Roles of vaccinia virus genes E3L and K3L and host genes PKR and RNase L during intratracheal infection of C57BL/6 mice
- PMID: 20943971
- PMCID: PMC3014211
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00254-10
Roles of vaccinia virus genes E3L and K3L and host genes PKR and RNase L during intratracheal infection of C57BL/6 mice
Abstract
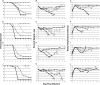
The importance of the 2'-5' oligoadenylate synthetase (OAS)/RNase L and double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-dependent protein kinase (PKR) pathways in host interferon induction resulting from virus infection in response to dsRNA has been well documented. In poxvirus infections, the interactions between the vaccinia virus (VV) genes E3L and K3L, which target RNase L and PKR, respectively, serve to prevent the induction of the dsRNA-dependent induced interferon response in cell culture. To determine the importance of these host genes in controlling VV infections, mouse single-gene knockouts of RNase L and PKR and double-knockout mice were studied following intratracheal infection with VV, VVΔK3L, or VVΔE3L. VV caused lethal disease in all mouse strains. The single-knockout animals were more susceptible than wild-type animals, while the RNase L(-/-) PKR(-/-) mice were the most susceptible. VVΔE3L infections of wild-type mice were asymptomatic, demonstrating that E3L plays a critical role in controlling the host immune response. RNase L(-/-) mice showed no disease, whereas 20% of the PKR(-/-) mice succumbed at a dose of 10(8) PFU. Lethal disease was routinely observed in RNase L(-/-) PKR(-/-) mice inoculated with 10(8) PFU of VVΔE3L, with a distinct pathology. VVΔK3L infections exhibited no differences in virulence among any of the mouse constructs, suggesting that PKR is not the exclusive target of K3L. Surprisingly, VVΔK3L did not disseminate to other tissues from the lung. Hence, the cause of death in this model is respiratory disease. These results also suggest that an unanticipated role of the K3L gene is to facilitate virus dissemination.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Blockade of interferon induction and action by the E3L double-stranded RNA binding proteins of vaccinia virus.J Virol. 2002 May;76(10):5251-9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.10.5251-5259.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11967338 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing Roles of Double-Stranded RNA Effector Pathways and Viral Defense Proteins Revealed with CRISPR-Cas9 Knockout Cell Lines and Vaccinia Virus Mutants.J Virol. 2016 Aug 12;90(17):7864-79. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00869-16. Print 2016 Sep 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27334583 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccinia virus E3L protein is an inhibitor of the interferon (i.f.n.)-induced 2-5A synthetase enzyme.Virology. 1998 Apr 10;243(2):406-14. doi: 10.1006/viro.1998.9072. Virology. 1998. PMID: 9568039
-
The interferon system and vaccinia virus evasion mechanisms.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009 Sep;29(9):581-98. doi: 10.1089/jir.2009.0073. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009. PMID: 19708815 Review.
-
Proteins that interact with PKR.Biochimie. 1994;76(8):779-91. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(94)90082-5. Biochimie. 1994. PMID: 7893827 Review.
Cited by
-
Species-specific inhibition of antiviral protein kinase R by capripoxviruses and vaccinia virus.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019 Feb;1438(1):18-29. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14000. Epub 2019 Jan 15. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019. PMID: 30644558 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant modified vaccinia virus Ankara generating excess early double-stranded RNA transiently activates protein kinase R and triggers enhanced innate immune responses.J Virol. 2014 Dec;88(24):14396-411. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02082-14. Epub 2014 Oct 8. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25297997 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of NYVAC Infection in HeLa Cells Requires RNase L but Is Independent of Protein Kinase R Activity.J Virol. 2015 Dec 9;90(4):2135-41. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02576-15. Print 2016 Feb 15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26656695 Free PMC article.
-
Species-specific inhibition of capripoxvirus replication by host antiviral protein kinase R.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019 Feb;1438(1):3-17. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13976. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019. PMID: 30381842 Free PMC article.
-
Variola virus E3L Zα domain, but not its Z-DNA binding activity, is required for PKR inhibition.RNA. 2014 Feb;20(2):214-27. doi: 10.1261/rna.042341.113. Epub 2013 Dec 13. RNA. 2014. PMID: 24335187 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beattie, E., E. B. Kauffman, H. Martinez, M. E. Perkus, B. L. Jacobs, E. Paoletti, and J. Tartaglia. 1996. Host-range restriction of vaccinia virus E3L-specific deletion mutants. Virus Genes 12:89-94. - PubMed
-
- Beattie, E., E. Paoletti, and J. Tartaglia. 1995. Distinct patterns of IFN sensitivity observed in cells infected with vaccinia K3L− and E3L− mutant viruses. Virology 210:254-263. - PubMed
-
- Beattie, E., J. Tartaglia, and E. Paoletti. 1991. Vaccinia virus-encoded eIF-2 alpha homolog abrogates the antiviral effect of interferon. Virology 183:419-422. - PubMed
-
- Brandt, T., M. C. Heck, S. Vijaysri, G. M. Jentarra, J. M. Cameron, and B. L. Jacobs. 2005. The N-terminal domain of the vaccinia virus E3L-protein is required for neurovirulence, but not induction of a protective immune response. Virology 333:263-270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

