Roles of host and viral microRNAs in human cytomegalovirus biology
- PMID: 20969901
- PMCID: PMC3383804
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.10.011
Roles of host and viral microRNAs in human cytomegalovirus biology
Abstract
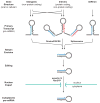
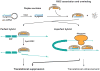
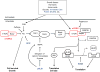
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) has a relatively large and complex genome, a protracted lytic replication cycle, and employs a strategy of replicational latency as part of its lifelong persistence in the infected host. An important form of gene regulation in plants and animals revolves around a type of small RNA known as microRNA (miRNA). miRNAs can serve as major regulators of key developmental pathways, as well as provide subtle forms of regulatory control. The human genome encodes over 900 miRNAs, and miRNAs are also encoded by some viruses, including HCMV, which encodes at least 14 miRNAs. Some of the HCMV miRNAs are known to target both viral and cellular genes, including important immunomodulators. In addition to expressing their own miRNAs, infections with some viruses, including HCMV, can result in changes in the expression of cellular miRNAs that benefit virus replication. In this review, we summarize the connections between miRNAs and HCMV biology. We describe the nature of miRNA genes, miRNA biogenesis and modes of action, methods for studying miRNAs, HCMV-encoded miRNAs, effects of HCMV infection on cellular miRNA expression, roles of miRNAs in HCMV biology, and possible HCMV-related diagnostic and therapeutic applications of miRNAs.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Human cytomegalovirus latent infection alters the expression of cellular and viral microRNA.Gene. 2014 Feb 25;536(2):272-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.12.012. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24361963
-
High-resolution profiling and analysis of viral and host small RNAs during human cytomegalovirus infection.J Virol. 2012 Jan;86(1):226-35. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05903-11. Epub 2011 Oct 19. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22013051 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus microRNA miR-US25-1-5p inhibits viral replication by targeting multiple cellular genes during infection.Gene. 2015 Oct 1;570(1):108-14. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.06.009. Epub 2015 Jun 6. Gene. 2015. PMID: 26055091
-
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV)-encoded microRNAs: potential biomarkers and clinical applications.RNA Biol. 2021 Dec;18(12):2194-2202. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1930757. Epub 2021 May 26. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 34039247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs expressed by human cytomegalovirus.Virol J. 2020 Mar 12;17(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12985-020-1296-4. Virol J. 2020. PMID: 32164742 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current Knowledge on the Interaction of Human Cytomegalovirus Infection, Encoded miRNAs, and Acute Aortic Syndrome.Viruses. 2023 Sep 29;15(10):2027. doi: 10.3390/v15102027. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37896804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in infectious diseases: potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2023 Dec 20;36(4):e0001523. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00015-23. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37909789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional annotation of human cytomegalovirus gene products: an update.Front Microbiol. 2014 May 19;5:218. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00218. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24904534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Replication competent HIV-1 viruses that express intragenomic microRNA reveal discrete RNA-interference mechanisms that affect viral replication.Cell Biosci. 2011 Nov 23;1(1):38. doi: 10.1186/2045-3701-1-38. Cell Biosci. 2011. PMID: 22112720 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease and microorganisms: the non-coding RNAs crosstalk.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Jan 5;17:1256100. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1256100. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38249527 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexiou P, Maragkakis M, Papadopoulos GL, Reczko M, Hatzigeorgiou AG. Lost in translation: an assessment and perspective for computational microRNA target identification. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:3049–3055. - PubMed
-
- Alwine JC. Modulation of host cell stress responses by human cytomegalovirus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;325:263–279. - PubMed
-
- Bartels CL, Tsongalis GJ. MicroRNAs: novel biomarkers for human cancer. Clin Chem. 2009;55:623–631. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

