Push-and-pull regulation of the fusion pore by synaptotagmin-7
- PMID: 20956309
- PMCID: PMC2973888
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1014070107
Push-and-pull regulation of the fusion pore by synaptotagmin-7
Abstract
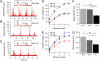
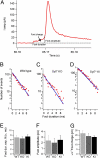
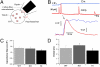
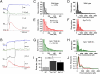
In chromaffin cells, Ca(2+) binding to synaptotagmin-1 and -7 triggers exocytosis by promoting fusion pore opening and fusion pore expansion. Synaptotagmins contain two C2 domains that both bind Ca(2+) and contribute to exocytosis; however, it remains unknown whether the C2 domains act similarly or differentially to promote opening and expansion of fusion pores. Here, we use patch amperometry measurements in WT and synaptotagmin-7-mutant chromaffin cells to analyze the role of Ca(2+) binding to the two synaptotagmin-7 C2 domains in exocytosis. We show that, surprisingly, Ca(2+) binding to the C2A domain suffices to trigger fusion pore opening but that the resulting fusion pores are unstable and collapse, causing a dramatic increase in kiss-and-run fusion events. Thus, synaptotagmin-7 controls fusion pore dynamics during exocytosis via a push-and-pull mechanism in which Ca(2+) binding to both C2 domains promotes fusion pore opening, but the C2B domain is selectively essential for continuous expansion of an otherwise unstable fusion pore.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synaptotagmin-1 and -7 are functionally overlapping Ca2+ sensors for exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Mar 11;105(10):3998-4003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0712373105. Epub 2008 Feb 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18308932 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptotagmin-Ca2+ triggers two sequential steps in regulated exocytosis in rat PC12 cells: fusion pore opening and fusion pore dilation.J Physiol. 2006 Jan 15;570(Pt 2):295-307. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.097378. Epub 2005 Nov 17. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16293646 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of exocytosis and fusion pores by synaptotagmin-effector interactions.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Aug 15;21(16):2821-31. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-04-0285. Epub 2010 Jun 23. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20573977 Free PMC article.
-
The C2 domains of synaptotagmin--partners in exocytosis.Trends Biochem Sci. 2004 Mar;29(3):143-51. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2004.01.008. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004. PMID: 15003272 Review.
-
C2-domain containing calcium sensors in neuroendocrine secretion.J Neurochem. 2016 Dec;139(6):943-958. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13865. Epub 2016 Nov 9. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 27731902 Review.
Cited by
-
Electroanalytical eavesdropping on single cell communication.Anal Chem. 2011 Oct 1;83(19):7242-9. doi: 10.1021/ac200666c. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Anal Chem. 2011. PMID: 21766792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synaptotagmin-7 links fusion-activated Ca²⁺ entry and fusion pore dilation.J Cell Sci. 2014 Dec 15;127(Pt 24):5218-27. doi: 10.1242/jcs.153742. Epub 2014 Oct 24. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 25344253 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptotagmin-7 places dense-core vesicles at the cell membrane to promote Munc13-2- and Ca2+-dependent priming.Elife. 2021 Mar 22;10:e64527. doi: 10.7554/eLife.64527. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33749593 Free PMC article.
-
The high-affinity calcium sensor synaptotagmin-7 serves multiple roles in regulated exocytosis.J Gen Physiol. 2018 Jun 4;150(6):783-807. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201711944. Epub 2018 May 24. J Gen Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29794152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Ever-Growing Puzzle of Asynchronous Release.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Feb 12;13:28. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00028. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30809127 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Katz B. In: The Release of Neural Transmitter Substances. Katz B, editor. Liverpool: Liverpool Univ Press; 1969. p. 60.
-
- Sudhof TC. The synaptic vesicle cycle. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2004;27:509–547. - PubMed
-
- Geppert M, et al. Synaptotagmin I: A major Ca2+ sensor for transmitter release at a central synapse. Cell. 1994;79:717–727. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

