Xanthines as adenosine receptor antagonists
- PMID: 20859796
- PMCID: PMC3882893
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-13443-2_6
Xanthines as adenosine receptor antagonists
Abstract
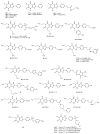
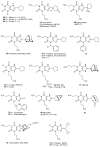
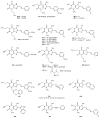
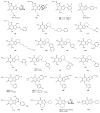
The natural plant alkaloids caffeine and theophylline were the first adenosine receptor (AR) antagonists described in the literature. They exhibit micromolar affinities and are non-selective. A large number of derivatives and analogues were subsequently synthesized and evaluated as AR antagonists. Very potent antagonists have thus been developed with selectivity for each of the four AR subtypes.
Figures




Similar articles
-
1,3-Dialkyl-substituted tetrahydropyrimido[1,2-f]purine-2,4-diones as multiple target drugs for the potential treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.Bioorg Med Chem. 2013 Dec 1;21(23):7435-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.09.044. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 24139167
-
Selectivity is species-dependent: Characterization of standard agonists and antagonists at human, rat, and mouse adenosine receptors.Purinergic Signal. 2015 Sep;11(3):389-407. doi: 10.1007/s11302-015-9460-9. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Purinergic Signal. 2015. PMID: 26126429 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the aryl substituent kind and distance from pyrimido[2,1-f]purindiones on the adenosine receptor selectivity and antagonistic properties.Eur J Med Chem. 2003 Apr;38(4):397-402. doi: 10.1016/s0223-5234(03)00051-5. Eur J Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 12750027
-
Progress in the pursuit of therapeutic adenosine receptor antagonists.Med Res Rev. 2006 Mar;26(2):131-59. doi: 10.1002/med.20048. Med Res Rev. 2006. PMID: 16380972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xanthine derivatives in the heart: blessed or cursed?Curr Med Chem. 2011;18(24):3695-706. doi: 10.2174/092986711796642391. Curr Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21774759 Review.
Cited by
-
Fast, Efficient, and Versatile Synthesis of 6-amino-5-carboxamidouracils as Precursors for 8-Substituted Xanthines.Front Chem. 2019 Feb 18;7:56. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00056. eCollection 2019. Front Chem. 2019. PMID: 30834241 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of caffeine on circadian phase, amplitude and period evaluated in cells in vitro and peripheral organs in vivo in PER2::LUCIFERASE mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Dec;171(24):5858-69. doi: 10.1111/bph.12890. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25160990 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal bone growth is impaired by direct involvement of caffeine with chondrocyte differentiation in the growth plate.J Anat. 2017 Jan;230(1):117-127. doi: 10.1111/joa.12530. Epub 2016 Aug 3. J Anat. 2017. PMID: 27484046 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic Signaling in Mast Cell Degranulation and Asthma.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Dec 22;8:947. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00947. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29311944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of S1P1 receptor pathway in angiogenic effects of a novel adenosine-like nucleic acid analog COA-Cl in cultured human vascular endothelial cells.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2014 Oct;2(5):e00068. doi: 10.1002/prp2.68. Epub 2014 Aug 6. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2014. PMID: 25505610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abo-Salem OM, Hayallah AM, Bilkei-Gorzo A, Filipek B, Zimmer A, Müller CE. Antinociceptive effects of novel A2B adenosine receptor antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004;308:358–366. - PubMed
-
- Antoniou K, Daifoti-Papadopoulou Z, Hyphantis T, Papathanasiou G, Bekris E, Marselos M, Panlilio L, Müller CE, Goldberg SR, Ferré S. A detailed behavioural analysis of the acute motor effects of caffeine in the rat: involvement of adenosine A1 and A2A receptors. Psychopharmacology. 2005;183:154–162. - PubMed
-
- Akkari R, Burbiel JC, Hockemeyer J, Müller CE. Recent progress in the development of adenosine receptor ligands as antiinflammatory drugs. Curr Top Med Chem. 2006;6:1375–1399. - PubMed
-
- Auchampach JA, Jin X, Wan TC, Caughey GH, Linden J. Canine mast cell adenosine receptors: cloning and expression of the A3 receptor and evidence that degranulation is mediated by the A2B receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1997;52:846–860. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

