Regulation of specific target genes and biological responses by estrogen receptor subtype agonists
- PMID: 20951642
- PMCID: PMC3010356
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coph.2010.09.009
Regulation of specific target genes and biological responses by estrogen receptor subtype agonists
Abstract
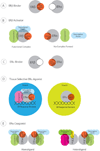
Estrogenic effects are mediated through two estrogen receptor (ER) subtypes, ERα and ERβ. Estrogens are the most commonly prescribed drugs to treat menopausal conditions, but by non-selectively triggering both ERα and ERβ pathways in different tissues they can cause serious adverse effects. The different sizes of the binding pockets and sequences of their activation function domains indicate that ERα and ERβ should have different specificities for ligands and biological responses that can be exploited for designing safer and more selective estrogens. ERα and ERβ regulate different genes by binding to different regulatory elements and recruiting different transcription and chromatin remodeling factors that are expressed in a cell-specific manner. ERα-selective and ERβ-selective agonists have been identified that demonstrate that the two ERs produce distinct biological effects. ERα and ERβ agonists are a promising new approach for treating specific conditions associated with menopause.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cell proliferation and modulation of interaction of estrogen receptors with coregulators induced by ERα and ERβ agonists.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014 Sep;143:376-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.06.002. Epub 2014 Jun 9. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24923734
-
Novel ligands balance estrogen receptor β and α agonism for safe and effective suppression of the vasomotor response in the ovariectomized female rat model of menopause.Endocrinology. 2014 Jul;155(7):2480-91. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1976. Epub 2014 May 13. Endocrinology. 2014. PMID: 24823389
-
Genome-wide dynamics of chromatin binding of estrogen receptors alpha and beta: mutual restriction and competitive site selection.Mol Endocrinol. 2010 Jan;24(1):47-59. doi: 10.1210/me.2009-0252. Epub 2009 Nov 6. Mol Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 19897598 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of estrogen action: selective ligands and receptor pharmacology.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2000 Nov 30;74(5):279-85. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(00)00104-7. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 11162936 Review.
-
Estrogen receptors alpha (ERα) and beta (ERβ): subtype-selective ligands and clinical potential.Steroids. 2014 Nov;90:13-29. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2014.06.012. Epub 2014 Jun 24. Steroids. 2014. PMID: 24971815 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a recombinant human ovarian (BG1) cell line containing estrogen receptor α and β for improved detection of estrogenic/antiestrogenic chemicals.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2016 Jan;35(1):91-100. doi: 10.1002/etc.3146. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26139245 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptors regulate innate immune cells and signaling pathways.Cell Immunol. 2015 Apr;294(2):63-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2015.01.018. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Cell Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25682174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen, Angiogenesis, Immunity and Cell Metabolism: Solving the Puzzle.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 15;19(3):859. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030859. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29543707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen and thyroid cancer is a stem affair: A preliminary study.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jan;85:399-411. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.11.043. Epub 2016 Nov 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 27899250 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptors regulate an inflammatory pathway of dendritic cell differentiation: mechanisms and implications for immunity.Horm Behav. 2012 Aug;62(3):254-62. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2012.04.011. Epub 2012 Apr 25. Horm Behav. 2012. PMID: 22561458 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
-
Risks and benefits of estrogen plus progestin in healthy postmenopausal women: principal results From the Women's Health Initiative randomized controlled trial. Jama. 2002;288:321–333. This seminal study was the first randomized, placebo controlled study to evaluate the effects of hormone therapy on postmenopausal women. The study found that the risks of hormone therapy exceed the benefits.
-
-
- Shang Y. Molecular mechanisms of oestrogen and SERMs in endometrial carcinogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:360–368. - PubMed
-
- Heldring N, Pike A, Andersson S, Matthews J, Cheng G, Hartman J, Tujague M, Strom A, Treuter E, Warner M, et al. Estrogen receptors: how do they signal and what are their targets. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:905–931. - PubMed
-
- Stauffer SR, Coletta CJ, Tedesco R, Nishiguchi G, Carlson K, Sun J, Katzenellenbogen BS, Katzenellenbogen JA. Pyrazole ligands: structure-affinity/activity relationships and estrogen receptor-alpha-selective agonists. J Med Chem. 2000;43:4934–4947. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

