Ganglioside metabolism in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease: expression of Chol-1α antigens in the brain
- PMID: 20930939
- PMCID: PMC2948441
- DOI: 10.1042/AN20100021
Ganglioside metabolism in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease: expression of Chol-1α antigens in the brain
Abstract
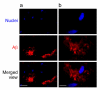
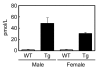
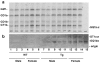
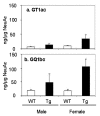
The accumulation of Aβ (amyloid β-protein) is one of the major pathological hallmarks in AD (Alzheimer's disease). Gangliosides, sialic acid-containing glycosphingolipids enriched in the nervous system and frequently used as biomarkers associated with the biochemical pathology of neurological disorders, have been suggested to be involved in the initial aggregation of Aβ. In the present study, we have examined ganglioside metabolism in the brain of a double-Tg (transgenic) mouse model of AD that co-expresses mouse/human chimaeric APP (amyloid precursor protein) with the Swedish mutation and human presenilin-1 with a deletion of exon 9. Although accumulation of Aβ was confirmed in the double-Tg mouse brains and sera, no statistically significant change was detected in the concentration and composition of major ganglio-N-tetraosyl-series gangliosides in the double-Tg brain. Most interestingly, Chol-1α antigens (cholinergic neuron-specific gangliosides), such as GT1aα and GQ1bα, which are minor species in the brain, were found to be increased in the double-Tg mouse brain. We interpret that the occurrence of these gangliosides may represent evidence for generation of cholinergic neurons in the AD brain, as a result of compensatory neurogenesis activated by the presence of Aβ.
Keywords: AD, Alzheimer's disease; APP, amyloid precursor protein; Alzheimer's disease; Aβ, amyloid β-peptide; Chol-1α antigen; HPTLC, high-performance TLC; PSEN, presenilin; PSEN1dE9, PSEN-1 with a deletion of exon 9; Tg, transgenic; WT, wild-type; amyloid β-peptide; cholinergic neuron; ganglioside; transgenic mouse.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brain gangliosides of a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease with deficiency in GD3-synthase: expression of elevated levels of a cholinergic-specific ganglioside, GT1aα.ASN Neuro. 2013 May 30;5(2):141-8. doi: 10.1042/AN20130006. ASN Neuro. 2013. PMID: 23565921 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Gangliosides in Alzheimer's Disease: Increased Expression of Cholinergic Neuron-Specific Gangliosides.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2017;14(6):586-591. doi: 10.2174/1567205014666170117094038. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2017. PMID: 28124591
-
The Pathogenic Role of Ganglioside Metabolism in Alzheimer's Disease-Cholinergic Neuron-Specific Gangliosides and Neurogenesis.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Jan;54(1):623-638. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9641-0. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 26748510 Review.
-
Ganglioside-Dependent Neural Stem Cell Proliferation in Alzheimer's Disease Model Mice.ASN Neuro. 2015 Dec 23;7(6):1759091415618916. doi: 10.1177/1759091415618916. Print 2015 Nov-Dec. ASN Neuro. 2015. PMID: 26699276 Free PMC article.
-
APP transgenic modeling of Alzheimer's disease: mechanisms of neurodegeneration and aberrant neurogenesis.Brain Struct Funct. 2010 Mar;214(2-3):111-26. doi: 10.1007/s00429-009-0232-6. Epub 2009 Nov 29. Brain Struct Funct. 2010. PMID: 20091183 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential proteomic and behavioral effects of long-term voluntary exercise in wild-type and APP-overexpressing transgenics.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 Jun;78:45-55. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.03.018. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 25818006 Free PMC article.
-
Functional roles of gangliosides in neurodevelopment: an overview of recent advances.Neurochem Res. 2012 Jun;37(6):1230-44. doi: 10.1007/s11064-012-0744-y. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Neurochem Res. 2012. PMID: 22410735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct analysis of sialylated or sulfated glycosphingolipids and other polar and neutral lipids using TLC-MS interfaces.J Lipid Res. 2014 Apr;55(4):773-81. doi: 10.1194/jlr.D046128. Epub 2014 Jan 29. J Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 24482490 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting GM2 Ganglioside Accumulation in Dementia: Current Therapeutic Approaches and Future Directions.Curr Mol Med. 2024;24(11):1329-1345. doi: 10.2174/0115665240264547231017110613. Curr Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 37877564 Review.
-
Brain gangliosides of a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease with deficiency in GD3-synthase: expression of elevated levels of a cholinergic-specific ganglioside, GT1aα.ASN Neuro. 2013 May 30;5(2):141-8. doi: 10.1042/AN20130006. ASN Neuro. 2013. PMID: 23565921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdipranoto A, Wu S, Stayte S, Vissel B. The role of neurogenesis in neurodegenerative diseases and its implications for therapeutic development. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2008;7:187–210. - PubMed
-
- Ando S, Hirabayashi Y, Kon K, Inagaki F, Tate S, Whittaker VP. A trisialoganglioside containing a sialyl alpha 2–6 N-acetylgalactosamine residue is a cholinergic-specific antigen, Chol-1 alpha. J Biochem. 1992;111:287–290. - PubMed
-
- Ando S, Tanaka Y, Waki H, Kon K, Iwamoto M, Fukui F. Gangliosides and sialylcholesterol as modulators of synaptic functions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998;845:232–239. - PubMed
-
- Ando S, Tanaka Y, Kobayashi S, Fukui F, Iwamoto M, Waki H, Tai T, Hirabayashi Y. Synaptic function of cholinergic-specific Chol-1alpha ganglioside. Neurochem Res. 2004;29:857–867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

