Effect of correlated tRNA abundances on translation errors and evolution of codon usage bias
- PMID: 20862306
- PMCID: PMC2940732
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001128
Effect of correlated tRNA abundances on translation errors and evolution of codon usage bias
Abstract
Despite the fact that tRNA abundances are thought to play a major role in determining translation error rates, their distribution across the genetic code and the resulting implications have received little attention. In general, studies of codon usage bias (CUB) assume that codons with higher tRNA abundance have lower missense error rates. Using a model of protein translation based on tRNA competition and intra-ribosomal kinetics, we show that this assumption can be violated when tRNA abundances are positively correlated across the genetic code. Examining the distribution of tRNA abundances across 73 bacterial genomes from 20 different genera, we find a consistent positive correlation between tRNA abundances across the genetic code. This work challenges one of the fundamental assumptions made in over 30 years of research on CUB that codons with higher tRNA abundances have lower missense error rates and that missense errors are the primary selective force responsible for CUB.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
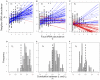
 . The solid lines represent the regression lines between
. The solid lines represent the regression lines between  and
and  for each genome. Genomes with a negative
for each genome. Genomes with a negative  are coded in red, while genomes with a positive
are coded in red, while genomes with a positive  are represented by blue lines. Panels (D–F) present the distribution of correlation coefficients
are represented by blue lines. Panels (D–F) present the distribution of correlation coefficients  between
between  and
and  across all the genomes. The mean of the distribution of
across all the genomes. The mean of the distribution of  values for all the three degenerate classes differ significantly from 0 (Wilcox test,
values for all the three degenerate classes differ significantly from 0 (Wilcox test,  ).
).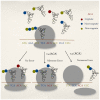
 or premature termination of translation due to recognition by release factors, spontaneous ribosome drop-off or frameshifting leading to a nonsense error with a rate
or premature termination of translation due to recognition by release factors, spontaneous ribosome drop-off or frameshifting leading to a nonsense error with a rate  .
.
 and (B) nonsense errors
and (B) nonsense errors  are negatively correlated with the rate of elongation by cognate tRNAs at that codon. The dashed line indicates the regression line between
are negatively correlated with the rate of elongation by cognate tRNAs at that codon. The dashed line indicates the regression line between  and
and  . This is consistent with expectations under the standard model. However, in the case of twofold degenerate amino acids (
. This is consistent with expectations under the standard model. However, in the case of twofold degenerate amino acids ( ), whose two codons are joined together by solid lines, we see that
), whose two codons are joined together by solid lines, we see that  increases with
increases with  for 8 out of 10 amino acids. In the case of
for 8 out of 10 amino acids. In the case of  every amino acid showed a decrease in
every amino acid showed a decrease in  with
with  .
.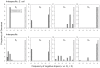
 and
and  , while panels (E–H) represent the distribution of 73 genomes for the same. Amino acids in every degenerate class (
, while panels (E–H) represent the distribution of 73 genomes for the same. Amino acids in every degenerate class ( ) show a negative relationship between cognate elongation rate
) show a negative relationship between cognate elongation rate  and nonsense error rates (
and nonsense error rates ( ) both intra-specifically as well as inter-specifically. A majority of amino acids in the 2-fold degenerate class (
) both intra-specifically as well as inter-specifically. A majority of amino acids in the 2-fold degenerate class ( ) show an increase in missense error rate
) show an increase in missense error rate  with
with  across genomes. As the degeneracy of amino acids increases, we see an increase in the frequency of the expected negative relationship between
across genomes. As the degeneracy of amino acids increases, we see an increase in the frequency of the expected negative relationship between  and
and  across E. coli strains as well as other bacterial species.
across E. coli strains as well as other bacterial species.Similar articles
-
Translational Selection for Speed Is Not Sufficient to Explain Variation in Bacterial Codon Usage Bias.Genome Biol Evol. 2018 Feb 1;10(2):562-576. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evy018. Genome Biol Evol. 2018. PMID: 29385509 Free PMC article.
-
Codon usage bias from tRNA's point of view: redundancy, specialization, and efficient decoding for translation optimization.Genome Res. 2004 Nov;14(11):2279-86. doi: 10.1101/gr.2896904. Epub 2004 Oct 12. Genome Res. 2004. PMID: 15479947 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Competing tRNA Abundance on Translation: Quantifying the Efficiency of Sense Codon Reassignment at Rarely Used Codons.Chembiochem. 2020 Aug 17;21(16):2274-2286. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202000052. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Chembiochem. 2020. PMID: 32203635
-
Codon usage bias.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jan;49(1):539-565. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06749-4. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34822069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Speeding with control: codon usage, tRNAs, and ribosomes.Trends Genet. 2012 Nov;28(11):574-81. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2012.07.006. Epub 2012 Aug 23. Trends Genet. 2012. PMID: 22921354 Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive biophysical modeling and understanding of the dynamics of mRNA translation and its evolution.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Nov 2;44(19):9031-9049. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw764. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27591251 Free PMC article.
-
Translational Selection for Speed Is Not Sufficient to Explain Variation in Bacterial Codon Usage Bias.Genome Biol Evol. 2018 Feb 1;10(2):562-576. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evy018. Genome Biol Evol. 2018. PMID: 29385509 Free PMC article.
-
A nutrient-driven tRNA modification alters translational fidelity and genome-wide protein coding across an animal genus.PLoS Biol. 2014 Dec 9;12(12):e1002015. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002015. eCollection 2014 Dec. PLoS Biol. 2014. PMID: 25489848 Free PMC article.
-
Examining the Effects of Temperature on the Evolution of Bacterial tRNA Pools.Genome Biol Evol. 2024 Jun 4;16(6):evae116. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evae116. Genome Biol Evol. 2024. PMID: 38805023 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating Gene Expression and Codon-Specific Translational Efficiencies, Mutation Biases, and Selection Coefficients from Genomic Data Alone.Genome Biol Evol. 2015 May 14;7(6):1559-79. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evv087. Genome Biol Evol. 2015. PMID: 25977456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lobley GE, Milne V, Lovie JM, Reeds PJ, Pennie K. Whole body and tissue protein synthesis in cattle. Br J Nutr. 1980;43:491–502. - PubMed
-
- Pannevis MC, Houlihan DF. The energetic cost of protein synthesis in isolated hepatocytes of rainbow trout (oncorhynchus mykiss). J Comp Physiol B, Biochem Syst Environ Physiol. 1992;162:393–400. - PubMed
-
- Warner JR. The economics of ribosome biosynthesis in yeast. Trends Biochem Sci. 1999;24:437–40. - PubMed
-
- Sharp PM, Li WH. An evolutionary perspective on synonymous codon usage in unicellular organisms. J Mol Evol. 1986;24:28–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

