A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing
- PMID: 20981092
- PMCID: PMC3042601
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09534
A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing
Erratum in
- Nature. 2011 May 26;473(7348):544. Xue, Yali [added]; Cartwright, Reed A [added]; Altshuler, David L [corrected to Altshuler, David]; Kebbel, Andrew [corrected to Keebler, Jonathan]; Koko-Gonzales, Paula [corrected to Kokko-Gonzales, Paula]; Nickerson, Debbie A [corrected to Nickerson, Debo
Abstract
The 1000 Genomes Project aims to provide a deep characterization of human genome sequence variation as a foundation for investigating the relationship between genotype and phenotype. Here we present results of the pilot phase of the project, designed to develop and compare different strategies for genome-wide sequencing with high-throughput platforms. We undertook three projects: low-coverage whole-genome sequencing of 179 individuals from four populations; high-coverage sequencing of two mother-father-child trios; and exon-targeted sequencing of 697 individuals from seven populations. We describe the location, allele frequency and local haplotype structure of approximately 15 million single nucleotide polymorphisms, 1 million short insertions and deletions, and 20,000 structural variants, most of which were previously undescribed. We show that, because we have catalogued the vast majority of common variation, over 95% of the currently accessible variants found in any individual are present in this data set. On average, each person is found to carry approximately 250 to 300 loss-of-function variants in annotated genes and 50 to 100 variants previously implicated in inherited disorders. We demonstrate how these results can be used to inform association and functional studies. From the two trios, we directly estimate the rate of de novo germline base substitution mutations to be approximately 10(-8) per base pair per generation. We explore the data with regard to signatures of natural selection, and identify a marked reduction of genetic variation in the neighbourhood of genes, due to selection at linked sites. These methods and public data will support the next phase of human genetic research.
Figures

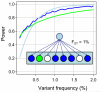
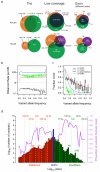
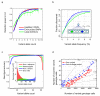
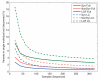

Comment in
-
Genomics: In search of rare human variants.Nature. 2010 Oct 28;467(7319):1050-1. doi: 10.1038/4671050a. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20981085 No abstract available.
-
Genomics: A picture worth 1000 Genomes.Nat Rev Genet. 2010 Dec;11(12):814. doi: 10.1038/nrg2906. Epub 2010 Nov 10. Nat Rev Genet. 2010. PMID: 21063440 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Comprehensive characterization of human genome variation by high coverage whole-genome sequencing of forty four Caucasians.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e59494. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059494. Epub 2013 Apr 5. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23577066 Free PMC article.
-
A global reference for human genetic variation.Nature. 2015 Oct 1;526(7571):68-74. doi: 10.1038/nature15393. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26432245 Free PMC article.
-
An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes.Nature. 2012 Nov 1;491(7422):56-65. doi: 10.1038/nature11632. Nature. 2012. PMID: 23128226 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Analysis in the Age of Human Genome Sequencing.Cell. 2019 Mar 21;177(1):70-84. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.02.032. Cell. 2019. PMID: 30901550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole-genome sequencing approaches for conservation biology: Advantages, limitations and practical recommendations.Mol Ecol. 2017 Oct;26(20):5369-5406. doi: 10.1111/mec.14264. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Mol Ecol. 2017. PMID: 28746784 Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling the effect of changing selective pressures on polymorphism and divergence.Theor Popul Biol. 2013 May;85:73-85. doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2012.10.001. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Theor Popul Biol. 2013. PMID: 23178187 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitive detection of somatic point mutations in impure and heterogeneous cancer samples.Nat Biotechnol. 2013 Mar;31(3):213-9. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2514. Epub 2013 Feb 10. Nat Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23396013 Free PMC article.
-
Have we learnt all we need to know from genetic studies - is genetics over in Alzheimer's disease?Alzheimers Res Ther. 2013 Mar 18;5(2):11. doi: 10.1186/alzrt165. eCollection 2013. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 23510020 Free PMC article.
-
Distinguishing between selective sweeps from standing variation and from a de novo mutation.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(10):e1003011. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003011. Epub 2012 Oct 11. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23071458 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput sequencing and rare genetic diseases.Mol Syndromol. 2012 Nov;3(5):197-203. doi: 10.1159/000343941. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Mol Syndromol. 2012. PMID: 23293577 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium Finishing the euchromatic sequence of the human genome. Nature. 2004;431:931–45. - PubMed
-
- Sachidanandam R, et al. A map of human genome sequence variation containing 1.42 million single nucleotide polymorphisms. Nature. 2001;409:928–33. - PubMed
-
- NHGRI Office of Population Genomics A catalog of published genome-wide association studies. 2010
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01HG5208/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- WT085532AIA/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 075491/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U54 HG002750/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM059290/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG004719-02/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- WT086084/Z/08/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01HG4960/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 077192/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 077009/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- N01HG62088/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH084698/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HG005552-01/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/09/012/28096/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HG004960/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- WT081407/Z/06/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 01MH84698/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM72861/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG004719-01/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG005208/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U41 HG002371/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG004333/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HG002371/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG004719-04/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P41HG2371/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002651/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG004719/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 HG004222/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HG4333/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HG3698/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM072861/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HG005552/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG2757/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- WT089088/Z/09/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U54 HG002757/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 089088/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01GM59290/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG5210/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U41HG4568/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG005211/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG005214/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- WT075491/Z/04/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HG003229/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 HG002371/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003273/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG5211/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG3079/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- G0801823/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0801823(89305)/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01HG5214/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U41 HG004568/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG2750/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 089062/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG005210/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HG005552-02/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 077014/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HG003698/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2HG5552/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P01HG4120/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG5209/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 089061/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 086084/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 01HG3229/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG3067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P41HG4221/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002510/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 081407/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 085532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HG004719-02S1/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG004719-03/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 HG005201/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P50HG2357/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG003229-05/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG005209/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AA022707/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P41 HG004221/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HG004120/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P41HG4222/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- S10RR025056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01HG2651/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HG4719/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HG002357/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG3273/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

