review.
-
Prognostic value of survivin expression in breast cancer patients: a meta-analysis.Tumour Biol. 2013 Aug;34(4):2053-62. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-0848-2. Epub 2013 May 21. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23690235 Review.
Cited by
-
Cigarette smoke affects the onco-suppressor DAB2IP expression in bronchial epithelial cells of COPD patients.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 30;9(1):15682. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52179-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31666665 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-140-5p inhibits salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma progression and metastasis via targeting survivin.Cancer Cell Int. 2019 Nov 16;19:301. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-1018-4. eCollection 2019. Cancer Cell Int. 2019. PMID: 31762692 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of survivin reduces HIF-1α, TGF-β1 and TFE3 in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 8;9(12):e114051. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114051. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25485635 Free PMC article.
-
Factors that may influence polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma growth.Virchows Arch. 2017 Apr;470(4):437-443. doi: 10.1007/s00428-017-2085-3. Epub 2017 Feb 10. Virchows Arch. 2017. PMID: 28188441
-
Small interfering RNA survivin and GRIM-19 co-expression salmonella plasmid inhibited the growth of laryngeal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013 Sep 15;6(10):2071-81. eCollection 2013. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013. PMID: 24133585 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Greiner TC, Robinson RA, Maves MD. Adenoid cystic carcinoma. A clinicopathologic study with flow cytometric analysis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1989;92(6):711–720. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

