ATM- and NEMO-dependent ELKS ubiquitination coordinates TAK1-mediated IKK activation in response to genotoxic stress
- PMID: 20932476
- PMCID: PMC3048026
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.010
ATM- and NEMO-dependent ELKS ubiquitination coordinates TAK1-mediated IKK activation in response to genotoxic stress
Abstract
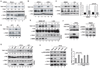
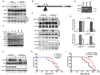
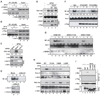
Activation of the transcription factor NF-κB by multiple genotoxic stimuli modulates cancer cell survival. This response is mediated by a conserved pathway involving the nuclear ATM kinase and cytoplasmic IκB kinase (IKK); however, the molecular link between them remains incompletely understood. Here we show that ATM activates the IKK kinase TAK1 in a manner dependent on IKKγ/NEMO and ELKS (a protein rich in glutamate, leucine, lysine, and serine). K63-linked polyubiquitination of ELKS, dependent on the ubiquitin ligase XIAP and the conjugating enzyme UBC13, allows ELKS association with TAK1 via its ubiquitin-binding subunits TAB2/3. Although NEMO mutants defective in ubiquitin binding permit ATM-dependent TAK1 activation, they block NEMO association with ELKS and IKK activation. Thus, ATM- and NEMO-dependent ubiquitination of ELKS leads to the ubiquitin-dependent assembly of TAK1/TAB2/3 and NEMO/IKK complexes, resulting in IKK and NF-κB activation following genotoxic stimuli.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
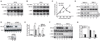


Similar articles
-
A cytoplasmic ATM-TRAF6-cIAP1 module links nuclear DNA damage signaling to ubiquitin-mediated NF-κB activation.Mol Cell. 2010 Oct 8;40(1):63-74. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.008. Mol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20932475
-
A cytosolic ATM/NEMO/RIP1 complex recruits TAK1 to mediate the NF-kappaB and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/MAPK-activated protein 2 responses to DNA damage.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Jul;31(14):2774-86. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01139-10. Epub 2011 May 23. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21606198 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular linkage between the kinase ATM and NF-kappaB signaling in response to genotoxic stimuli.Science. 2006 Feb 24;311(5764):1141-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1121513. Science. 2006. PMID: 16497931
-
Ubiquitination in signaling to and activation of IKK.Immunol Rev. 2012 Mar;246(1):95-106. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01108.x. Immunol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22435549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear initiated NF-κB signaling: NEMO and ATM take center stage.Cell Res. 2011 Jan;21(1):116-30. doi: 10.1038/cr.2010.179. Epub 2010 Dec 28. Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21187855 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The diverse and complex roles of NF-κB subunits in cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2012 Jan 19;12(2):121-32. doi: 10.1038/nrc3204. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22257950 Review.
-
DNA damage induces NF-κB-dependent microRNA-21 up-regulation and promotes breast cancer cell invasion.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 22;287(26):21783-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.355495. Epub 2012 Apr 30. J Biol Chem. 2012. Retraction in: J Biol Chem. 2019 Nov 22;294(47):18015. doi: 10.1074/jbc.W119.011598. PMID: 22547075 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Mechanisms of DNA damage-mediated neurotoxicity in neurodegenerative disease.EMBO Rep. 2022 Jun 7;23(6):e54217. doi: 10.15252/embr.202154217. Epub 2022 May 2. EMBO Rep. 2022. PMID: 35499251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Copper is a potent inhibitor of both the canonical and non-canonical NFκB pathways.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(6):1006-14. doi: 10.4161/cc.27922. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24552822 Free PMC article.
-
TAK1 signaling regulates p53 through a mechanism involving ribosomal stress.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 13;10(1):2517. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59340-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32054925 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biswas SK, Bist P, Dhillon MK, Kajiji T, Del Fresno C, Yamamoto M, Lopez-Collazo E, Akira S, Tergaonkar V. Role for MyD88-independent, TRIF pathway in lipid A/TLR4-induced endotoxin tolerance. J Immunol. 2007;179:4083–4092. - PubMed
-
- Chen ZJ, Bhoj V, Seth RB. Ubiquitin, TAK1 and IKK: is there a connection? Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:687–692. - PubMed
-
- Chen ZJ, Sun LJ. Nonproteolytic Functions of Ubiquitin in Cell Signaling. Mol Cell. 2009;33:275–286. - PubMed
-
- Chew J, Biswas S, Shreeram S, Humaidi M, Wong ET, Dhillion MK, Teo H, Hazra A, Fang CC, López-Collazo E, Bulavin DV, Tergaonkar V. WIP1 phosphatase is a negative regulator of NF-kappaB signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:659–666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

