Simian virus 40 inhibits differentiation and maturation of rhesus macaque DC-SIGN(+) dendritic cells
- PMID: 20952346
- PMCID: PMC3351904
- DOI: 10.1186/2047-783x-15-9-377
Simian virus 40 inhibits differentiation and maturation of rhesus macaque DC-SIGN(+) dendritic cells
Abstract
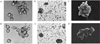
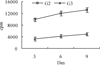
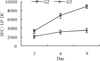
Dendritic cells (DC) are the initiators and modulators of the immune responses. Some species of pathogenic microorganisms have developed immune evasion strategies by controlling antigen presentation function of DC. Simian virus 40 (SV40) is a DNA tumor virus of rhesus monkey origin. It can induce cell transformation and tumorigenesis in many vertebrate species, but often causes no visible effects and persists as a latent infection in rhesus monkeys under natural conditions. To investigate the interaction between SV40 and rhesus monkey DC, rhesus monkey peripheral blood monocyte-derived DC were induced using recombinant human Interleukin-4 (rhIL-4) and infective SV40, the phenotype and function of DC-specific intracellular adhesion molecule-3 grabbing nonintegrin (DC-SIGN)(+) DC were analyzed by flow cytometry (FCM) and mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR). Results showed that SV40 can down-regulate the expression of CD83 and CD86 on DC and impair DC-induced activation of T cell proliferation. These findings suggest that SV40 might also cause immune suppression by influencing differentiation and maturation of DC.
Figures
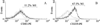

Similar articles
-
[Effect of simian vacuolating virus 40 on development and differentiation of dendritic cells from Rhesus macaque].Bing Du Xue Bao. 2009 Sep;25(5):344-8. Bing Du Xue Bao. 2009. PMID: 19954110 Chinese.
-
Antigen presentation and immune regulatory capacity of immature and mature-enriched antigen presenting (dendritic) cells derived from human bone marrow.Hum Immunol. 2004 Feb;65(2):93-103. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2003.11.002. Hum Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14969764
-
Spontaneous or Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced apoptotic neutrophils exert opposite effects on the dendritic cell-mediated immune response.Eur J Immunol. 2007 Jun;37(6):1524-37. doi: 10.1002/eji.200636771. Eur J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17506030
-
Increased expression of DC-SIGN+IL-12+IL-18+ and CD83+IL-12-IL-18- dendritic cell populations in the colonic mucosa of patients with Crohn's disease.Eur J Immunol. 2003 Jan;33(1):143-51. doi: 10.1002/immu.200390017. Eur J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12594843
-
Role of Dendritic Cell-Specific ICAM-3-Grabbing Nonintegrin on Dendritic Cells in the Recognition of Hepatitis B Virus.Viral Immunol. 2015 Jul-Aug;28(6):331-8. doi: 10.1089/vim.2014.0128. Viral Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26133046
Cited by
-
Serum IgG against Simian Virus 40 antigens are hampered by high levels of sHLA-G in patients affected by inflammatory neurological diseases, as multiple sclerosis.J Transl Med. 2016 Jul 22;14(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-0981-y. J Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27443345 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of morphine and SIV on dendritic cell trafficking into the central nervous system of rhesus macaques.J Neurovirol. 2014 Apr;20(2):175-83. doi: 10.1007/s13365-013-0182-x. Epub 2013 Aug 14. J Neurovirol. 2014. PMID: 23943466 Free PMC article.
-
Non-permissive human conventional CD1c+ dendritic cells enable trans-infection of human primary renal tubular epithelial cells and protect BK polyomavirus from neutralization.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Feb 16;17(2):e1009042. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009042. eCollection 2021 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33592065 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

