Similar impact of CD8+ T cell responses on early virus dynamics during SIV infections of rhesus macaques and sooty mangabeys
- PMID: 20865048
- PMCID: PMC2928736
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000901
Similar impact of CD8+ T cell responses on early virus dynamics during SIV infections of rhesus macaques and sooty mangabeys
Abstract
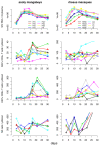
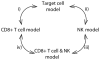
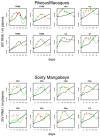
Despite comparable levels of virus replication, simian immunodeficiency viruses (SIV) infection is non-pathogenic in natural hosts, such as sooty mangabeys (SM), whereas it is pathogenic in non-natural hosts, such as rhesus macaques (RM). Comparative studies of pathogenic and non-pathogenic SIV infection can thus shed light on the role of specific factors in SIV pathogenesis. Here, we determine the impact of target-cell limitation, CD8+ T cells, and Natural Killer (NK) cells on virus replication in the early SIV infection. To this end, we fit previously published data of experimental SIV infections in SMs and RMs with mathematical models incorporating these factors and assess to what extent the inclusion of individual factors determines the quality of the fits. We find that for both rhesus macaques and sooty mangabeys, target-cell limitation alone cannot explain the control of early virus replication, whereas including CD8+ T cells into the models significantly improves the fits. By contrast, including NK cells does only significantly improve the fits in SMs. These findings have important implications for our understanding of SIV pathogenesis as they suggest that the level of early CD8+ T cell responses is not the key difference between pathogenic and non-pathogenic SIV infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduced Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Replication in Macrophages of Sooty Mangabeys Is Associated with Increased Expression of Host Restriction Factors.J Virol. 2015 Oct;89(20):10136-44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00710-15. Epub 2015 Jul 22. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26202248 Free PMC article.
-
Depletion of CD8+ cells in sooty mangabey monkeys naturally infected with simian immunodeficiency virus reveals limited role for immune control of virus replication in a natural host species.J Immunol. 2007 Jun 15;178(12):8002-12. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.12.8002. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17548637
-
Divergent host responses during primary simian immunodeficiency virus SIVsm infection of natural sooty mangabey and nonnatural rhesus macaque hosts.J Virol. 2005 Apr;79(7):4043-54. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.7.4043-4054.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15767406 Free PMC article.
-
A case for innate immune effector mechanisms as contributors to disease resistance in SIV-infected sooty mangabeys.Curr HIV Res. 2009 Jan;7(1):12-22. doi: 10.2174/157016209787048465. Curr HIV Res. 2009. PMID: 19149550 Review.
-
The paradox of simian immunodeficiency virus infection in sooty mangabeys: active viral replication without disease progression.Front Biosci. 2004 Jan 1;9:521-39. doi: 10.2741/1123. Front Biosci. 2004. PMID: 14766388 Review.
Cited by
-
Prolonged persistence of measles virus RNA is characteristic of primary infection dynamics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Sep 11;109(37):14989-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1211138109. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22872860 Free PMC article.
-
Double-negative T cells during HIV/SIV infections: potential pinch hitters in the T-cell lineup.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2012 Mar;7(2):164-71. doi: 10.1097/COH.0b013e3283504a66. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2012. PMID: 22241163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The well-tempered SIV infection: Pathogenesis of SIV infection in natural hosts in the wild, with emphasis on virus transmission and early events post-infection that may contribute to protection from disease progression.Infect Genet Evol. 2016 Dec;46:308-323. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2016.07.006. Epub 2016 Jul 6. Infect Genet Evol. 2016. PMID: 27394696 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling the Effects of Morphine on Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Dynamics.PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 Sep 26;12(9):e1005127. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005127. eCollection 2016 Sep. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016. PMID: 27668463 Free PMC article.
-
High cell-free virus load and robust autologous humoral immune responses in breast milk of simian immunodeficiency virus-infected african green monkeys.J Virol. 2011 Sep;85(18):9517-26. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00796-11. Epub 2011 Jul 6. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21734053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chakrabarti LA. The paradox of simian immunodeficiency virus infection in sooty mangabeys: active viral replication without disease progression. Front Biosci. 2004;9:521–539. - PubMed
-
- Paiardini M, Pandrea I, Apetrei C, Silvestri G. Lessons Learned from the Natural Hosts of HIV-Related Viruses. Annu Rev Med. 2009;60:485–495. - PubMed
-
- Silvestri G, Sodora DL, Koup RA, Paiardini M, O'Neil SP, et al. Nonpathogenic SIV infection of sooty mangabeys is characterized by limited bystander immunopathology despite chronic high-level viremia. Immunity. 2003;18:441–452. - PubMed
-
- Mandl JN, Barry AP, Vanderford TH, Kozyr N, Chavan R, et al. Divergent TLR7 and TLR9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish pathogenic and nonpathogenic AIDS virus infections. Nat Med. 2008;14:1077–1087. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

